Basics | Python flow control statements
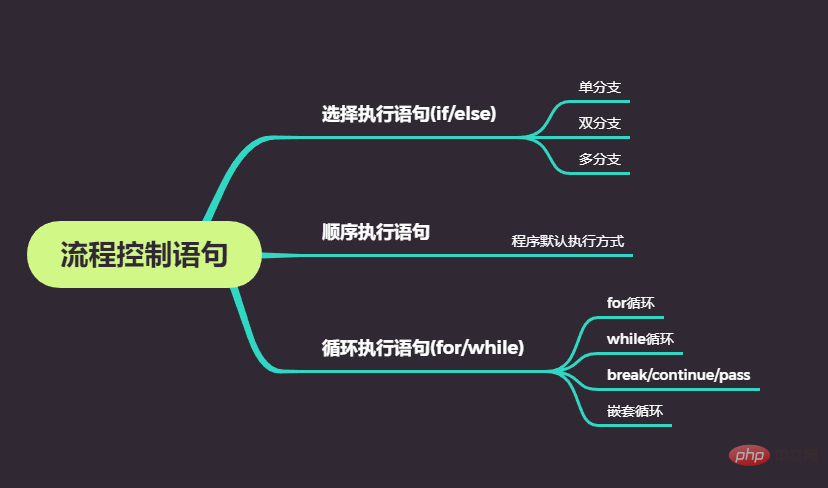
The sequential structure has no keywords. The default execution structure of the computer program is the sequential structure, that is, from top to bottom, from left to right, sequential execution. Statement format: Example: ##2.2 Dual Branch 语句格式: 2.3 多分支 语句格式: 依次遍历每个判断条件,如果判断条件为真,则执行相应代码块,否则执行最后一个代码块,所有代码块中有且仅有一个代码块会被执行。 3.1 for循环 语句格式: 依次遍历迭代对象,执行循环体语句 关于 range (前闭后开): range(100): Generate an integer ranging from 0 to 100. Note that 100 cannot be obtained. range(1, 100): Generate an integer ranging from 1 to 100. range(1, 100, 2): Generate odd numbers from 1 to 100, 2 is the step size. range(100, 0, -2): Generate an even number from 100 to 1, -2 is the step size. 语句格式: 当判断条件为真时,执行代码块,直到判断条件为假时退出。 3.3 break、continue、pass break: 在代码块执行过程中终止循环,并且跳出整个循环 continue: Terminate the current loop during the execution of the code block, jump out of the loop, and execute the next loop. pass: is an empty statement to maintain the integrity of the program structure. Example: 语句格式: 示例:
#if 判断条件:
代码块if 判断条件: 一句代码
"""
登录密码
"""
user = 'Python 当打之年'
password = '123456'
# 用法1
if user == 'Python 当打之年':
print('用户名正确!')
# 用法2
if password == '123456': print('密码正确!')
# 用法3
if user == 'Python 当打之年':
if password == '123456':
print('用户名和密码正确!')
# 用法4
if user == 'Python 当打之年' and password == '123456':
print('用户名和密码正确!')if 判断条件:
代码块1
else:
代码块2user = 'Python 当打之年'
password = '123456'
if user == 'Python 当打之年':
print('用户名正确!')
else:
print('用户名错误!')
if password == '123456':
print('密码正确!')
else:
print('密码错误!')if 判断条件1:
代码块1
elif 判断条件2:
代码块2
...
elif 判断条件n:
代码块n
else:
代码块n+1"""
成绩等级
"""
score = float(input('请输入成绩: '))
if score >= 90:
grade = 'A'
elif score >= 80:
grade = 'B'
elif score >= 70:
grade = 'C'
elif score >= 60:
grade = 'D'
else:
grade = 'E'
print('学生成绩等级为: ', grade)for 迭代变量 in 可迭代对象:
循环体语句for i in range(10):
print('i = ', i)
# 100以内偶数和
sum = 0
for i in range(2, 101, 2):
sum += i
print('sum = ', sum)while 判断条件:
代码块# 用法1
i = 0
while i < 10:
print('i = ', i)
i += 1
# 用法2
i = 0
while True:
if i < 10:
print('i = ', i)
i += 1
else:
break"""
输出 0-10 之间大于 2 的奇数
"""
n = 10
while n > 0:
n -= 1
if n == 2:
break
if n % 2 == 0:
continue
else:
pass
print('执行pass语句')
print(n)
# 执行pass语句
# 9
# 执行pass语句
# 7
# 执行pass语句
# 5
# 执行pass语句
# 3# while 嵌套
while 条件表达式1:
while 条件表达式2:
循环体2
循环体1
# for 嵌套
for 迭代变量1 in 迭代对象1:
for 迭代变量2 in 迭代对象2:
循环体2
循环体1
"""
九九乘法表
"""
for i in range(1, 10):
for j in range(1, i + 1):
print(f'{i}*{j}={i * j}', end='\t')
print()
# 1*1=1
# 2*1=2 2*2=4
# 3*1=3 3*2=6 3*3=9
# 4*1=4 4*2=8 4*3=12 4*4=16
# 5*1=5 5*2=10 5*3=15 5*4=20 5*5=25
# 6*1=6 6*2=12 6*3=18 6*4=24 6*5=30 6*6=36
# 7*1=7 7*2=14 7*3=21 7*4=28 7*5=35 7*6=42 7*7=49
# 8*1=8 8*2=16 8*3=24 8*4=32 8*5=40 8*6=48 8*7=56 8*8=64
# 9*1=9 9*2=18 9*3=27 9*4=36 9*5=45 9*6=54 9*7=63 9*8=72 9*9=81
The above is the detailed content of Basics | Python flow control statements. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 What are class methods in Python
Aug 21, 2025 am 04:12 AM
What are class methods in Python
Aug 21, 2025 am 04:12 AM
ClassmethodsinPythonareboundtotheclassandnottoinstances,allowingthemtobecalledwithoutcreatinganobject.1.Theyaredefinedusingthe@classmethoddecoratorandtakeclsasthefirstparameter,referringtotheclassitself.2.Theycanaccessclassvariablesandarecommonlyused
 python asyncio queue example
Aug 21, 2025 am 02:13 AM
python asyncio queue example
Aug 21, 2025 am 02:13 AM
