
In PHP, the definition of a method includes two parts: the method declaration and the method body, the syntax "method declaration part {method body part}"; and a pair of curly brackets after the method declaration and the middle The content is called the method body of the method. The content of the method body includes the declaration of local variables and PHP statements. Simply put, the method body is the code block of a method, that is, the part wrapped in curly braces.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, PHP8 version, DELL G3 computer
A class is composed of two parts: the declaration of variables and the definition of methods. The definition of a method consists of two parts: the declaration of the method and the method body
方法声明部分{
方法体的部分
}The pair of braces after the method declaration and the content in the middle are called the method body of the method, and the content of the method body includes local variables. declarations and php statements.
Simply put: The method body is the code block of a method, that is, the part wrapped in curly braces.
1. The relationship between classes and objects
The materialization result of a class is an object, and the abstraction of an object is a class. During the development process, we usually abstract (imagine) a class first, and then use the class to create objects (realize the fantasy content). In the program, we directly use our (fantasy) objects instead of abstract (fantasy) classes.
2. How to abstract a class
class 类名{
成员属性:
姓名、性别、年龄、身高、体重
成员方法:
说话、走路、学习、吃饭、开车
} All classes are declared from two aspects: member attributes and member methods. Attributes and Methods are all members of a class, so attributes are also called member attributes, and methods are also called member methods
1. Member attributes -->Characteristics
Directly declaring variables in an object is called a member attribute. Multiple member variables can be declared in a class, that is, there can be multiple member attributes in an object.
class Person{
var $name; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的名字
var age; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的年龄
var $sex; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的性别
}2. Members Method -->Function
class Person{
var $name; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的名字
var $age; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的年龄
var $sex; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的性别
function say(){ //声明第一个方法
echo '人在说话'; //定义人说话的功能
}
function run(){ //声明第二个方法
echo '人在跑步'; //定义人跑步的功能
}
function eat(){ //声明第三个方法
echo '人在吃饭'; //定义人吃饭的功能
}
}Object is to organize related properties and methods together. Both member attributes and member methods are optional. You can have only member attributes, only member methods, or no members.
3. Instantiate objects
A class can declare multiple objects, allowing the objects to access member properties and member methods
class Person{
var $name; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的名字
var $age; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的年龄
var $sex; //声明第一个成员属性,用于储存人的性别
function say(){ //声明第一个方法
echo '人在说话'; //定义人说话的功能
}
function run(){ //声明第二个方法
echo '人在跑步'; //定义人跑步的功能
}
function eat(){ //声明第三个方法
echo '人在吃饭'; //定义人吃饭的功能
}
}
// 实例化对象
$sqyy = new Person();
//成员属性赋值
$sqyy -> name = "伊川";
$sqyy -> sex = "男";
$sqyy -> age = 26;
//访问对象中的成员方法
$sqyy->eat();4. Special object reference "$this"
In the above example, we instantiate an object and then Assign values to member properties and access member methods. Then $this can also be used in member methods, which represents the current object.
Who is the object before the member method is called? $this represents who
class Person{
var $name;
function info(){
$this ->name = "SQYY";
}
}5. Construction method and destruction method
1. Construction method
The construction method is the first object to be automatically created after the object is created. The method called will initialize the object and will be automatically triggered when the new keyword is used to instantiate the object.
