
Component is a feature of vue, it is one of the most powerful features of Vue. In Vue, components can extend HTML elements and encapsulate reusable code; at a high level, components are custom elements, and Vue's compiler adds special functions to them; in some cases, components can also be native HTML elements form, extended with the is attribute.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue3 version, DELL G3 computer.
Vue.js is an excellent JavaScript library for front-end interface development. The reason why it is very popular is that it has many outstanding features, the main ones of which are as follows.
1) Lightweight framework
Vue.js can automatically track dependent template expressions and calculated properties, provide MVVM data binding and a composable The component system has a simple and flexible API, making it easier for readers to understand and get started faster.
2) Two-way data binding
Declarative rendering is the main embodiment of two-way data binding and is also the core of Vue.js. It allows the use of concise templates The syntax integrates declarative rendering of data into the DOM.
3) Instructions
Vue.js interacts with the page, mainly through built-in instructions. The function of the instruction is when the value of its expression changes. Apply certain behaviors to the DOM accordingly.
4) Componentization
Component (Component) is one of the most powerful features of Vue.js. Components can extend HTML elements, encapsulating reusable code. At a high level, a component is a custom element to which Vue.js's compiler adds special functionality. In some cases, components can also take the form of native HTML elements, extended with the is attribute.
In Vue, parent-child components communicate through props, one-way transmission from parent to child. The child component communicates with the parent component and notifies the parent component of data changes by triggering events. This forms a basic father-child communication model.
When the components during development have a very close relationship with HTML, JavaScript, etc., the components can be customized according to actual needs, making development more convenient and greatly reducing the amount of code writing.
The component also supports hot reload. When we make changes, the page will not be refreshed, but the component itself will be reloaded immediately, without affecting the current state of the entire application. CSS also supports hot reloading.
Advantages of components:
Reduce the coupling of the entire system. While keeping the interface unchanged, we can replace different components to quickly complete the requirements, such as input box, which can be replaced with calendar, time, range and other components for specific implementation
It is easy to debug. Since the entire system is combined through components, when a problem occurs, you can use the troubleshooting It is not possible to directly remove the component, or to quickly locate the problem based on the component that reported the error. The reason why it can be quickly located is because each component has low coupling and single responsibility, so the logic is simpler than analyzing the entire system
Improve maintainability. Since each component has a single responsibility and the components are reused in the system, optimizing the code can achieve an overall upgrade of the system
5) Client routing
Vue-router is the official routing plug-in of Vue.js. It is deeply integrated with Vue.js and used to build single-page applications. Vue single-page applications are based on routing and components. Routing is used to set access paths and map paths and components. Traditional pages implement page switching and jumps through hyperlinks.
6) State management
State management is actually a one-way data flow. State drives the rendering of View, and the user operates the View to generate Action, which makes the State Changes occur, causing the View to re-render and form a separate component.
Create with new Multiple vue objects are named and can access each other through variables
Example: Object 2 modifies the name variable of Object 1
<!-- 第一个根元素 -->
<div>这里是:{{name}}</div>
<!-- 第二个根元素 -->
<div>
<p>这里是:{{name}}</p>
<br>
<button>change-one-name</button>
<!-- 点击后修改vue-app-one的name值-->
</div> // 第一个vue对象
var one = new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
data:{
"name":"ccy1"
}
})
// 第二个vue对象
var two = new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-two",
data:{
"name":"ccy2"
},
methods:{
// 修改vue-app-one的name为'ccy333'
changeName:function(){
one.name = 'ccy333'
}
}
})Effect: After clicking, modify "ccy1" to "ccy333"
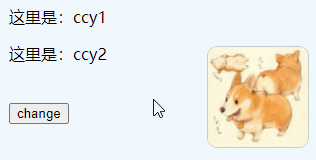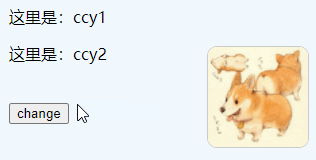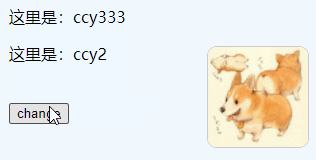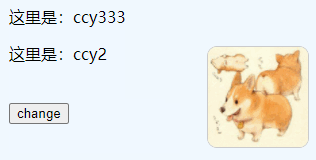
- To define a global component, you need to give the component a name. When calling, use the component name as the label name; it is equivalent to a custom label, which can contain many sub-html tags;
- These sub-html The label is defined in the template attribute of the component. Every time the component is called, the label in the template is rendered.
