This article summarizes and shares 20 Vue classic interview questions (with detailed source code-level explanations) to help you sort out basic knowledge and enhance Vue knowledge reserves. It is worth collecting, come and take a look!
Vue is a component-based development framework, so data communication between components is very important for vue applications. This question mainly tests everyone's basic Vue skills and proficiency in using Vue's basic API. Other boundary knowledge such as provide/inject/$attrs demonstrates the breadth of the interviewer's knowledge.
Various ways of passing parameters to components
##Idea analysis:
Answer sample:
1. There are 8 common methods of component communication:Pay attention to several abandoned APIs in vue3https://v3-migration.vuejs.org/breaking-changes/children.htmlhttps://v3-migration.vuejs.org/breaking-changes/listeners-removed.htmlhttps://v3-migration.vuejs.org/breaking-changes/events-api.html#overview
/$emit/$parent/ ref/$attrs /$root/eventbus/vuexvuex/provide injectAnalysis: This question tests common sense and has been explained in detail in the document
v2|v3; is also a good practice question, which is often encountered in projects, and can show the interviewer's API familiarity and application ability.
Idea analysis:
Example answer:
##In practiceIn
v-for has a higher priority than v-if , putting them together, it can be seen from the output rendering function that the loop will be executed first and then the conditions will be judged. Even if we only render a small part of the elements in the list, we have to traverse the entire list every time it is re-rendered, which will compare Waste; In addition, it should be noted that in vue3, it is exactly the opposite. v-if has a higher priority than v-for, so when v-if is executed, the variable it calls does not exist yet, which will cause Exceptions
There are usually two situations that cause us to do this:v-for="user in users" v-if="user.isActive"). At this time, define a calculated property (such as activeUsers) and let it return the filtered list (such as users.filter(u=>u.isActive)).
v-for="user in users" v-if="shouldShowUsers"). At this time, move v-if to the container element (such as ul, ol) or wrap it with a layer of template.
and v-for at the same time on the same element, obviously this is an important note.
Know why:
Do a test. When test.html is of the same level, the rendering function is as follows :
ƒ anonymous(
) {
with(this){return _c('div',{attrs:{"id":"app"}},_l((items),function(item){return (item.isActive)?_c('div',{key:item.id},[_v("\n "+_s(item.name)+"\n ")]):_e()}),0)}
}Take a test and find the answer in test-v3.html
source code
v2: https://github1s.com/vuejs/vue/blob/HEAD/src/compiler/codegen/index.js#L65-L66
v3:https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob /HEAD/packages/compiler-core/src/codegen.ts#L586-L587
Required questions to test the basic knowledge of vue.
Ideas
Give the concept
List the various aspects of the life cycle Stage
Explain the overall process
Combined with practice
Extension: vue3 changes
Answer example
#1. Each Vue component instance will go through a series of initialization steps after it is created, such as, It requires data observation, template compilation, mounting the instance to the DOM, and updating the DOM when the data changes. Functions called lifecycle hooks are run during this process to give users the opportunity to add their own code at certain stages.
2. The Vue life cycle can be divided into 8 stages in total: before and after creation, before and after loading, before and after updating, before and after destruction, as well as the life cycle of some special scenarios. Three new scenes for debugging and server-side rendering have been added to vue3.
| Lifecycle v2 | Lifecycle v3 | Description |
|---|---|---|
| beforeCreate | beforeCreate | When the component instance is created |
| created | created | Component instance Already fully created |
| beforeMount | beforeMount | Before the component is mounted |
| mounted | mounted | After the component is mounted to the instance |
| beforeUpdate | beforeUpdate | When the component data changes, before the update |
| updated | updated | Data data after data update |
| beforeDestroy | beforeUnmount | Before the component instance is destroyed |
| destroyed | unmounted | The component instance is destroyed After |
| Lifecycle v3 | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| activated | keep-alive When the cached component is activated | |
| deactivated | keep-alive Called when the cached component is deactivated | |
| errorCaptured | Capture a message from a descendant | |
| renderTracked | - | |
3、Vue生命周期流程图:
4、结合实践:
beforeCreate:通常用于插件开发中执行一些初始化任务
created:组件初始化完毕,可以访问各种数据,获取接口数据等
mounted:dom已创建,可用于获取访问数据和dom元素;访问子组件等。
beforeUpdate:此时view层还未更新,可用于获取更新前各种状态
updated:完成view层的更新,更新后,所有状态已是最新
beforeunmount:实例被销毁前调用,可用于一些定时器或订阅的取消
unmounted:销毁一个实例。可清理它与其它实例的连接,解绑它的全部指令及事件监听器
可能的追问
setup和created谁先执行?
setup中为什么没有beforeCreate和created?