asyncio.Queue is a queue tool for secure communication between asynchronous tasks. 1. The producer adds data through awaitqueue.put(item), and the consumer uses awaitqueue.get() to obtain data; 2. For each item you process, you need to call queue.task_done() to wait for queue.join() to complete all tasks; 3. Use None as the end signal to notify the consumer to stop; 4. When multiple consumers, multiple end signals need to be sent or all tasks have been processed before canceling the task; 5. The queue supports setting maxsize limit capacity, put and get operations automatically suspend and do not block the event loop, and the program finally passes Canc
 How to run a Python script and see the output in a separate panel in Sublime Text?
Aug 17, 2025 am 06:06 AM
How to run a Python script and see the output in a separate panel in Sublime Text?
Aug 17, 2025 am 06:06 AM
ToseePythonoutputinaseparatepanelinSublimeText,usethebuilt-inbuildsystembysavingyourfilewitha.pyextensionandpressingCtrl B(orCmd B).2.EnsurethecorrectbuildsystemisselectedbygoingtoTools→BuildSystem→Pythonandconfirming"Python"ischecked.3.Ifn
 How to use regular expressions with the re module in Python?
Aug 22, 2025 am 07:07 AM
How to use regular expressions with the re module in Python?
Aug 22, 2025 am 07:07 AM
Regular expressions are implemented in Python through the re module for searching, matching and manipulating strings. 1. Use re.search() to find the first match in the entire string, re.match() only matches at the beginning of the string; 2. Use brackets() to capture the matching subgroups, which can be named to improve readability; 3. re.findall() returns all non-overlapping matches, and re.finditer() returns the iterator of the matching object; 4. re.sub() replaces the matching text and supports dynamic function replacement; 5. Common patterns include \d, \w, \s, etc., you can use re.IGNORECASE, re.MULTILINE, re.DOTALL, re
 How to build and run Python in Sublime Text?
Aug 22, 2025 pm 03:37 PM
How to build and run Python in Sublime Text?
Aug 22, 2025 pm 03:37 PM
EnsurePythonisinstalledbyrunningpython--versionorpython3--versionintheterminal;ifnotinstalled,downloadfrompython.organdaddtoPATH.2.InSublimeText,gotoTools>BuildSystem>NewBuildSystem,replacecontentwith{"cmd":["python","-
 How to use variables and data types in Python
Aug 20, 2025 am 02:07 AM
How to use variables and data types in Python
Aug 20, 2025 am 02:07 AM
VariablesinPythonarecreatedbyassigningavalueusingthe=operator,anddatatypessuchasint,float,str,bool,andNoneTypedefinethekindofdatabeingstored,withPythonbeingdynamicallytypedsotypecheckingoccursatruntimeusingtype(),andwhilevariablescanbereassignedtodif
 How to pass command-line arguments to a script in Python
Aug 20, 2025 pm 01:50 PM
How to pass command-line arguments to a script in Python
Aug 20, 2025 pm 01:50 PM
Usesys.argvforsimpleargumentaccess,whereargumentsaremanuallyhandledandnoautomaticvalidationorhelpisprovided.2.Useargparseforrobustinterfaces,asitsupportsautomatichelp,typechecking,optionalarguments,anddefaultvalues.3.argparseisrecommendedforcomplexsc
 How to debug a remote Python application in VSCode
Aug 30, 2025 am 06:17 AM
How to debug a remote Python application in VSCode
Aug 30, 2025 am 06:17 AM
To debug a remote Python application, you need to use debugpy and configure port forwarding and path mapping: First, install debugpy on the remote machine and modify the code to listen to port 5678, forward the remote port to the local area through the SSH tunnel, then configure "AttachtoRemotePython" in VSCode's launch.json and correctly set the localRoot and remoteRoot path mappings. Finally, start the application and connect to the debugger to realize remote breakpoint debugging, variable checking and code stepping. The entire process depends on debugpy, secure port forwarding and precise path matching.







