What is the difference between threads and processes in go language
Difference: 1. Thread is the smallest unit of program execution, while process is the smallest unit of resources allocated by the operating system. 2. A process consists of one or more threads. Threads are different execution routes of code in a process. 3. Thread context switching is much faster than process context switching. 4. Process switching requires maximum resources and is very inefficient; thread switching requires average resources and has average efficiency. 5. The process has its own stack and the stack is not shared between processes; the thread has its own stack and shares the heap.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, GO version 1.18, Dell G3 computer.
What are threads and processes?
A process
- is a program with certain independent functions on a data set The A dynamic execution process
- is an independent unit for resource allocation and scheduling by the operating system
- It is the carrier for the operation of the application
- Thread is a single sequential control process in program execution
- It is the smallest unit of program execution flow
- Is the basic unit of processor scheduling and allocation
- A process can have one or more threads
- The memory space of the program is shared between each thread
Task Scheduling
The task scheduling of most operating systems (Windows, Linux) adopts the time slice rotation preemptive scheduling method.
The scheduling method is as follows:
In a process, when a thread task is executed for a few milliseconds, it will be scheduled by the operating system kernel
-
Interrupt the processor through the hardware counter, force the thread to pause and put the thread's register into the memory
Determine which thread to execute next by looking at the thread list
Then restore the register of the thread from the memory, and finally resume the execution of the thread to execute the next task
This method guarantees Each thread is executed in turn. Since the execution efficiency of the CPU is very high and the time slice is very short, it quickly switches between tasks. It gives the impression that multiple tasks are being performed at the same time. This is what we Talk about concurrency.

The difference between process and thread
- Thread is the smallest part of program execution Unit, and process is the smallest unit for the operating system to allocate resources
- A process consists of one or more threads, and threads are different execution routes of code in a process
- Process switching requires the largest resources and is very inefficient; thread switching requires average resources and has average efficiency .
- The process has its own stack, the stack is not shared between processes, and is scheduled by the operating system
-
Threads have their own stack, share the heap, and are also scheduled by the operating system
Multi-threading and multi-core
Multi-core processorrefers to integration on one processor Multiple computing cores are installed to improve computing power. That is to say, there are multiple processing cores for true parallel computing, and each processing core corresponds to a kernel thread.
Each processing core corresponds to a kernel thread. For example:
- A dual-core processor corresponds to two core threads
- A quad-core processor corresponds Four kernel threads
- Kernel Thread (KLT) is a thread directly supported by the operating system kernel. The thread is switched by the kernel. The kernel schedules the thread by operating the scheduler and is responsible for mapping the thread's tasks to each processor.
Hyper-threading technologyCurrently, processors use
Hyper-threading technologyto combine a physical processing core Simulated into two logical processing cores , that is, two kernel threads. So the computers we see are generally dual-core and four-thread, or four-core and eight-thread. In the operating system, we see that the number of CPUs is twice the number of actual physical CPUs. For example, dual-core and four-threads can see 4CPUs.
For example, the mbp I am currently writing the article on is an i7 6-core 12-thread:
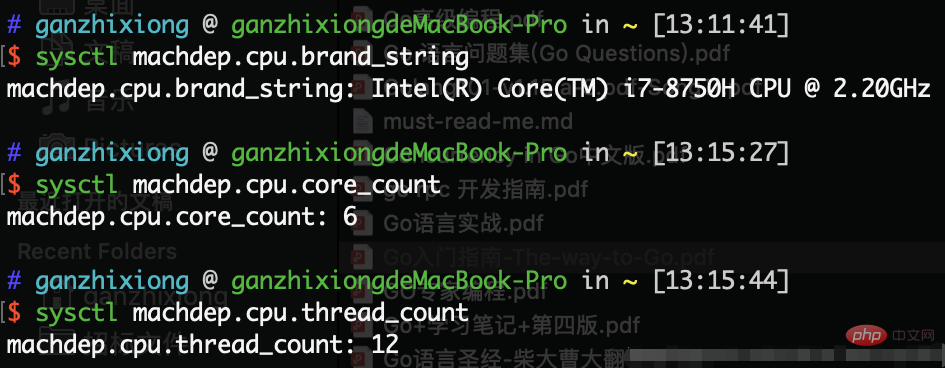 Programs generally do not use kernel threads directly, but use the kernel A high-level interface for threads—Lightweight Process (LWP), which is what we often call
Programs generally do not use kernel threads directly, but use the kernel A high-level interface for threads—Lightweight Process (LWP), which is what we often call
.
CoroutinesCoroutines are based on threads and are more lightweight than threads. A thread can have multiple coroutines.
In traditional applications, a thread is usually created for network requests to complete business logic. If there are multiple requests, multiple threads will be created.
If you encounter a time-consuming I/O behavior, the thread will always be in a blocked state. If many threads are in this idle state (waiting for the thread to complete execution before executing), this will cause resource application If it is not thorough, the throughput capacity of the system will decrease.
The most common time-consuming I/O behavior is such as JDBC. The CPU will always wait for the return of the data I/O operation. At this time, the thread does not use the CPU to perform operations at all, but is in an idle state. Using too many threads at the same time will also bring more context switching overhead.
