
If we write the code to analyze and extract elements from the URL ourselves, it may be more painful and troublesome. As one of the most "lazy" groups in this society, programmers are bound to find it intolerable to endlessly reinvent the wheel, so most browsers have built-in URL objects in their standard libraries.
So now, with this, we can pass the URL string as a parameter to the URL's constructor and create an instance of it to parse the URL content? The answer is: "Yes!".
To create a URL object using the URL constructor, we use new to create it in the following code:
new URL('https://www.grapecity.com.cn');
In the above code, we create an instance of the URL object with an absolute address. But at the same time, we can also pass in a relative address as the first parameter and the base URL of the relative address as the second parameter to create a URL object. It may be a mouthful, let’s give you an example:
new URL('/developer', 'https://www.grapecity.com.cn');
Look at the above code, the second basic URL parameter must be a valid absolute address, not a relative address fragment, it must be http :// or https://, we can also use it in the following code in a similar way to a chain definition:
const gcUrl = 'https://www.grapecity.com.cn/';
const gcDevUrl = new URL("/developer", gcUrl);
const gcUrl2 = new URL(gcUrl);
const gcSlnUrl = new URL('/solutions', gcUrl2);
const Url = new URL('aboutus', gcSlnUrl);If each parameter uses toString() If so, our execution results should be as follows:
https://www.grapecity.com.cn/
https://www.grapecity.com.cn/developer
https://www.grapecity.com.cn/
https://www.grapecity.com.cn/solutions
https://www.grapecity.com.cn /aboutus
The second parameter is an optional parameter and should be passed in only when the first parameter is a relative address. The string or URL object we pass in is converted to a USVString object, which corresponds to a set of possible sequences of Unicode scalar values. In our code we can treat them as regular strings. If both parameters are relative addresses, or the base URL and relative address together are invalid, a TypeError exception will be thrown. We can pass the URL object directly to the second parameter because the URL object's toString method will convert the URL object into a complete URL string before operating in the constructor.
URL objects can have the following attributes:
Hash, host, hostname, href, origin, username/password, pathname, port, protocol, search and other attributes. Next, let’s do it together Get to know them!
Hash attribute
The hash attribute can get the part of the URL after the # sign. Since the string is not percent decoded, the special symbols shown below are still encoded. They are encoded using the mapping below. During the encoding process, the characters on the left are converted to the characters on the right:
':' — :'/' — /'?' — ?'# ' — #'[' — [']' — ]'@' — @'!' — ! — $' ()*+ or const exampleUrl = new URL('https://www.grapecity.com.cn/developer/spreadjs#price'); console.log(exampleUrl.hash);
exampleUrl.hash = '#newHash';
const exampleUrl = new URL('https://www.grapecity.com.cn/developer/spreadjs#price'); exampleUrl.hash ='#newPrice'; console.log(exampleUrl.hash);
The host attribute of the URL object contains the host The USVString named. If the port is included after : , then we will also get the port number of the host. For example, if we have:
