
A network card is a piece of computer hardware used to allow computers to communicate on a computer network, allowing users to connect to each other via cables or wirelessly. In the Linux operating system, the traditional naming methods of network card devices are eth0, eth1, eth2, etc. Check the syntax of the network card model "lspci | grep -i ether", the syntax of the network card resource usage "sar -n DEV", and whether the network card supports Syntax for multi-queue "lspci -vvv | grep -i msi-x".

The operating environment of this tutorial: CentOS7 system, Dell G3 computer.
A network card is a piece of computer hardware designed to allow computers to communicate on a computer network. Since it has a MAC address, it falls between Layer 1 and Layer 2 of the OSI model. It allows users to connect to each other via cable or wirelessly.
Each network card has a unique 48-bit serial number called a MAC address, which is written in a ROM on the card. Every computer on the network must have a unique MAC address.
##1. Overview of network cards## The traditional naming methods of network card devices in #Linux operating systems are eth0, eth1, eth2, etc., while CentOS7 provides different naming rules. The default is to assign based on firmware, topology, and location information. The advantage of this is that the naming is fully automatic and predictable, but the disadvantage is that it is more difficult to read than eth0 and wlan0, such as ens33.
2. The difference between Eth0 and ens
##eno1: represents the network card built into the host biosRule 1:
For onboard device naming, merge the index number provided by the firmware or BIOS. If the information from the firmware or BIOS is readable, name it, such as eno1. This kind of naming is more common. , otherwise rule 2 is used.
Rule 2:
Name the PCI-E hot plug port index number provided by the merged firmware or BIOS, such as ens1. If the information is readable, use it, otherwise use it. Rule 3.
Rule 3:
Name the physical location of the merged hardware interface, such as enp2s0. Name it if it is available. If it fails, go directly to solution 5.
Rule 4:
Name the MAC address of the merged interface, such as enx78e7d1ea46da, which is not used by default unless the user chooses to use this scheme.
Rule 5:
Use traditional solutions. If all else fails, use a style like eth0.
4. The meaning of the network card name characters1. The meaning of the first 2 characters
