
The so-called function refers to: the code of certain specific functions is composed into a whole, and this whole is called a function.
What is the definition of a function : It’s equivalent to defining a function that can complete certain events; it’s like building a tool yourself.
Define function format:
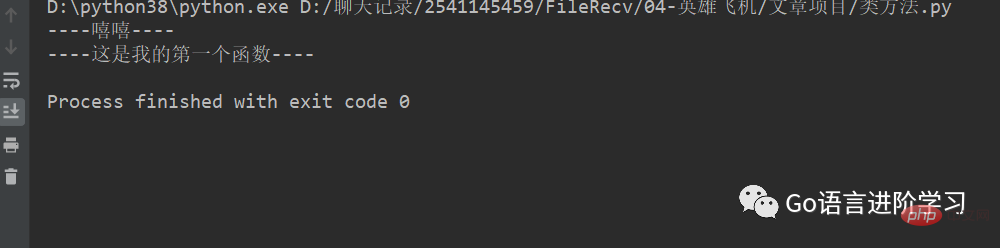
def test(): print('----嘻嘻----') print('----这是我的第一个函数----')
What is a function call: If you just define a function, it actually cannot It is automatically executed and must be called.
# In layman's terms: defining a function is equivalent to creating a tool, and calling a function is equivalent to using this tool to accomplish what you want to do.
# 定义一个函数
def test():
print('----嘻嘻----')
print('----这是我的第一个函数----')
# 调用函数
test() Running result:
开发中,经常需要打印一些调试的信息,此时就又必须要输出时间,这就需要一些时间函数。
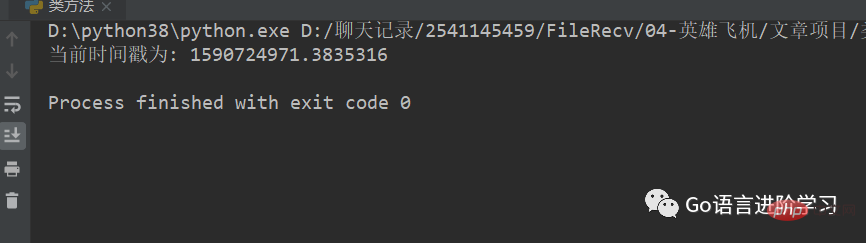
1. 获取当前日期:time.time()
import time # 引入time模块
currentTime = time.time()
print("当前时间戳为:", currentTime) 运行结果 :
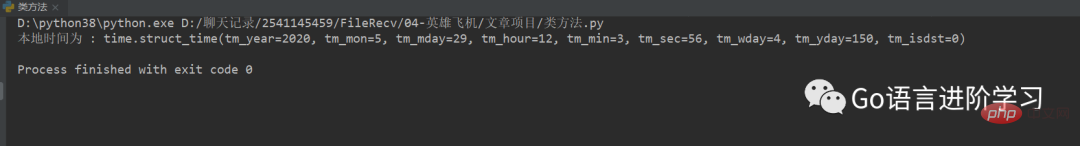
2. 获取元组形式的时间戳:time.local(time.time())
import time
localtime = time.localtime(time.time())
print ( "本地时间为 :", localtime) 运行结果 :
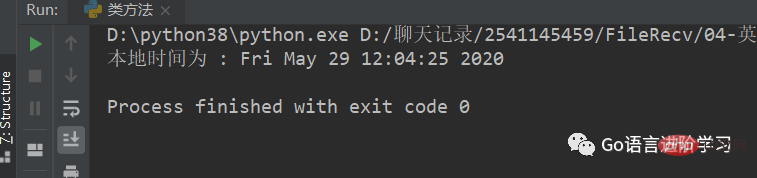
import time localtime = time.asctime( time.localtime(time.time()) ) print ( "本地时间为 :", localtime)
运行结果 :
1. 日期输出格式化 datetime => string
import datetime now = datetime.datetime.now() now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