- in the template must have only one root element
- in the component. data is a function, return the data back
- You can still use this to call the data defined in data
Example:
Define component:
① 定义一个组件,命名为my-component
② 其中包含数据:name和方法:changeName
③ 渲染出的html效果有一个p标签,包含一个按钮,点击按钮时,修改name
④ 命名规范:camelCase (驼峰命名法) 与kebab-case (短横线分隔命名)
- 当写成标签时,遇到有大写字母的命名,需要改成小写并用横杆链接前后两个部分,如定义组件时命名为myComponent,写成标签时应写成my-component>;
- 组件定义时也可以用横杆法命名;
- 如果定义时用myComponent,标签用my-component>是OK的,系统自动识别
// 自定义的全局组件my-component
// template中只有一个根元素p标签,里面包含一个button按钮
Vue.component('my-component',{
template:`<p>
我的名字是:{{name}}
<button>btn</button>
</p>`,
data(){
return {
name:'ccy'
}
},
methods:{
changeName:function(){
this.name = '安之'
}
}
})
// vue对象1
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
})
// vue对象2
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-two",
})使用组件:
① 在vue对象对应的根元素(el指定标签)下使用
② 由于定义的是全局组件,所以可以在任意的vue对象下使用
③ 组件可复用,在一个vue对象下可以使用多次,且组件间互相独立
<div> <my-component></my-component> <my-component></my-component> </div> <div> <my-component></my-component> </div>
效果:

在vue对象中,data属性值是一个对象,比如这样的:
但是在全局组件中,同一份data可能被多个vue对象使用,每个对象不单独维护一份data时,如果某一个vue对象修改了data中的一个变量,其他vue对象获取data时就会被影响;
如果用上面的例子做案例,若组件中的data是对象(引用),其他地方均不改变,两个vue对象便共享同一个name变量;当我通过其中一个vue对象改变name数据时(即点击任一个btn按钮),另一个对象获得的name也发生了改变(其他按钮处的’ccy’也都被改成了’安之’)
因此,为保证数据的独立性,即每个实例可以维护一份被返回对象的独立的拷贝,data为每个实例都return一份新创建的数据,不同的vue对象获取的data均互不影响
在vscode中不允许组件中的data是对象,会报错:
[Vue warn]: The “data” option should be a function that returns a per-instance value in component definitions.
- 局部组件注册在某个vue对象中,
- 只有注册过该局部组件的vue对象才能使用这个局部组件
例子:
局部组件定义:
// template仅一个根元素:ul
var msgComponent = {
// 数据是自身提供的 (hobbies)
template:`注册局部组件:
// 仅由注册过该局部组件的vue对象才能使用,此处为div#vue-app-one
// 注意命名规范,components中对象的key将会被作为标签名,多个单词拼接的命名需使用横杆法
// 可以写成msg-component,此处直接简化了命名为msg,
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
components:{
"msg": msgComponent
}
})html文件中使用<msg></msg>:
<div> <p>这里是vue-app-one</p> <mycomponent></mycomponent> <mycomponent></mycomponent> <p>我的爱好:</p> <msg></msg> <!--使用局部组件--> </div>
效果: 红框圈出的部分就是局部组件渲染出来的
创建子组件:
var titleComponent = {
props:["title"],
template:`<p>{{title}}</p>`
// 所需要的数据title由父组件提供
}在父组件的components属性中注册子组件:
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
components:{
"msg": msgComponent,
"titleComponent":titleComponent
},
})在父组件上使用子组件:
<!-- div#vue-app-one为父组件 --> <div> <p>这里是vue-app-one</p> <mycomponent></mycomponent> <mycomponent></mycomponent> <!--使用子组件title-component,并传值"我的爱好:"给子组件--> <title-component></title-component> <msg></msg> </div>
效果:红框标记处就是父向子传值并展示
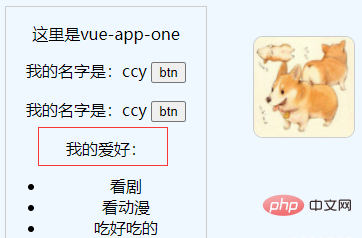
定义子组件:
var titleComponent = {
props:["title"],
template:`<p>{{title}}</p>`
}在父组件的components属性中注册子组件:
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
components:{
"msg": msgComponent,
"titleComponent":titleComponent
},
data(){
return {
title:"my hobbies are ",
}
}
})使用子组件,通过绑定父组件data中的变量title来实现动态传值:
<!-- div#vue-app-one为父组件 --> <div> <p>这里是vue-app-one</p> <mycomponent></mycomponent> <mycomponent></mycomponent> <!-- 动态绑定title --> <title-component></title-component> <msg></msg> </div>
效果:红框处就是动态绑定获取数据的展示

传递数组等复杂数据时,也可以使用v-bind来动态传值,如:
需要向子级传递hobbies数组,在vue实例对象(父)中创建数据hobbies:
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
components:{
"msg": msgComponent,
"titleComponent":titleComponent
},
data:{
title:"my hobbies are ",
hobbies:['看剧','看动漫','吃好吃的'], //需要向子组件传递的数据
}
})定义子组件:
var msgComponent = {
template:`
<p>{{hobby}}</p>
`,
props:["hobby"],
data(){
return {
}
}
}使用子组件:
<!-- div#vue-app-one为父组件 --> <div> <p>这里是vue-app-one</p> <mycomponent></mycomponent> <mycomponent></mycomponent> <title-component></title-component> <!-- 动态传值:hobbies --> <msg></msg> </div>
效果:
跳回“一点想法”处
子组件不能通过prop向父组件传递数据,需要使用事件向父组件抛出一个值,告知父组件我需要实现一个功能,由父组件处理这个事件
例子:点击按钮,改变名称chinesename
(由于data变量名不支持chinese-name形式,花括号里不支持chineseName形式,所以这里我都用了小写,此处记录一下,日后学到了新知再来填坑)
先在父组件的data中定义chinesename的初始值:
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
data:{
chinesename:"anzhi" // chinesename初始值
}
})创建子组件,并注册事件change-name(就像click事件一样,需要让系统能够辨认这是一个事件并监听,当事件被触发时,执行某项约定好的操作):
Vue.component('blog-post', {
props: ['chinesename'],
template: `
<div>
<h4>{{ chinesename }}</h4>
<button>
修改名字
</button>
</div>
`
// blog-post组件包含一个h4,显示chinesename,和一个按钮
// 点击这个按钮,触发change-name事件,将"ruosu"作为参数传递给指定的处理函数onChangeName
})在父组件中使用子组件,定义change-name的处理函数为onChangeName:
<div> <p>这里是vue-app-one</p> <!-- v-bind:通过prop给子组件传递chinesename的初始值 --> <!-- v-on:子组件通过$emit给父组件传递新的chinesename的值 --> <div> <blog-post></blog-post> </div> </div>
在父组件处定义事件处理函数onChangeName:
new Vue({
el:"#vue-app-one",
data:{
chinesename:"anzhi"
},
methods:{
onChangeName:function(value){
// 将chinesename换成传递过来的数据
this.chinesename=value
}
}
})效果:

关于父子组件的区分,在此写一点总结,还是日后学了新知识再来填坑
官网中没有很明确指明两者的定义和区别,在网上搜了一圈,觉得比较多人认可并且好理解的是:
在前面这些父子传值的例子中,我们可以看到,对于局部组件,我们会在某个html根元素中注册并使用,所以此时el指定的根元素在html文件中是这个局部组件的父组件,局部组件在html使用时便是这个父组件的一份子,承担数据传输的责任
跳转到父向子动态传值案例
再用绕口令说一波,即:title-component组件定义处与使用处,两者身份是不一样的,在定义处,它是局部组件,也是子组件,需注册才能使用;在使用处,它是根元素的包含一部分,根元素为父组件,而“它”,承担着父组件与子组件数据沟通的重任
这个总结在全局组件情况下也适用,使用该全局组件的根元素是父组件,如上面的子向父传值的案例,p#vue-app-one是父组件,
图示:
如果是子组件又嵌套了子组件,被嵌套的组件是子子组件,以此类推
The above is the detailed content of Are components a feature of Vue?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!