知其所以然
vue3中生命周期的派发时刻:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/componentOptions.ts#L554-L555
vue2中声明周期的派发时刻:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/vue/blob/HEAD/src/core/instance/init.js#L55-L56
题目分析:
双向绑定是vue的特色之一,开发中必然会用到的知识点,然而此题还问了实现原理,升级为深度考查。
思路分析:
给出双绑定义
双绑带来的好处
在哪使用双绑
使用方式、使用细节、vue3变化
原理实现描述
回答范例:
vue中双向绑定是一个指令v-model,可以绑定一个响应式数据到视图,同时视图中变化能改变该值。
v-model是语法糖,默认情况下相当于:value和@input。使用v-model可以减少大量繁琐的事件处理代码,提高开发效率。
通常在表单项上使用v-model,还可以在自定义组件上使用,表示某个值的输入和输出控制。
通过<input v-model="xxx">的方式将xxx的值绑定到表单元素value上;对于checkbox,可以使用true-value和false-value指定特殊的值,对于radio可以使用value指定特殊的值;对于select可以通过options元素的value设置特殊的值;还可以结合.lazy,.number,.trim对v-mode的行为做进一步限定;v-model用在自定义组件上时又会有很大不同,vue3中它类似于sync修饰符,最终展开的结果是modelValue属性和update:modelValue事件;vue3中我们甚至可以用参数形式指定多个不同的绑定,例如v-model:foo和v-model:bar,非常强大!
v-model是一个指令,它的神奇魔法实际上是vue的编译器完成的。我做过测试,包含v-model的模板,转换为渲染函数之后,实际上还是是value属性的绑定以及input事件监听,事件回调函数中会做相应变量更新操作。编译器根据表单元素的不同会展开不同的DOM属性和事件对,比如text类型的input和textarea会展开为value和input事件;checkbox和radio类型的input会展开为checked和change事件;select用value作为属性,用change作为事件。
可能的追问:
v-model和sync修饰符有什么区别
自定义组件使用v-model如果想要改变事件名或者属性名应该怎么做
知其所以然:
测试代码,test.html
观察输出的渲染函数:
// <input type="text" v-model="foo">
_c('input', {
directives: [{ name: "model", rawName: "v-model", value: (foo), expression: "foo" }],
attrs: { "type": "text" },
domProps: { "value": (foo) },
on: {
"input": function ($event) {
if ($event.target.composing) return;
foo = $event.target.value
}
}
})// <input type="checkbox" v-model="bar">
_c('input', {
directives: [{ name: "model", rawName: "v-model", value: (bar), expression: "bar" }],
attrs: { "type": "checkbox" },
domProps: {
"checked": Array.isArray(bar) ? _i(bar, null) > -1 : (bar)
},
on: {
"change": function ($event) {
var $$a = bar, $$el = $event.target, $$c = $$el.checked ? (true) : (false);
if (Array.isArray($$a)) {
var $$v = null, $$i = _i($$a, $$v);
if ($$el.checked) { $$i < 0 && (bar = $$a.concat([$$v])) }
else {
$$i > -1 && (bar = $$a.slice(0, $$i).concat($$a.slice($$i + 1))) }
} else {
bar = $$c
}
}
}
})// <select v-model="baz">
// <option value="vue">vue</option>
// <option value="react">react</option>
// </select>
_c('select', {
directives: [{ name: "model", rawName: "v-model", value: (baz), expression: "baz" }],
on: {
"change": function ($event) {
var $$selectedVal = Array.prototype.filter.call(
$event.target.options,
function (o) { return o.selected }
).map(
function (o) {
var val = "_value" in o ? o._value : o.value;
return val
}
);
