
flex Layout is the most frequently used and outstanding function in CSS3. It is a bit complicated and is divided into attributes applied to the container and attributes applied to the item, that is, those on the parent element and those on the child element. Attributes.
display: flex
<style>div{display: flex; background-color: yellow;}b{background-color: red;}</style><body> <div> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b><b>e</b><b>f</b><b>g</b><b>h</b><b>i</b> </div></body>When the parent element is set to flex, its parent element It will appear as a block-level element. If you want to display it as an inline element, you can use inline-flex. All child elements, whether block-level or inline, will immediately become inline layout. This is due to the default values of other attributes and can be modified later.

<style>div{display: flex; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px;}div.row{ flex-direction: row;}div.row-reverse{ flex-direction: row-reverse;}div.column{ flex-direction: column;}div.column-reverse{ flex-direction: column-reverse;}b{background-color: red;}</style><body> <div class="row"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="row-reverse"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="column"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="column-reverse"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>flex-direction determines the arrangement direction of child elements. Default value row.

<style>div{display: flex; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px; }div.nowrap{ flex-wrap: nowrap;}div.wrap{ flex-wrap: wrap;}div.wrap-reverse{ flex-wrap: wrap-reverse;}b{background-color: red; width: 100px;}</style><body> <div class="nowrap"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="wrap"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="wrap-reverse"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div></body> Determines how the child element should be handled when it exceeds one line. The default value nowrap will compress the width of child elements, wrap will wrap a new line, and wrap-reverse will add a new line upwards. Note: This is discussed under the premise that the main axis is the X-axis.

<style>b{background-color: red; }div{display: flex; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px; }div.start{ justify-content: flex-start;}div.end{justify-content: flex-end;}div.center{ justify-content: center;}div.space-between{ justify-content: space-between;}div.space-around{ justify-content: space-around;}</style><body> <div class="start"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="end"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="center"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="space-between"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="space-around"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>justify-content
Determines whether the child element is on the main axis (currently the X axis ), the default value isflex-start. The intervals between space-between and space-around are equally divided by the excess space, but the latter will also include space for the left and right ends.

<style>b{background-color: red; width: 40px;}b:nth-child(1){}b:nth-child(2){font-size: 30px; height: 40px;}b:nth-child(3){height: 50px;}b:nth-child(4){height: 60px;}div{display: flex; flex-wrap: wrap; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px; }div.start{ align-items: flex-start;}div.end{ align-items: flex-end;}div.center{ align-items: center;}div.baseline{ align-items: baseline;}div.stretch{ align-items: stretch;}</style><body> <div class="start"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="end"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="center"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="baseline"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="stretch"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>align-items
Determine the secondary axis (currently the Y axis) The alignment of elements. The default valuestretch means that when the child element does not set a height, it will fill the height of the parent class.

<style>b{background-color: red; width: 100px;}div{display: flex; flex-wrap: wrap; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px; height: 70px;}div.start{ align-content: flex-start;}div.end{ align-content: flex-end;}div.center{ align-content: center;}div.space-between{ align-content: space-between;}div.space-around{ align-content: space-around;}div.stretch{ align-content: stretch;}</style><body> <div class="start"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="end"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="center"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="space-between"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="space-around"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div> <div class="stretch"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b>c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>align-content
indicates that when the child element has multiple lines, each line Position on the secondary axis (currently the Y axis). The default valuestretch means changing the height of each row of child elements until the parent element is filled.

<style>div{display: flex; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px;}b{background-color: red; }b.test{order: -1;}</style><body> <div class="start"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b class="test">c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>order
means arranging elements of the same level from small to large, the default value is0.
 ##flex-grow
##flex-grow<style>div{display: flex; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px;}b{background-color: red; }b.test{flex-grow: 1; background-color: green;}</style><body> <div class="start"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b class="test">c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>means when the main axis (currently the X axis) is on When there is remaining space, the proportion occupied by dividing the space equally. The default value is
0, which means it does not occupy space. The current space bisection ratio is 0 : 0 : 1 : 0, so c occupies all remaining space.

<style>div{display: flex; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px;}b{background-color: red; width: 100px; flex-shrink: 0;}b.test{flex-shrink: 1; background-color: green;}</style><body> <div class="start"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b class="test">c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>1
, which means1 : 1 : 1 : 1, that is, equal-ratio compression. The current ratio is 0: 0: 1: 0, indicating that all space is compressed by c.
<style>div{display: flex; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px;}b{background-color: red; flex-grow: 1;}b.test{flex-basis: 100px; background-color: green;}</style><body> <div class="start"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b class="test">c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>
. When the main axis is the Y-axis, it is equivalent to setting
height. The default value auto means equal to width or height.
align-self
<style>div{display: flex; background-color: yellow; margin: 5px;}b{background-color: red; flex-grow: 1;}b:nth-child(1){height: 20px;}b:nth-child(2){height: 40px;}b:nth-child(3){height: 50px;}b:nth-child(4){height: 60px;}b.test{align-self: flex-end; background-color: green;}</style><body> <div class="start"> <b>a</b><b>b</b><b class="test">c</b><b>d</b> </div></body>align-self 表示当前元素可以覆盖父元素 align-items 所决定的副轴(当前为Y轴)上的方向。默认 auto,即不设置。可选择与 align-items 一致,auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch 。
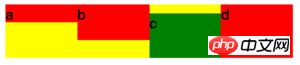
flex-direction:row 作为子元素排序方向为基础。如果改为 flex-direction:column ,主轴将为变成 Y 轴,而副轴将变成 X 轴,所有属性的效果将会改变,这个留给读者自行实践。学习过程中遇到什么问题或者想获取学习资源的话,欢迎加入学习交流群
The above is the detailed content of The most outstanding feature in css3-flex layout. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