<?php
class Person{
//下面是声明人的成员属性,都是没有初始值的,在创建对象时,使用构造方法赋给初始值
var $name; //定义人的名字
var $sex; //定义人的性别
var $age; //定义人的年龄
function __construct($name="SQYY",$sex="男",$age=1){
$this -> name = $name; //在创建对象时,使用传入的参数$name为成员属性 $this->name赋初值
$this -> sex = $sex; //在创建对象时,使用传入的参数$sex为成员属性 $this->sex赋初值
$this -> age = $age; //在创建对象时,使用传入的参数$sex为成员属性 $this->age赋初值
}
//下面声明人的成员方法
function say(){
echo "我的名字:" .$this ->name. " ,性别:" .$this -> sex ." 年龄" .$this ->age. "。<br>";
}
}
$person1 = new Person(); //创建对象$person1时会自动执行构造方法,默认传参
$person2 = new Person('张三'); //创建对象$person2时会自动执行构造方法,传入第一个参数,其他默认传参
$person3 = new Person('李四','男'); //创建对象$person3时会自动执行构造方法,传入前两个参数,其他默认传参
$person4 = new Person('王五','女','20'); //创建对象$person4时会自动执行构造方法,传入所有参数
$person1 ->say();
$person2 ->say();
$person3 ->say();
$person4 ->say();
?>Running results
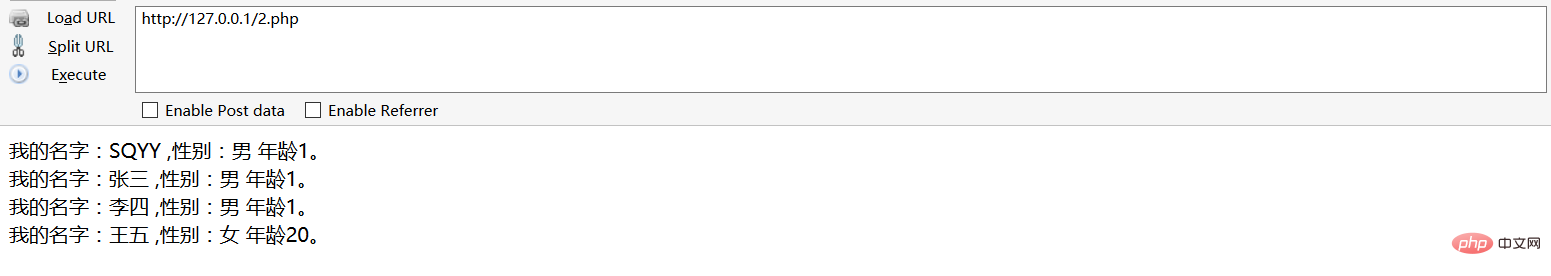
2. Destruction method
The object is automatically the last object before it is destroyed The calling method first creates the incoming variable and then destroys it
<?php
header('Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8');
// 定义一个汽车的类
class car{
// 成员属性
public $name;
public $color;
//构造方法
public function __construct($name,$color){
$this->name = $name;
$this->color = $color;
echo "你创建了".$this->name.'<br>';
}
// 析构方法
public function __destruct(){
echo "你销毁了".$this->name.'<br>';
}
}
// 实例化对象
$hanma = new car('悍马','粉色','H2');
$bmw = new car('宝马','红色','X7');
$benchi = new car('奔驰','黑色','s600');
// unset($bmw);
$bmw = '1111';
?>Run result
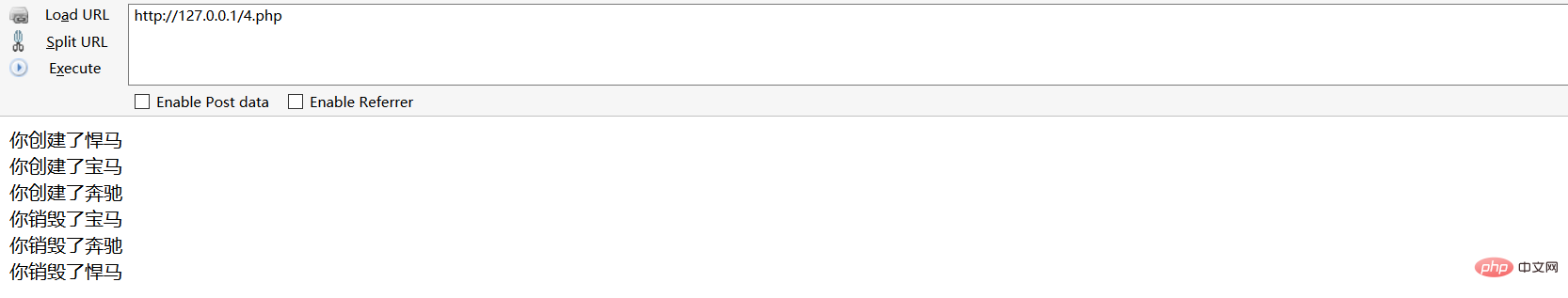
If we do not reference the variable, the object will be created after destroy.
<?php
header('Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8');
// 定义一个汽车的类
class car{
// 成员属性
public $name;
public $color;
//构造方法
public function __construct($name,$color){
$this->name = $name;
$this->color = $color;
echo "你创建了".$this->name.'<br>';
}
// 析构方法
public function __destruct(){
echo "你销毁了".$this->name.'<br>';
}
}
// 实例化对象
new car('悍马','粉色','H2');
new car('宝马','红色','X7');
new car('奔驰','黑色','s600');
?>Run results

Recommended learning: "PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is the php method body?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!