baz = $event.target.multiple ? $$selectedVal : $$selectedVal[0]
}
}
}, [
_c('option', { attrs: { "value": "vue" } }, [_v("vue")]), _v(" "),
_c('option', { attrs: { "value": "react" } }, [_v("react")])
])此题属于实践题,考察大家对vue常用api使用熟练度,答题时不仅要列出这些解决方案,同时最好说出他们异同。
答题思路:
按照逻辑扩展和内容扩展来列举,
逻辑扩展有:mixins、extends、composition api;
内容扩展有slots;
分别说出他们使用方法、场景差异和问题。
作为扩展,还可以说说vue3中新引入的composition api带来的变化
回答范例:
常见的组件扩展方法有:mixins,slots,extends等
混入mixins是分发 Vue 组件中可复用功能的非常灵活的方式。混入对象可以包含任意组件选项。当组件使用混入对象时,所有混入对象的选项将被混入该组件本身的选项。
// 复用代码:它是一个配置对象,选项和组件里面一样
const mymixin = {
methods: {
dosomething(){}
}
}
// 全局混入:将混入对象传入
Vue.mixin(mymixin)
// 局部混入:做数组项设置到mixins选项,仅作用于当前组件
const Comp = {
mixins: [mymixin]
}插槽主要用于vue组件中的内容分发,也可以用于组件扩展。
子组件Child
<div> <slot>这个内容会被父组件传递的内容替换</slot> </div>
父组件Parent
<div> <Child>来自老爹的内容</Child> </div>
如果要精确分发到不同位置可以使用具名插槽,如果要使用子组件中的数据可以使用作用域插槽。
组件选项中还有一个不太常用的选项extends,也可以起到扩展组件的目的
// 扩展对象
const myextends = {
methods: {
dosomething(){}
}
}
// 组件扩展:做数组项设置到extends选项,仅作用于当前组件
// 跟混入的不同是它只能扩展单个对象
// 另外如果和混入发生冲突,该选项优先级较高,优先起作用
const Comp = {
extends: myextends
}混入的数据和方法不能明确判断来源且可能和当前组件内变量产生命名冲突,vue3中引入的composition api,可以很好解决这些问题,利用独立出来的响应式模块可以很方便的编写独立逻辑并提供响应式的数据,然后在setup选项中组合使用,增强代码的可读性和维护性。例如:
// 复用逻辑1
function useXX() {}
// 复用逻辑2
function useYY() {}
// 逻辑组合
const Comp = {
setup() {
const {xx} = useXX()
const {yy} = useYY()
return {xx, yy}
}
}可能的追问
Vue.extend方法你用过吗?它能用来做组件扩展吗?
知其所以然
mixins原理:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/apiCreateApp.ts#L232-L233
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/componentOptions.ts#L545
slots原理:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/componentSlots.ts#L129-L130
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts#L1373-L1374
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/helpers/renderSlot.ts#L23-L24
分析
这是一个实践知识点,组件化开发过程中有个单项数据流原则,不在子组件中修改父组件是个常识问题。
参考文档:https://staging.vuejs.org/guide/components/props.html#one-way-data-flow
思路
讲讲单项数据流原则,表明为何不能这么做
举几个常见场景的例子说说解决方案
结合实践讲讲如果需要修改父组件状态应该如何做
回答范例
所有的 prop 都使得其父子之间形成了一个单向下行绑定:父级 prop 的更新会向下流动到子组件中,但是反过来则不行。这样会防止从子组件意外变更父级组件的状态,从而导致你的应用的数据流向难以理解。另外,每次父级组件发生变更时,子组件中所有的 prop 都将会刷新为最新的值。这意味着你不应该在一个子组件内部改变 prop。如果你这样做了,Vue 会在浏览器控制台中发出警告。
const props = defineProps(['foo']) // ❌ 下面行为会被警告, props是只读的! props.foo = 'bar'
实际开发过程中有两个场景会想要修改一个属性:
**这个 prop 用来传递一个初始值;这个子组件接下来希望将其作为一个本地的 prop 数据来使用。**在这种情况下,最好定义一个本地的 data,并将这个 prop 用作其初始值:
const props = defineProps(['initialCounter']) const counter = ref(props.initialCounter)
