
php modulo equal refers to "%=", which is an extended assignment operator, meaning that the modulo operation is first performed, and then the result is assigned to the variable on the left side of the operator; the syntax is "x %= y", the equivalent form is "x = x % y". The extended assignment operator combines = with other operators (including arithmetic operators, bitwise operators and logical operators) to expand it into a more powerful assignment operator; the expanded assignment operator will make the assignment expression Writing is more elegant and convenient.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, PHP8 version, DELL G3 computer
In php, module equals refers to " %=" is a type of extended assignment operator.
The "%=" operator can perform a modulo operation first, and then assign the result to the variable on the left side of the operator.
Syntax:
x %= y
This is equivalent to:
x = x % y
Example:
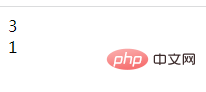
<?php $k1=15; $k1 %= 4; echo $k1."<br/>"; // 输出 3 $k2=15; $k2 %= 2; echo $k2."<br/>"; // 输出 1 ?>
Extended knowledge: PHP assignment operator
The assignment operator is used to transfer the value on the right to the variable (or constant) on the left; you can directly transfer the value on the right The value can be transferred to the variable on the left, or it can be transferred to the variable on the left after performing certain operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, function calls, logical operations, etc.
The most basic assignment operator in PHP is the equal sign =; combined with other operators, = can also be extended to more powerful assignment operators.
Basic assignment operator
= is the most common and basic assignment operator in PHP, used to assign the value of an expression to Assign to another variable, please see the following example:
<?php $a=20; echo $a."<br/>"; // 输出 20
Expanded assignment operator
= can also be used with other operators (including arithmetic operators, bit operators and logical operators) are combined and expanded into a more powerful assignment operator, as shown in Table 1. The expanded assignment operator will make assignment expressions more elegant and convenient to write.
| Operator | Description | Usage example | Equivalent form |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | The most basic assignment operation | x = y | x = y |
| = | Add assignment | x = y | x = x y |
| -= | Subtractive assignment | x -= y | x = x - y |
| *= | Multiply assignment | x *= y | x = x * y |
| /= | Division assignment | x /= y | x = x / y |
| %= | Take the remainder and assign the value | x %= y | x = x % y |
| Power assignment | x **= y | x = x ** y | |
| Take integer assignment | x //= y | x = x // y | |
| Bitwise AND assignment | x &= y | x = x & y | |
| Bitwise OR assignment | x |= y | x = x | y | |
| Bitwise XOR assignment | x ^= y | x = x ^ y | |
| Left shift assignment | x <<= y | x = x << y, where y refers to left shift Number of digits | |
| Right shift assignment | x >>= y | x = x >> y, where y refers to the number of digits to shift to the right |
<?php $z=50; $z -= 25; echo $z."<br/>"; // 输出 25 $i=5; $i *= 5; echo $i."<br/>"; // 输出 25 $j=10; $j /= 5; echo $j."<br/>"; // 输出 2 $k=15; $k %= 4; echo $k."<br/>"; // 输出 3 ?>

PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What does php module equal mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!