2. 日期输出格式化 string => datetime
import datetime t_str = '2019-04-07 16:11:21' d = datetime.datetime.strptime(t_str, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') print(d)
运行结果:
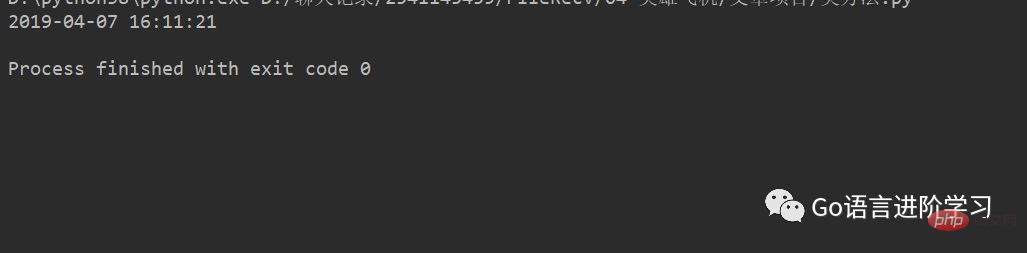
strptime是datetime类的静态方法。
3. 日期比较操作
在datetime模块中有timedelta类,这个类的对象用于表示一个时间间隔,比如两个日期或者时间的差别。
构造方法:
import datetime datetime.timedelta(days=0, seconds=0, microseconds=0, milliseconds=0, minutes=0, hours=0, weeks=0)
所有的参数都有默认值0,这些参数可以是int或float,正的或负的。
可以通过 timedelta.days、tiemdelta.seconds 等获取相应的时间值。
timedelta 类的实例,支持加、减、乘、除等操作,所得的结果也是 timedelta 类的实例。
import datetime year = datetime.timedelta(days=365) t_years = year *10 new_years = ten_years - year print(t_years) print(new_years)
运行结果:
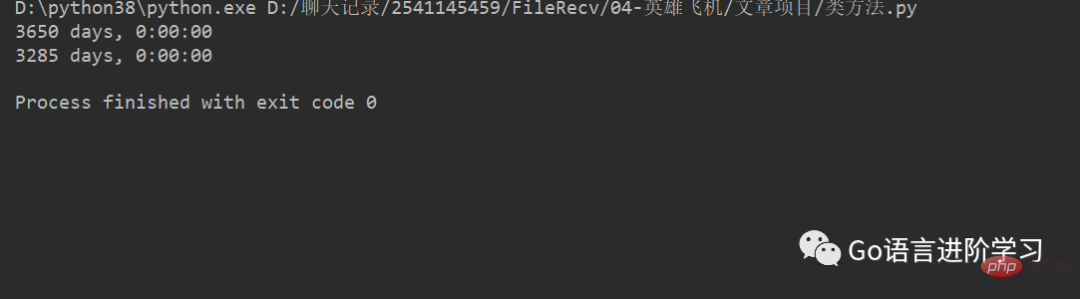
date、time和datetime类也支持与timedelta的加、减运算。
datetime1 = datetime2 + timedelta timedelta = datetime1 - datetime2
这样,可以很方便的实现一些功能。
import calendar dar = calendar.month(2016, 8) print ( "2016年8月份的日历:") print (dar)
运行结果:
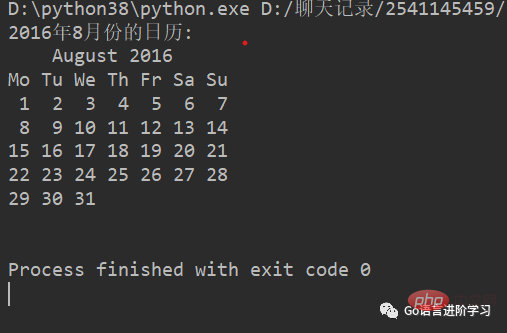
import random
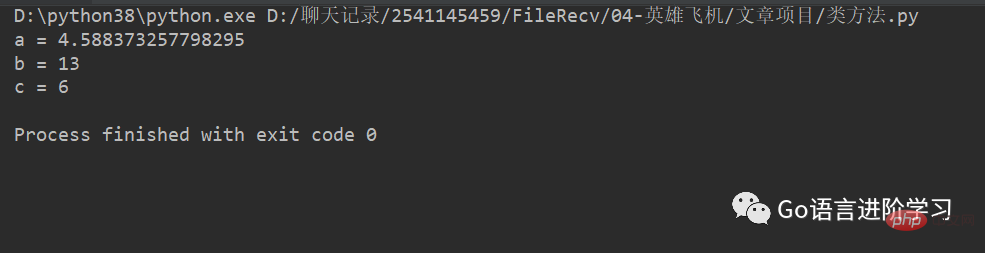
a = random.uniform(1, 5)
print("a =", a)
b = random.randint(10, 50)
print ("b =", b)
c = random.randrange(0, 51, 2)
print ("c =", c)运行结果:
本文详细的讲解了Python基础之函数的定义,调用 。介绍了常用的三种函数的使用方法。通过一个个的小项目使读者更好的认识和运用函数,希望可以帮助你更好的学习Python。
The above is the detailed content of An article teaches you the use of three simple functions in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!