
In the previous article "What is a hierarchical selector in CSS? how to use?", we learned about 4 types of hierarchical selectors. Let's talk about pseudo-selectors. They provide more complex functions, but do not directly correspond to the elements that HTML documents should have. There are two main types of pseudo-selectors: pseudo-elements and pseudo-classes. Let’s first talk about pseudo-element selectors in detail.

Pseudo-element selectorin CSS is to add keywords to the specified CSS selector. Used to describe the styling of a specific part of a specified element. [Recommended learning:css video tutorial]
Through pseudo-elements, developers can define styles for specific parts of the selected element without using the ID or class attributes of the element. For example, through pseudo-elements you can set the style of the first letter in a paragraph, or insert some content before or after the element, etc.
In CSS1 and CSS2, the use of pseudo-elements is the same as pseudo-classes, and a colon:is connected to the selector. However, in CSS3, the use of single colon for pseudo elements was changed to double colon::to distinguish pseudo classes and pseudo elements. Therefore, it is recommended to use double colons instead of single colons when using pseudo-elements.
The syntax structure is as follows:
/* CSS3 语法 */ 选择器::伪元素 { 属性 : 属性值; } /* CSS2 过时语法 (仅用来支持 IE8) */ 选择器:伪元素 { 属性 : 属性值; }
should now use two colons, unless you are also compatible with IE8.
Note: Only one pseudo-element can be used in a selector, and the pseudo-element must follow the selector. According to the latest W3C specification, you should use double colon
::instead of single colon:when defining pseudo-elements to distinguish pseudo-classes and pseudo-elements. However, since the old version of the W3C specification did not make a special distinction, most browsers currently support both single colon and double colon methods to define pseudo-elements.
CSS provides a series of pseudo-elements, as shown in the following table:
::before和::after伪元素
::before伪元素的作用是作为定位的HTML元素的第一个子级元素,::after** 伪元素** 的作用是作为定位的 HTML元素的最后一个子级元素。
如下示例代码展示了::before和::after伪元素的用法:
nbsp;html>::before和::after伪元素 这是一段测试内容
代码运行结果如下图所示:
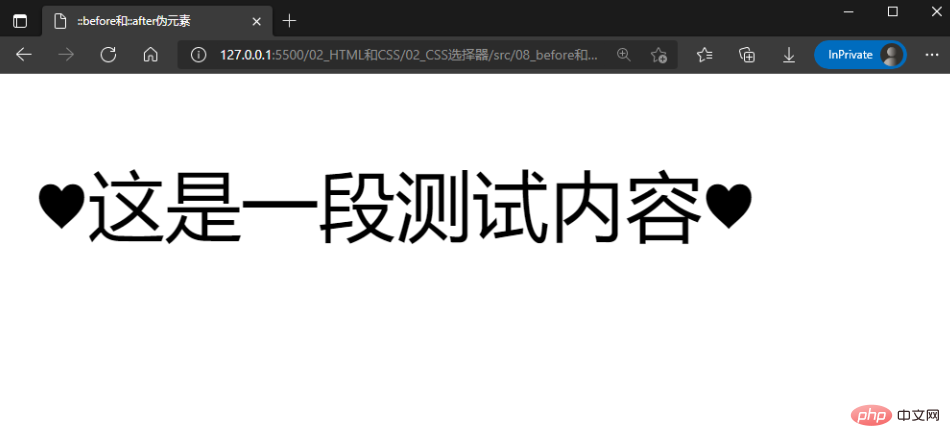
如上述示例代码所示,::before伪元素和::after伪元素通常会配合content属性来为该元素增加装饰内容。
content属性用于在元素的::before伪元素和::after伪元素中插入内容。该属性具有的值如下所示:
none:不会产生伪类元素。
normal:::before伪元素和::after伪类元素中会被视为 none。
text:文本内容。
url:格式为url(),指定一个外部资源(比如图片)。如果该资源或图片不能显示,它就会被忽略或显示一些占位。
::first-letter和::first-line伪元素
::first-letter和::first-line伪元素分别匹配文本的第一个字和第一行的样式内容。示例代码如下:
nbsp;html>::first-letter和::first-line伪元素 我如果爱你——绝不像攀援的凌霄花,借你的高枝炫耀自己;
代码运行结果如下图所示:
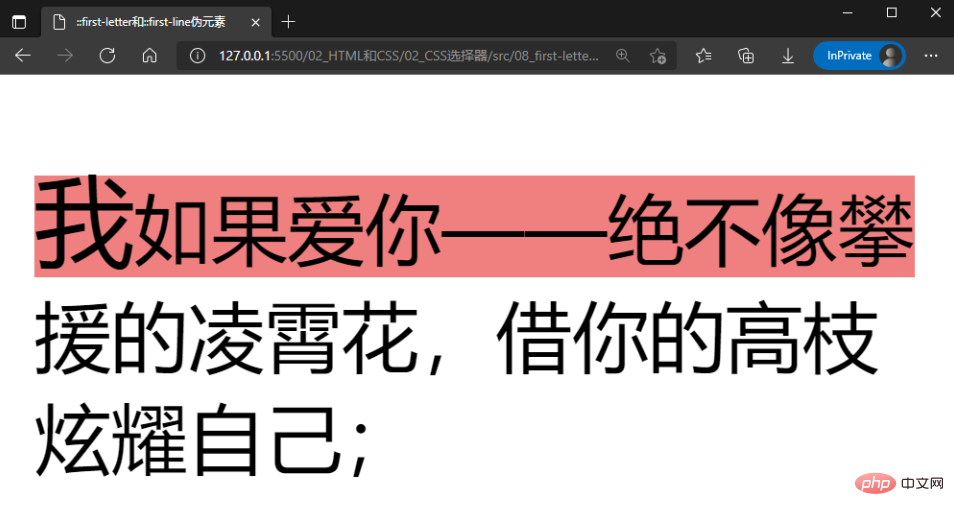
值得注意的是::first-letter和::first-line伪元素可以使用的CSS属性是有限制的。
::first-letter选择器可以设置的CSS属性:
font属性
color属性
background属性
margin属性
padding属性
border属性
text-decoration属性
vertical-align属性
text-transform属性
line-height属性
float属性
clear属性
::first-line选择器可以设置的CSS属性:
font属性
color属性
background属性
word-spacing属性
letter-spacing属性
text-decoration属性
vertical-align属性
text-transform属性
line-height属性
clear属性
::selection伪元素
::selection伪元素的作用是匹配用户在HTML页面选中的文本内容(比如使用鼠标或其他选择设备选中的部分)设置高亮效果。如下示例代码展示了::selection伪元素的用法:
nbsp;html>::first-letter和::first-line伪元素 我如果爱你——绝不像攀援的凌霄花,借你的高枝炫耀自己;
代码运行结果如下图所示:
::placeholder伪元素
伪元素::placeholder用来设置表单元素(、
代码运行结果如下图所示:
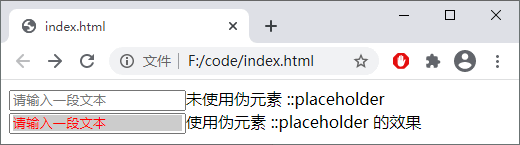
(学习视频分享:web前端入门)
| Pseudo-elements | Example | Example description |
|---|---|---|
| ::after | p::after | Insert content after each element |
| ::before | p::before | Insert content before each element |
| ::first-letter | p::first-letter | Matches the first letter of the content in each element |
| ::first-line | p::first-line | Matches the first line of content in each element |
| p::selection | Match the part of the element selected by the user | |
| input::placeholder | Match the placeholder attribute of each form input box (such as) |
The above is the detailed content of CSS pseudo-selector learning pseudo-element selector analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!