
How to use Redis in
Node? The following article will introduce to you how to use Redis in Node.js. You will find that it is so simple. I hope it will be helpful to you!

In the previous article, we actually left two places that can be optimized with redis:
token generation and verification of the token information sent by the client through JWT. [Related tutorial recommendations: nodejs video tutorial, Programming video]JWT token The implementation method is to put the basic information directly in token to facilitate the use of distributed systems, but we do not set a limited period (this is possible implemented), and the server cannot actively invalidate token. Redis naturally supports expiration time, and can also allow the server to actively expire token.
Of course, this does not mean that JWT token is not as good as redis token implementation. It depends on the usage scenario. Here we do not discuss which one is better, but only provide an implementation solution to let everyone know how to implement it.
For front-end friends, Redis may be relatively unfamiliar. First, let’s get to know
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), memory-based data structure storage system. It can be used as a database, cache and message middleware. It is one of the most popular NoSQL databases now. .
It has the following characteristics:
Caching
Caching can be said to be one of the most commonly used functions of Redis. Reasonable caching can not only speed up access, but also reduce the pressure on the back-end database.Ranking system
Using the characteristics of Redis lists and ordered collections, a ranking system can be created. The ranking system is currently used in shopping malls, news, blogs, etc. It is indispensable.Counter application
The application of counter is basically the same as the ranking system, which is a common requirement of most websites, such as the play count of video websites, The number of views on e-commerce websites, etc., but these numbers are generally relatively large. If stored in a relational database, it will still pose a great challenge to MySQL or other relational databases, and Redis can basically be said to naturally support counter applications.(Live video) message barrage
The online user list, gift rankings, barrage messages and other information in the live broadcast room are all suitable for storage using the SortedSet structure in Redis .For example, barrage messages can be sorted and returned usingZREVRANGEBYSCORE. In Redis5.0, new zpopmax and zpopmin commands are added. More convenient for message processing.
Talking on paper is ultimately shallow, you must practice it~I will not introduce the installation and simple use of Redis one by one here. Here are two articles I wrote before: You can quickly install, understand Redis data types and Commonly used commands.
RedisClient under Windows, and Redis Desktop Manager## under mac #RedisClient download link: https://github.com/caoxinyu/RedisClient
After downloading, double-click the
redisclient-win32.x86.2.0.exe file to run After
 is started, click
is started, click
After connecting, you can see the overall situation:
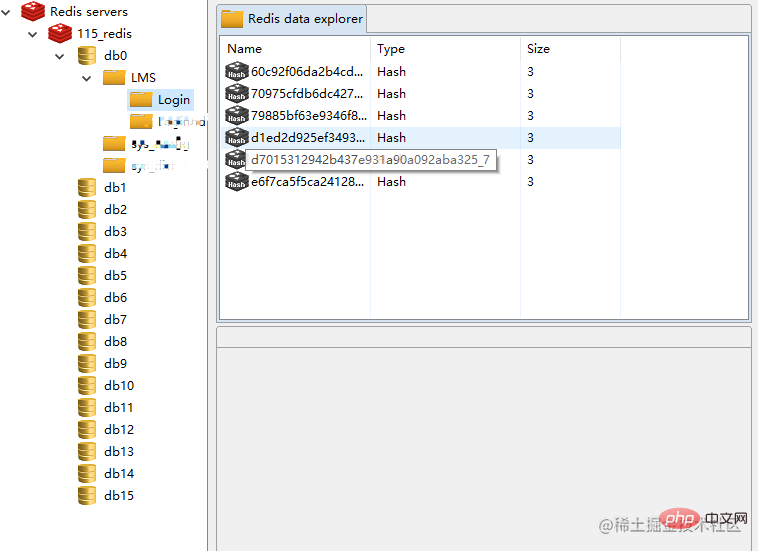
Different from SQL-type data, redis does not provide the operation of creating a new database because it comes with 16 (0 -15) databases (0 database is used by default). In the same library, key is the only one that exists and is not allowed to be repeated. It is like a "key" and can only open one "lock". The essence of key-value storage is to use key to identify value. When you want to retrieve value, you must use the key corresponding to value to search.
