
Return function, simply put, the return value is a function.
Returns a function, and the result will be returned only when the returned function is called.
Relevant parameters and variables are saved in the returned function, which is called "Closure".
def returnre(a, b):
def re():
return a + b
return re
test01 = returnre(1, 2)
test02 = returnre(1, 2)
print(test01 == test02) # 每次调用都会返回新生成的函数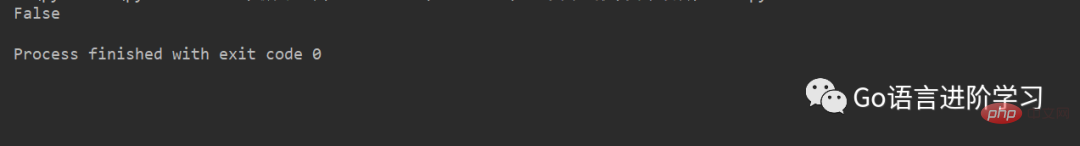
#For example, the characteristics of the re function closure in the above example, nested functions defined in the non-global scope , able to remember the enclosing namespace it was in when it was defined.
Let’s look at an example:
def closur(a):
def myprint():
print(a)
return myprint
test = closur(1)
test()
Code analysis:
Variable a is a local variable of the function closure. It should only exist when the function is running. However, because of the characteristics of the closure, the value of a is encapsulated into the return function.
def closuretest02(*args):
f = []
for i in args:
def test():
return i**2
f.append(test)
return f
test = closuretest02(1,2,3,4)
for i in test:
print(i())
返回闭包时牢记的一点就是:
返回函数不要引用任何循环变量,或者后续会发生变化的变量。
如果一定要引用循环变量怎么办?
方法是再创建一个函数,用该函数的参数绑定循环变量当前的值,无论该循环变量后续如何更改,已绑定到函数参数的值不变:
def count():
def f(j):
def g():
return j*j
return g
fs = []
for i in range(1, 4):
fs.append(f(i)) # f(i)立刻被执行,因此i的当前值被传入f()
return fs再看看结果:
f1, f2, f3 = count() print(f1()) print(f2()) print(f3())

注:
缺点是代码较长,可利用lambda函数缩短代码。
一个函数可以返回一个计算结果,也可以返回一个函数。返回一个函数时,牢记该函数并未执行,返回函数中不要引用任何可能会变化的变量。
nonlocal
nonlocal适用于嵌套函数中内部函数修改外部变量的值。
def outside():
a = 1
print('outside' + str(id(a)))
def inside():
nonlocal a
print('inside ' + str(id(a)))
inside()
outside()因为使用nonlocal后,返回了闭包中有父函数的变量,所以父函数那里不会被回收。

本文基于Python基础,介绍了返回函数。常见的返回函数的应用。函数作为返回值,闭包在实际应用中需要的点,遇到的难点,提供有效的解决方案。使用Python语言,能够更好的理解。
The above is the detailed content of An article will guide you through Python return functions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!