There are two solutions to the above problems:
- Single thread plus asynchronous callback
For example, Node.js, Java’s Vert.x - Coroutine
The purpose of the coroutine is to give up the current coroutine schedule and execute the next task when a long-term I/O operation occurs to eliminate the overhead of ContexSwith
- Thread switching is scheduled by the operating system, and coroutines are scheduled by users themselves, thus reducing context switching and improving efficiency
- The default Stack size of the thread is 1M, while the coroutine is more lightweight, close to 1K. Therefore, more coroutines can be opened in the same memory
- Because the coroutines are on the same thread, competition can be avoided. 2. Use locks
- Suitable for blocked and requiring a lot of concurrency Scenes. But it is not suitable for multi-threading of large amounts of calculations
The process of coroutine :
When I/O blocking occurs, the scheduler of the coroutine will schedule it
By yielding the data stream immediately ( Actively give up), and record the data on the current stack
After the blocking is completed, immediately restore the stack through the thread, and put the blocking result on this thread to run
The thread running in the Coroutine is called Fiber. For example, the go keyword in Golang is actually responsible for opening a Fiber, let func logic run on it.
Because the suspension of the coroutine is completely controlled by the program and occurs in the user state; the blocking state of the thread is switched by the operating system kernel and occurs in the kernel state.
Therefore, the overhead of coroutines is much less than that of threads, and there is no overhead of context switching.
Comparison of threads and coroutines
| Thread | Coroutine | |
|---|---|---|
| The initial unit is 1MB, fixed and immutable | The initial unit is generally 2KB , can be increased as needed | |
| Completed by OS kernel | Completed by user | |
| Design mode switching (switching from user mode to kernel mode), refreshing of 16 registers, PC, SP and other registers | Only three register values are modified: PC, SP , DX | |
| The resource occupancy is too high, frequent creation and destruction will cause serious performance problems | The resource occupancy is small, and it will not bring Serious performance issues arise | |
| Requires mechanisms such as locks to ensure data consistency and visibility | Does not require multi-threaded locking mechanisms , so there is only one thread. There is no conflict in writing variables at the same time. Shared resources are controlled in the coroutine without locking. You only need to determine the status, so the execution efficiency is much higher than that of threads |
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between threads and processes in go language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Golang vs. C : Performance and Speed Comparison
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Golang vs. C : Performance and Speed Comparison
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Golang is suitable for rapid development and concurrent scenarios, and C is suitable for scenarios where extreme performance and low-level control are required. 1) Golang improves performance through garbage collection and concurrency mechanisms, and is suitable for high-concurrency Web service development. 2) C achieves the ultimate performance through manual memory management and compiler optimization, and is suitable for embedded system development.
 Golang and C : Concurrency vs. Raw Speed
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Golang and C : Concurrency vs. Raw Speed
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Golang is better than C in concurrency, while C is better than Golang in raw speed. 1) Golang achieves efficient concurrency through goroutine and channel, which is suitable for handling a large number of concurrent tasks. 2)C Through compiler optimization and standard library, it provides high performance close to hardware, suitable for applications that require extreme optimization.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Golang vs. Python: The Pros and Cons
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Golang vs. Python: The Pros and Cons
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Golangisidealforbuildingscalablesystemsduetoitsefficiencyandconcurrency,whilePythonexcelsinquickscriptinganddataanalysisduetoitssimplicityandvastecosystem.Golang'sdesignencouragesclean,readablecodeanditsgoroutinesenableefficientconcurrentoperations,t
 Go vs. Other Languages: A Comparative Analysis
Apr 28, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Go vs. Other Languages: A Comparative Analysis
Apr 28, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Goisastrongchoiceforprojectsneedingsimplicity,performance,andconcurrency,butitmaylackinadvancedfeaturesandecosystemmaturity.1)Go'ssyntaxissimpleandeasytolearn,leadingtofewerbugsandmoremaintainablecode,thoughitlacksfeatureslikemethodoverloading.2)Itpe
 Choosing Between Golang and Python: The Right Fit for Your Project
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:21 AM
Choosing Between Golang and Python: The Right Fit for Your Project
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:21 AM
Golangisidealforperformance-criticalapplicationsandconcurrentprogramming,whilePythonexcelsindatascience,rapidprototyping,andversatility.1)Forhigh-performanceneeds,chooseGolangduetoitsefficiencyandconcurrencyfeatures.2)Fordata-drivenprojects,Pythonisp
 Common Use Cases for the init Function in Go
Apr 28, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Common Use Cases for the init Function in Go
Apr 28, 2025 am 12:13 AM
ThecommonusecasesfortheinitfunctioninGoare:1)loadingconfigurationfilesbeforethemainprogramstarts,2)initializingglobalvariables,and3)runningpre-checksorvalidationsbeforetheprogramproceeds.Theinitfunctionisautomaticallycalledbeforethemainfunction,makin
 Golang: Concurrency and Performance in Action
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang: Concurrency and Performance in Action
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang achieves efficient concurrency through goroutine and channel: 1.goroutine is a lightweight thread, started with the go keyword; 2.channel is used for secure communication between goroutines to avoid race conditions; 3. The usage example shows basic and advanced usage; 4. Common errors include deadlocks and data competition, which can be detected by gorun-race; 5. Performance optimization suggests reducing the use of channel, reasonably setting the number of goroutines, and using sync.Pool to manage memory.