Redis recognition is a prerequisite for the article. This is the end of the article. Let’s get to the point~
This article mainly uses Redis to implement the cache function.
in Nest.js Version:
| Library | Version |
|---|---|
| Nest.js | V8.1.2 |
project is based on the Nest.js 8.x version, which is different from the Nest.js 9.x version. The following article specifically sorts out the differences between the two versions. Instructions and how to upgrade from V8 to V9 will not be discussed here.
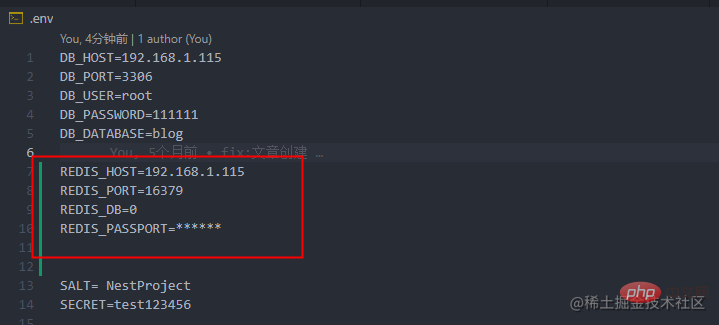
First, we connect Redis in the Nest.js project. The parameters required to connect Redis:
REDIS_HOST:Redis 域名 REDIS_PORT:Redis 端口号 REDIS_DB: Redis 数据库 REDIS_PASSPORT:Redis 设置的密码
Write the parameters into .env and .env. prodIn the configuration file:
Use the method officially recommended by Nest, which only requires 3 simple steps:
1. Introduce dependency files
npm install cache-manager --save npm install cache-manager-redis-store --save npm install @types/cache-manager -D
Nest Provides a unified API for various cache storage. The built-in data storage is in-memory, but you can also use cache-manager to use other solutions. For example, use Redis for caching.
To enable caching, import ConfigModule, and call register() or registerAsync() to pass in the response configuration parameters.
2. Create module file src/db/redis-cache.module.ts, implemented as follows:
import { ConfigModule, ConfigService } from '@nestjs/config';
import { RedisCacheService } from './redis-cache.service';
import { CacheModule, Module, Global } from '@nestjs/common';
import * as redisStore from 'cache-manager-redis-store';
@Module({
imports: [
CacheModule.registerAsync({
isGlobal: true,
imports: [ConfigModule],
inject: [ConfigService],
useFactory: async (configService: ConfigService) => {
return {
store: redisStore,
host: configService.get('REDIS_HOST'),
port: configService.get('REDIS_PORT'),
db: 0, //目标库,
auth_pass: configService.get('REDIS_PASSPORT') // 密码,没有可以不写
};
},
}),
],
providers: [RedisCacheService],
exports: [RedisCacheService],
})
export class RedisCacheModule {}CacheModule registerAsyncMethod uses Redis Store configuration to communicate store Attribute value redisStore, indicating 'cache-manager-redis-store' library isGlobal property is set to true to declare it as a global module, when we import RedisCacheModule in AppModule , other modules can be used directly without importing again. registerAsync() method is used to process asynchronous data. If it is static data, you can Use register3, create a new redis-cache.service.ts file, and implement cache read and write
import { Injectable, Inject, CACHE_MANAGER } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Cache } from 'cache-manager';
@Injectable()
export class RedisCacheService {
constructor(
@Inject(CACHE_MANAGER)
private cacheManager: Cache,
) {}
cacheSet(key: string, value: string, ttl: number) {
this.cacheManager.set(key, value, { ttl }, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
});
}
async cacheGet(key: string): Promise<any> {
return this.cacheManager.get(key);
}
} connections in the service Come down and import RedisCacheModule in app.module.ts.
We use redis to implement token expiration processing, automatic token renewal, and unique user login.
After logging in At this time, store the token generated by jwt into redis and set the validity period to 30 minutes. The key stored in redis consists of user information, and value is the token value.
// auth.service.ts
async login(user: Partial<User>) {
const token = this.createToken({
id: user.id,
username: user.username,
role: user.role,
});
+ await this.redisCacheService.cacheSet(
+ `${user.id}&${user.username}&${user.role}`,
+ token,
+ 1800,
+ );
return { token };
}When verifying the token, get the token from redis. If you cannot get the token, the token may have expired.