**这个 prop 以一种原始的值传入且需要进行转换。**在这种情况下,最好使用这个 prop 的值来定义一个计算属性:
const props = defineProps(['size']) // prop变化,计算属性自动更新 const normalizedSize = computed(() => props.size.trim().toLowerCase())
实践中如果确实想要改变父组件属性应该emit一个事件让父组件去做这个变更。注意虽然我们不能直接修改一个传入的对象或者数组类型的prop,但是我们还是能够直接改内嵌的对象或属性。
分析
综合实践题目,实际开发中经常需要面临权限管理的需求,考查实际应用能力。
权限管理一般需求是两个:页面权限和按钮权限,从这两个方面论述即可。
思路
权限管理需求分析:页面和按钮权限
权限管理的实现方案:分后端方案和前端方案阐述
说说各自的优缺点
回答范例
权限管理一般需求是页面权限和按钮权限的管理
具体实现的时候分后端和前端两种方案:
前端方案会把所有路由信息在前端配置,通过路由守卫要求用户登录,用户登录后根据角色过滤出路由表。比如我会配置一个asyncRoutes数组,需要认证的页面在其路由的meta中添加一个roles字段,等获取用户角色之后取两者的交集,若结果不为空则说明可以访问。此过滤过程结束,剩下的路由就是该用户能访问的页面,最后通过router.addRoutes(accessRoutes)方式动态添加路由即可。
后端方案会把所有页面路由信息存在数据库中,用户登录的时候根据其角色查询得到其能访问的所有页面路由信息返回给前端,前端再通过addRoutes动态添加路由信息
按钮权限的控制通常会实现一个指令,例如v-permission,将按钮要求角色通过值传给v-permission指令,在指令的moutned钩子中可以判断当前用户角色和按钮是否存在交集,有则保留按钮,无则移除按钮。
纯前端方案的优点是实现简单,不需要额外权限管理页面,但是维护起来问题比较大,有新的页面和角色需求就要修改前端代码重新打包部署;服务端方案就不存在这个问题,通过专门的角色和权限管理页面,配置页面和按钮权限信息到数据库,应用每次登陆时获取的都是最新的路由信息,可谓一劳永逸!
知其所以然
路由守卫
https://github1s.com/PanJiaChen/vue-element-admin/blob/HEAD/src/permission.js#L13-L14
路由生成
https://github1s.com/PanJiaChen/vue-element-admin/blob/HEAD/src/store/modules/permission.js#L50-L51
动态追加路由
https://github1s.com/PanJiaChen/vue-element-admin/blob/HEAD/src/permission.js#L43-L44
可能的追问
类似Tabs这类组件能不能使用v-permission指令实现按钮权限控制?
<el-tabs> <el-tab-pane label="⽤户管理" name="first">⽤户管理</el-tab-pane> <el-tab-pane label="⻆⾊管理" name="third">⻆⾊管理</el-tab-pane> </el-tabs>
服务端返回的路由信息如何添加到路由器中?
// 前端组件名和组件映射表
const map = {
//xx: require('@/views/xx.vue').default // 同步的⽅式
xx: () => import('@/views/xx.vue') // 异步的⽅式
}
// 服务端返回的asyncRoutes
const asyncRoutes = [
{ path: '/xx', component: 'xx',... }
]
// 遍历asyncRoutes,将component替换为map[component]
function mapComponent(asyncRoutes) {
asyncRoutes.forEach(route => {
route.component = map[route.component];
if(route.children) {
route.children.map(child => mapComponent(child))
}
})
}
mapComponent(asyncRoutes)分析
这是一道必问题目,但能回答到位的比较少。如果只是看看一些网文,通常没什么底气,经不住面试官推敲,但像我们这样即看过源码还造过轮子的,回答这个问题就会比较有底气啦。
答题思路:
啥是响应式?
为什么vue需要响应式?
它能给我们带来什么好处?
vue的响应式是怎么实现的?有哪些优缺点?
vue3中的响应式的新变化
回答范例:
所谓数据响应式就是能够使数据变化可以被检测并对这种变化做出响应的机制。
MVVM框架中要解决的一个核心问题是连接数据层和视图层,通过数据驱动应用,数据变化,视图更新,要做到这点的就需要对数据做响应式处理,这样一旦数据发生变化就可以立即做出更新处理。
Taking vue as an example, through data responsiveness plus virtual DOM and patch algorithm, developers only need to operate data and care about business, without having to deal with cumbersome DOM operations at all, thus greatly improving development efficiency. , Reduce development difficulty.
