
html5 has new attributes, such as contextmenu, contentEditable, hidden, draggable, "data-*", placeholder, required, pattern, autofocus, autocomplete, etc.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, HTML5 version, Dell G3 computer.
The function of contextmenu is to specify the right-click menu.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1" style="height:900px; background: lightgreen;" contextmenu="menuShare">
</div>
<menu id="menuShare" type="context">
<menuitem label="分享到QQ空间" onclick="alert('QQ');"></menuitem>
<menuitem label="分享到朋友圈" onclick="alert('朋友圈');"></menuitem>
<menuitem label="分享到微博" onclick="alert('微博');"></menuitem>
</menu>
</body>
</html>Running effect:
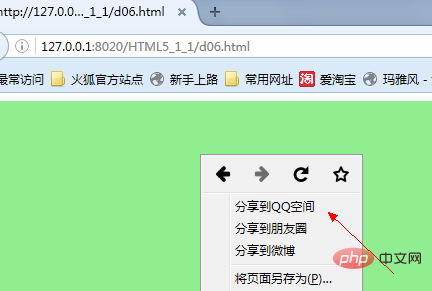
contextmenu In Html5, each element has a new attribute: contextmenu, contextmenu is the context menu, that is, right-click the mouse A menu will appear for the element.
menu To realize that a menu will appear when you right-click an element, you must also understand another new element in HTML5: menu. As the name suggests, menu defines the menu. The menu element attributes: type: menu type attribute. There are three values 1) context: context; 2) toolbar: toolbar; 3) list: list
.
menuitem attributes:
label: the name displayed by the menu item
icon: the icon displayed on the left side of the menu item
onclick: the event triggered by clicking the menu item
Specifies whether the content of the element can be edited
Attribute value:
true -----The content of the element can be edited
false -----The element cannot be edited Content
inherit -----Inherit the contenteditable attribute of the parent element
When it is an empty string, the effect is the same as true.
When the contenteditable status of an element is true (the contenteditable attribute is an empty string, or is true, or is inherit and its parent element status is true), it means that the element is editable. Otherwise, the element is not editable.
document.body.contentEditable=true; You can modify the published website
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>contentEditable属性</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>contentEditable属性</h2>
<div contenteditable="true">
Hello contentEditable
</div>
</body>
</html>
The hidden attribute is used to hide the element. Once this attribute is used, the element will not be displayed in the browser
2 Boolean values
true specifies that the element is visible.
false specifies that the element is invisible.
<div hidden="hidden">
Hello Hidden
</div>In order to be compatible with some browsers (IE8) that do not support this attribute, you can add the following style to CSS:
*[hidden]{
display: none;
}var p1=document.querySelector("body #p1");
p1.innerHTML+=" +++";Specifies whether the element can be dragged
3 enumeration values
true specifies whether the element is draggable.
false specifies that the element is not draggable.
auto uses the browser's default features.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html><html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="Scripts/jquery-1.11.3.min.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
<title></title>
<style>
#p1,
#p3 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid #00f;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
#p2 {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
<script>
var p1, p2, p3, msg;
window.onload = function() {
p1 = document.getElementById("p1");
p2 = document.getElementById("p2");