// jwt.strategy.ts
+ import { RedisCacheService } from './../core/db/redis-cache.service';
export class JwtStrategy extends PassportStrategy(Strategy) {
constructor(
@InjectRepository(User)
private readonly userRepository: Repository<User>,
private readonly authService: AuthService,
private readonly configService: ConfigService,
+ private readonly redisCacheService: RedisCacheService,
) {
super({
jwtFromRequest: ExtractJwt.fromAuthHeaderAsBearerToken(),
secretOrKey: configService.get('SECRET'),
+ passReqToCallback: true,
} as StrategyOptions);
}
async validate(req, user: User) {
+ const token = ExtractJwt.fromAuthHeaderAsBearerToken()(req);
+ const cacheToken = await this.redisCacheService.cacheGet(
+ `${user.id}&${user.username}&${user.role}`,
+ );
+ if (!cacheToken) {
+ throw new UnauthorizedException('token 已过期');
+ }
const existUser = await this.authService.getUser(user);
if (!existUser) {
throw new UnauthorizedException('token不正确');
}
return existUser;
}
}When a user logs in, each new token issued will overwrite the previous token and determine the token in redis and the request incoming Are the tokens the same? If not, it may be that the user has logged in elsewhere and a token error is displayed.
// jwt.strategy.ts
async validate(req, user: User) {
const token = ExtractJwt.fromAuthHeaderAsBearerToken()(req);
const cacheToken = await this.redisCacheService.cacheGet(
`${user.id}&${user.username}&${user.role}`,
);
if (!cacheToken) {
throw new UnauthorizedException('token 已过期');
}
+ if (token != cacheToken) {
+ throw new UnauthorizedException('token不正确');
+ }
const existUser = await this.authService.getUser(user);
if (!existUser) {
throw new UnauthorizedException('token不正确');
}
return existUser;
}There are many implementation solutions, you can generate access_token (jwt valid for 30 minutes) and through background jwt refresh_token, refresh_token has a longer validity period than access_token. The client caches these two tokens. When access_token expires, the client carries again. refresh_tokenGet the new access_token. This solution requires the cooperation of the developer of the interface call.
I will mainly introduce here, the automatic renewal of token implemented by pure backend
Implementation process:
Set the token generated by jwt so that it does not expire. This part of the code is in the auth.module.ts file. If you don’t understand, you can read the article Nest.js Practical Series. Part 2 - Implement registration, scan code login, jwt authentication
// auth.module.ts
const jwtModule = JwtModule.registerAsync({
inject: [ConfigService],
useFactory: async (configService: ConfigService) => {
return {
secret: configService.get('SECRET', 'test123456'),
- signOptions: { expiresIn: '4h' }, // 取消有效期设置
};
},
}); and then reset the expiration time after the token authentication is passed, because the cache-manager used has not been updated directly The validity period method is implemented by resetting:
// jwt.strategy.ts
async validate(req, user: User) {
const token = ExtractJwt.fromAuthHeaderAsBearerToken()(req);
const cacheToken = await this.redisCacheService.cacheGet(
`${user.id}&${user.username}&${user.role}`,
);
if (!cacheToken) {
throw new UnauthorizedException('token 已过期');
}
if (token != cacheToken) {
throw new UnauthorizedException('token不正确');
}
const existUser = await this.authService.getUser(user);
if (!existUser) {
throw new UnauthorizedException('token不正确');
}
+ this.redisCacheService.cacheSet(
+ `${user.id}&${user.username}&${user.role}`,
+ token,
+ 1800,
+ );
return existUser;
}At this point, the token expiration processing, token automatic renewal, and user only login are completed in Nest. It is easier to remove the token when logging out. Here are the codes one by one.
In addition to using the officially recommended method in Nest, you can also use nestjs-redis to implement it. If you want to save the token, you want to save the hash structure. , when using cache-manager-redis-store, you will find that there is no hash value storage and retrieval method (it takes some effort to find out).
Note: If you use
nest-redisto implement redis caching, an error will be reported under Nest.js 8 version. Friends can use@chenjm/nestjs-redisinstead, or refer to the solution on the issue: Nest 8 redis bug.
Source code address: https://github.com/koala-coding/nest-blog
More programming related For knowledge, please visit: programming teaching! !
The above is the detailed content of How to use Redis in Node.js? It turns out it's that simple!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!