The data responsiveness in vue2 will be processed differently according to the data type. If it is an object, use Object.defineProperty() to define data interception. When When the data is accessed or changed, we sense and respond; if it is an array, we overwrite the 7 change methods of the array object prototype so that these methods can provide additional update notifications and respond. This mechanism solves the problem of data responsiveness very well, but it also has some shortcomings in actual use: for example, recursive traversal during initialization will cause performance loss; when adding or deleting attributes, users need to use Vue.set/delete. Only special APIs can take effect; problems such as the new Map and Set data structures generated in es6 are not supported.
Know why
vue2 responsiveness:Analysis Almost all existing frameworks introduce virtual DOM to abstract the real DOM, which is what everyone knows now VNode and VDOM, so why do we need to introduce virtual DOM? Just answer this question!
Thoughts
Answer example
Object, but it describes a view structure through different attributes.
There are limitations to directly operating the dom, such as diff, clone and other operations. There is a lot of content on a real element. If you perform a diff operation directly on it, additional diff will be performed. Necessary content; similarly, if you need to clone, you need to copy all its contents, which is not necessary. However, if you move these operations to JavaScript objects, it becomes simpler.
The same VNode node can be rendered into corresponding content on different platforms, for example: rendering in the browser is dom Element nodes are rendered into corresponding controls in Native (iOS, Android), can implement SSR, render into WebGL, etc.
Know whyvnode definition:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts#L127-L128
Observe the rendering function: 21-vdom/test- render-v3.html
Create vnode:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/ packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts#L291-L292
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD /packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts#L486-L487
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/ blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/apiCreateApp.ts#L283-L284
mount:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/ HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts#L1171-L1172
Debug the mount process: mountComponent
21-vdom/test-render-v3.html
Analysis
Required questions, involving vue update principles, comparatively test the depth of understanding.
Thoughts
What does the diff algorithm do
Its necessity
When it is executed
Specific execution method
Highlight: Let’s talk about optimization in vue3
##Answer example
1. The diff algorithm in Vue is called the patching algorithm, which is modified from Snabbdom. If the virtual DOM is to be converted into a real DOM, it needs to be converted through the patch method. 2. Initially, each dependency in the Vue1.x view has an update function corresponding to it, which can be updated accurately. Therefore, virtual DOM and patching algorithm support are not needed. However, such fine granularity makes Vue1.x unable to carry it. Larger applications; in Vue 2.x, in order to reduce the Watcher granularity, each component has only one Watcher corresponding to it. At this time, the patching algorithm needs to be introduced to accurately find the changes and update them efficiently. 3. The moment when diff is executed in Vue is when the responsive data change in the component triggers the instance to execute its update function. The update function will execute the render function again to obtain the latest virtual DOM, and then execute the patch function and pass in Compare the old and new virtual DOM to find the changes, and finally convert them into corresponding DOM operations. 4. The patch process is a recursive process, following the strategy of depth first and same-layer comparison; take vue3 patch as an example:Know why
patch key codehttps: //github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts#L354-L355Debug test-v3.htmlAnalysis
The most noteworthy new features listed on the official website: https ://v3-migration.vuejs.org/Answer example
1. The new features of Vue3 at the api level mainly include: Composition API, SFC Composition API syntax sugar, Teleport transmission Doors, Fragments, Emits options, custom renderers, SFC CSS variables, Suspense2. In addition, Vue3.0 also has many eye-catching improvements at the framework level:Know why
Experience compiler optimizationhttps://sfc.vuejs.org/
reactive implementation
https://github1s .com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/reactivity/src/reactive.ts#L90-L91
Analysis
API questions test basic abilities. There is no room for error. Please be as detailed as possible.
Thoughts
What is dynamic routing
When to use it Dynamic routing, how to define dynamic routing
How to obtain parameters
Details and precautions
Answer Example
Many times, we need to map routes for a given matching pattern to the same component, in this case dynamic routing needs to be defined.