p3 = document.getElementById("p3");
msg = document.getElementById("msg");
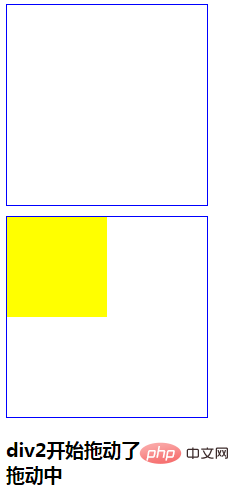
p2.ondragstart=function(){
msg.innerHTML+="p2开始拖动了<br/>";
}
p2.ondrag=function(){
msg.innerHTML+="拖动中<br/>";
}
p2.ondragend=function(){
msg.innerHTML+="拖动结束<br/>";
}
p1.ondragover = function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
}
p1.ondrop = function(e) {
p1.appendChild(p2);
}
p3.ondragover = function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
}
p3.ondrop = function(e) {
p3.appendChild(p2);
}
$("#p1").data("name","电池");
alert($("#p1").data("name"));
p1.setAttribute("data-order-price",998.7);
alert(p1.getAttribute("data-order-price"));
} </script>
</head>
<body>
<p id="p1" data-order-price="98.5" data-name="充电宝"></p>
<p id="p3"></p>
<p id="p2" draggable="true"></p>
<h3 id="msg"></h3>
</body></html>Run result:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title></head><body>
<p style="height: 300px; background: lightgoldenrodyellow;" ondrop="ondropEvent(event)" ondragover="ondragoverEvent(event)"></p>
<img src="img/x.png" width="200" draggable="true" ondragstart="ondragstartEvent(event)"/>
<img src="img/tv.png" width="200" draggable="true" ondragstart="ondragstartEvent(event)"/>
<script>
var target; function ondragstartEvent(e){
target=e.target; //记住当前被拖动的对象 console.log(e.target);
} function ondropEvent(e){
e.preventDefault();
e.target.appendChild(target);
} function ondragoverEvent(e){
e.preventDefault();
} </script></body></html>
Value:
getAttribute('data-order-amount')
dataset.orderAmount
The data() method in jQuery can also be accessed
<!DOCTYPE html><html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>data-*</title>
<script src="js/jquery-1.11.3.min.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>data-*</h2>
<p id="p1" data-student-name="Tom" data-stu='{"a":1,"b":2}'></p>
<button onclick="addData()">添加数据</button>
<button onclick="getData()">获取数据</button>
<script type="text/javascript">
var p1=document.getElementById("p1"); function addData()
{ //给p1添加属性data-student-name,值为rose p1.setAttribute("data-student-name","Rose");
$("#p1").data("stu-mark","99分");
} function getData()
{ //原生JavaScript
//alert(p1.getAttribute("data-student-name"));
//jQuery alert($("#p1").data("student-name"));
alert($("#p1").data("stu").a);
alert($("#p1").data("stu-mark"));
}
var x="{a:1}";
alert(eval("("+x+")").a); </script>
</body></html>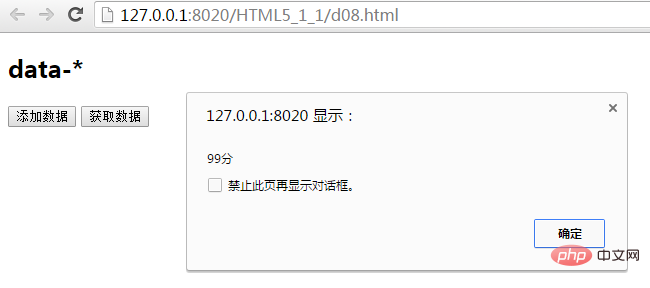
<p>
<label>邮箱:</label>
<input type="email" name="mail" id="mail" value="" placeholder="请输入邮箱"/>
</p>
<p>
<label>博客:</label>
<input type="url" name="blog" id="blog" value="" required="required"/>
</p>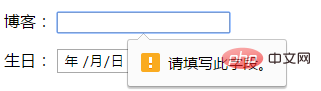
<p>
<label>帐号:</label>
<input type="text" required="required" pattern="^[0-9a-zA-Z]{6,16}$" />请输入a-zA-Z0-9且长度6-16位的字符
</p>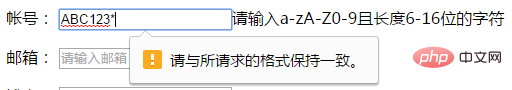
<p>
<label>博客:</label>
<input type="url" name="blog" id="blog" value="" required="required" autofocus="autofocus"/>
</p>
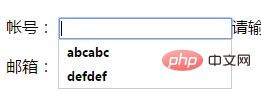
该属性默认是打开的。
novalidate 属性规定在提交表单时不应该验证 form 或 input 域。
<form action="demo_form.asp" method="get" novalidate="true"> <button formnovalidate="formnovalidate" >提交</button>
multiple 属性规定输入域中可选择多个内容,如:email 和 file
<input type="file" multiple="multiple” />
<p>
<label>相片:</label>
<input type="file" multiple="multiple"/>
</p>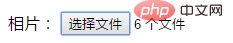
推荐教程:html视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Does html5 have new attributes?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!