en Ethernet Ethernet
wl Wireless LAN WLANww Wireless WAN WWAN 2. The third character is selected according to the device type
##o
vim /etc/sysconfig/grub # 其实是/etc/default/grub的软连接
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=cl/root rd.lvm.lv=cl/swap net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0 rhgb quiet"
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
然后重新启动 Linux 操作系统,通过 ip addr 可以看到网卡名称已经变为 eth0 。
3、修改网卡配置文件
原来网卡配置文件名称为 ifcfg-ens33,这里需要修改为 ethx 的格式,并适当调整网卡配置文件。
mv /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 # 修改ifcfg-eth0文件如下内容(其它内容不变) NAME=eth0 DEVICE=eth0
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart network.service # 重启网络服务
注意:ifcfg-ens33 文件最好删除掉,否则重启 network 服务时候会报错
TYPE=Ethernet # 网卡类型:为以太网 PROXY_METHOD=none # 代理方式:关闭状态 BROWSER_ONLY=no # 只是浏览器:否 BOOTPROTO=dhcp # 网卡的引导协议:DHCP[中文名称: 动态主机配置协议] DEFROUTE=yes # 默认路由:是, 不明白的可以百度关键词 `默认路由` IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no # 是不开启IPV4致命错误检测:否 IPV6INIT=yes # IPV6是否自动初始化: 是[不会有任何影响, 现在还没用到IPV6] IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes # IPV6是否自动配置:是[不会有任何影响, 现在还没用到IPV6] IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes # IPV6是否可以为默认路由:是[不会有任何影响, 现在还没用到IPV6] IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no # 是不开启IPV6致命错误检测:否 IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy # IPV6地址生成模型:stable-privacy [这只一种生成IPV6的策略] NAME=ens33 # 网卡物理设备名称 UUID=f47bde51-fa78-4f79-b68f-d5dd90cfc698 # 通用唯一识别码, 每一个网卡都会有, 不能重复, 否两台linux只有一台网卡可用 DEVICE=ens33 # 网卡设备名称, 必须和 `NAME` 值一样 ONBOOT=no # 是否开机启动, 要想网卡开机就启动或通过 `systemctl restart network`控制网卡,必须设置为 `yes`
/etc/sysconfig/network # 包括主机基本网络信息,用于系统启动 /etc/sysconfig/network-script/ # 此目录下是系统启动最初始化网络的信息 /etc/sysconfig/network-script/ifcfg-em1 # 网络配置信息,每个人的配置名字不一样通过命令查看 /etc/xinetd.conf 定义了由超级进程XINETD启动的网络服务 /etc/protocols # 设定了主机使用的协议以及各个协议的协议号 /etc/services # 设定了主机的不同端口的网络服务
六、查看虚拟化有没有开启
Ctrl+alt+delete
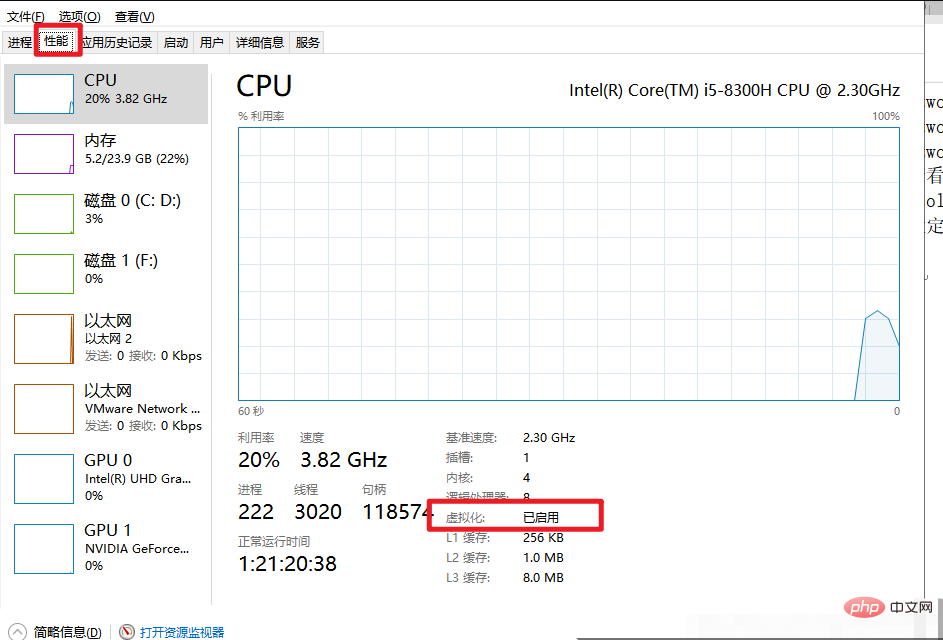
七、基础命令
查看网卡型号: lspci | grep -i ether;
查看网卡资源使用情况: sar -n DEV(重点看网络带宽);
查看网卡eth0的队列:/sys/class/net/eth0/queues;
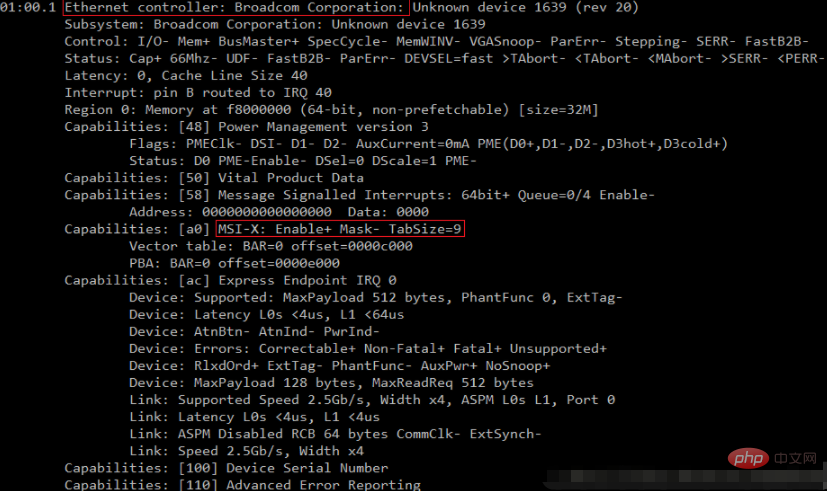
查看网卡是否支持多队列: lspci -vvv | grep -i msi-x;
如下图所示,查看Ethernet controller的条目内容,如果有MSI-X && Enable+ && TabSize > 1,则该网卡是多队列网卡,TabSize表示该网卡支持的队列数。
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of What is a network card in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!