For example, we might have a User component that should render to all users, but with different user IDs. In Vue Router, we can use a dynamic field in the path to achieve this, for example: { path: '/users/:id', component: User }, where :id It is the path parameter
#The path parameter is represented by colon :. When a route is matched, the value of its params will be exposed in every component as this.$route.params.
There can be multiple parameters, such as /users/:username/posts/:postId; in addition to $route.params , the $route object also exposes other useful information, such as $route.query, $route.hash, etc.
How to respond to changes in dynamic routing parameters
https ://router.vuejs.org/zh/guide/essentials/dynamic-matching.html#Response to changes in routing parameters
How do we handle 404 Not Found routing
https://router.vuejs.org/zh/guide/essentials/dynamic-matching.html#Capture all routes or -404-not-found-routes
Idea analysis:
First think about the problem that vue routing needs to solve: when the user clicks on the jump link to switch content, the page does not refresh.
Answer example:
The routing of a SPA application needs to be solved The problem is that the page jump content changes without refreshing , and the route also needs to exist in the form of a plug-in, so:
First I will define a createRouterFunction, returns the router instance, and does several things inside the instance:
Define the router as a Vue plug-in, that is, implement the install method, and do two things internally:
Know why:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/router/blob/HEAD/src/router.ts#L355-L356
https: //github1s.com/vuejs/router/blob/HEAD/src/history/html5.ts#L314-L315
RouterView
https://github1s.com/vuejs/router/blob/HEAD/src/RouterLink.ts#L184-L185
https://github1s.com/vuejs/router/blob/HEAD/src/RouterView.ts#L43-L44
Analysis:
This is a particularly common question, which mainly tests everyone’s mastery of virtual DOM and patch details. Can reflect the interviewer's level of understanding.
Idea analysis:
The conclusion is given that the role of key is to optimize patch performance
Necessity of key
Actual usage
Summary: How to judge vue can be described from the source code level Are the two nodes the same
key的作用主要是为了更高效的更新虚拟DOM。
vue在patch过程中判断两个节点是否是相同节点是key是一个必要条件,渲染一组列表时,key往往是唯一标识,所以如果不定义key的话,vue只能认为比较的两个节点是同一个,哪怕它们实际上不是,这导致了频繁更新元素,使得整个patch过程比较低效,影响性能。
实际使用中在渲染一组列表时key必须设置,而且必须是唯一标识,应该避免使用数组索引作为key,这可能导致一些隐蔽的bug;vue中在使用相同标签元素过渡切换时,也会使用key属性,其目的也是为了让vue可以区分它们,否则vue只会替换其内部属性而不会触发过渡效果。