const exampleUrl = new URL('http://huozige.grapecity.com.cn:8080/'); console.log(exampleUrl.host);
我们就能获得huozige.grapecity.com.cn:8080。与其他USVString属性一样,当我们检索它时,它会转换为字符串。同样的,它也不是只读属性,所以我们也可以像hash属性一样为它赋值:
const exampleUrl = new URL('http:// huozige.grapecity.com.cn:8080/功能演示'); exampleUrl.host = 'es.grapecity.com.cn:80'; console.log(exampleUrl);
这样我们一样能够获得全新的URL。
Hostname 属性
使用hostname属性,可以从URL得到端口外的主机名:
const exampleUrl = new URL('http:// huozige.grapecity.com.cn:8080/功能演示'); console.log(exampleUrl.hostname)
你同样也可以像修改其他属性一样修改hostname属性,例如:
exampleUrl.hostname = ‘newExample.com’;
Href 属性
URL对象的href属性包含了传入URL对象的整个地址字符串,例如:
const exampleUrl = new URL('https://www.grapecity.com.cn/developer/spreadjs#price'); console.log(exampleUrl.href);
打出来的就是我们传给URL构造函数的内容,和其他属性一样,href属性也不是只读的。
Origin 属性
区别于其他属性,Origin是一个只读属性,它将为你返回具有URL来源的Unicode序列化USVString。Origin的结构是由传入的URL类型决定的,对于http或https 的链接,得到的Origin将会为 协议(http/https)+ (://) + 域名 + (:端口),一般情况下,默认端口将会被忽略。对于BLOB 链接,Origin返回的则是BLOB:后面的部分。例如:
const url1 = new URL("https://www.grapecity.com.cn/:443")
const url2 = new URL("blob:https://www.grapecity.com.cn/:443")
console.log(url1.origin);
console.log(url2.origin)你将会得到
https://www.grapecity.com.cn
UserName & Password属性
UserName和Password属性也是可写属性,它能提取域名前的用户名和密码部分的内容,例如:
<p>const url = new URL('https://username:password@www.grapecity.com.cn');<br/>console.log(url.username);<br/>console.log(url.password);<br/>url.username = “username1”;<br/>url.password = “password1”;<br/>console.log(url.username);<br/>console.log(url.password);</p>
Pathname属性
这个属性是指获得传入url的第一个斜杠(/) 后面除参数外的部分,例如:
<p>const url = new URL ("https://www.grapecity.com.cn/developer/spreadjs#price")<br/>console.log(url.pathname);</p>Port属性
Port属性是指可以获得传入Url地址的端口值,这个属性也是可写的。
<p>const url = new URL('http://huozige.grapecity.com.cn:8080/功能演示');<br/>console.log(url.port);</p>
Protocol属性
可以获得传入Url地址参数的协议名,一般是指类似http:,https:,ftp:,file:等这样的协议。
<p>const url = new URL('https://www.grapecity.com.cn/');<br/>console.log(url.protocol);</p>
Search属性
可以获得传入Url地址参数?后的部分,但该属性只能获得整个查询字符串,如若需要了解各个参数的值,可以使用searchParams属性。
<p>const url = new URL('https://www.grapecity.com.cn:443?key1=value1&key2=value2');<br/>console.log(url.search);</p>
searchParams属性
search属性只为我们获取了整个参数字符串,如果有把字符串解析为键值对,这时候searchParams属性就派上了用场,该属性将获得一个URLSearchParams对象,该对象具有列出查询字符串键值对列表的能力,例如,要获取参数列表,我们可以这样使用。
<p>const url = new URL(' https://www.grapecity.com.cn/?key1=value1&key2=value2'); <br/>console.log(url.searchParams.get('key1')); <br/>console.log(url.searchParams.get('key2'));</p>
从第一个console.log语句中获得value1,从第二个console.log语句中获得value2。URLSearchParams对象有一个get方法,通过键名获取给定查询字符串键的值。
静态方法
URL构造函数里有2个静态方法,它有createObjectURL()方法和revokeObjectURL()方法。
URL.createObjectURL()静态方法会创建一个 DOMString,其中包含一个表示参数中给出的对象的URL。这个 URL 的生命周期和创建它的窗口中的 document 绑定。这个新的URL 对象表示指定的 File 对象或 Blob 对象。
URL.revokeObjectURL()方法会释放一个通过URL.createObjectURL()创建的对象URL. 当你要已经用过了这个对象URL,然后要让浏览器知道这个URL已经不再需要指向对应的文件的时候,就需要调用这个方法。
总结
最后为大家带来一张表,希望能更好的帮助大家通览
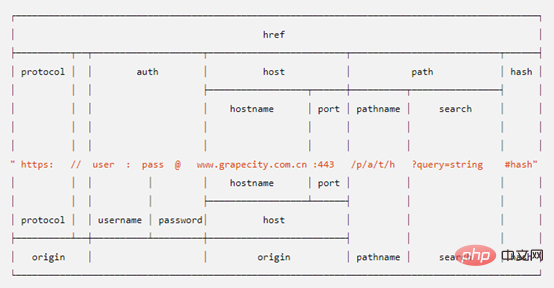
有了URL对象,操纵和从URL中提取部分不再是一件痛苦的事情,因为我们不必自己编写所有代码来完成这项工作。大多数浏览器的标准库中都内置了URL对象。现在我们可以将URL作为字符串传递给URL构造函数并创建URL的实例。然后,我们可以使用方便的值属性和方法来操作并获得我们想要的URL部分。
本文转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/powertoolsteam/p/urlobject.html
相关教程推荐:JavaScript视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about the URL object in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!