从源码中可以知道,vue判断两个节点是否相同时主要判断两者的key和元素类型等,因此如果不设置key,它的值就是undefined,则可能永远认为这是两个相同节点,只能去做更新操作,这造成了大量的dom更新操作,明显是不可取的。
知其所以然
测试代码,test-v3.html
上面案例重现的是以下过程
不使用key
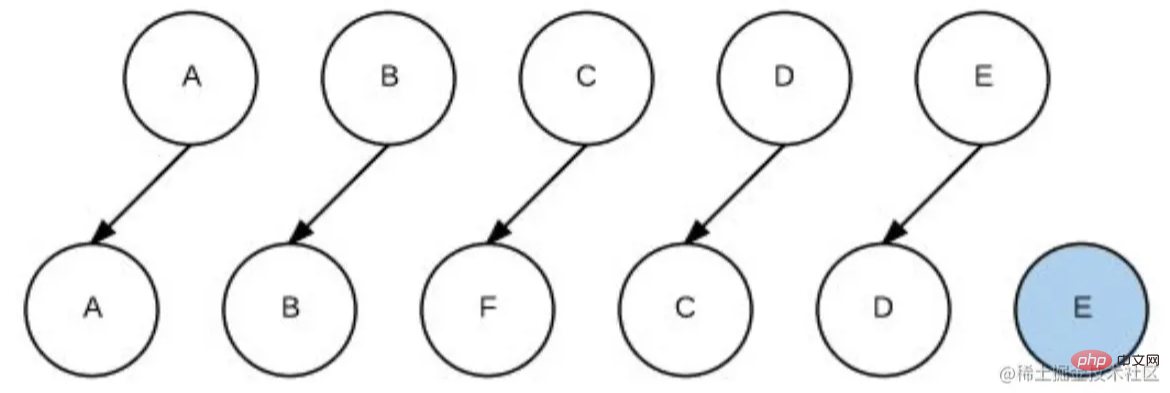
如果使用key
// 首次循环patch A A B C D E A B F C D E // 第2次循环patch B B C D E B F C D E // 第3次循环patch E C D E F C D E // 第4次循环patch D C D F C D // 第5次循环patch C C F C // oldCh全部处理结束,newCh中剩下的F,创建F并插入到C前面
源码中找答案:
判断是否为相同节点
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts#L342-L343
更新时的处理
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts#L1752-L1753
不使用key
如果使用key
// 首次循环patch A A B C D E A B F C D E // 第2次循环patch B B C D E B F C D E // 第3次循环patch E C D E F C D E // 第4次循环patch D C D F C D // 第5次循环patch C C F C // oldCh全部处理结束,newCh中剩下的F,创建F并插入到C前面
源码中找答案:
判断是否为相同节点
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts#L342-L343
更新时的处理
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts#L1752-L1753
分析
这道题及考察使用,有考察原理,nextTick在开发过程中应用的也较少,原理上和vue异步更新有密切关系,对于面试者考查很有区分度,如果能够很好回答此题,对面试效果有极大帮助。
答题思路
nextTick是做什么的?
为什么需要它呢?
开发时何时使用它?抓抓头,想想你在平时开发中使用它的地方
下面介绍一下如何使用nextTick
原理解读,结合异步更新和nextTick生效方式,会显得你格外优秀
回答范例:
1、nextTick是等待下一次 DOM 更新刷新的工具方法。
2、Vue有个异步更新策略,意思是如果数据变化,Vue不会立刻更新DOM,而是开启一个队列,把组件更新函数保存在队列中,在同一事件循环中发生的所有数据变更会异步的批量更新。这一策略导致我们对数据的修改不会立刻体现在DOM上,此时如果想要获取更新后的DOM状态,就需要使用nextTick。
3、开发时,有两个场景我们会用到nextTick:
created中想要获取DOM时;
响应式数据变化后获取DOM更新后的状态,比如希望获取列表更新后的高度。
4、nextTick签名如下:function nextTick(callback?: () => void): Promise<void>
所以我们只需要在传入的回调函数中访问最新DOM状态即可,或者我们可以await nextTick()方法返回的Promise之后做这件事。
5、在Vue内部,nextTick之所以能够让我们看到DOM更新后的结果,是因为我们传入的callback会被添加到队列刷新函数(flushSchedulerQueue)的后面,这样等队列内部的更新函数都执行完毕,所有DOM操作也就结束了,callback自然能够获取到最新的DOM值。
知其所以然:
源码解读:
组件更新函数入队:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts#L1547-L1548
入队函数:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/scheduler.ts#L84-L85
nextTick定义:
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/scheduler.ts#L58-L59
测试案例,test-v3.html
两个重要API,反应应聘者熟练程度。
computed特点:具有响应式的返回值
const count = ref(1) const plusOne = computed(() => count.value + 1)
watch特点:侦测变化,执行回调
const state = reactive({ count: 0 })
watch(
() => state.count,
(count, prevCount) => {
/* ... */
}
)回答范例
计算属性可以从组件数据派生出新数据,最常见的使用方式是设置一个函数,返回计算之后的结果,computed和methods的差异是它具备缓存性,如果依赖项不变时不会重新计算。侦听器可以侦测某个响应式数据的变化并执行副作用,常见用法是传递一个函数,执行副作用,watch没有返回值,但可以执行异步操作等复杂逻辑。
计算属性常用场景是简化行内模板中的复杂表达式,模板中出现太多逻辑会是模板变得臃肿不易维护。侦听器常用场景是状态变化之后做一些额外的DOM操作或者异步操作。选择采用何用方案时首先看是否需要派生出新值,基本能用计算属性实现的方式首选计算属性。
使用过程中有一些细节,比如计算属性也是可以传递对象,成为既可读又可写的计算属性。watch可以传递对象,设置deep、immediate等选项。
vue3中watch选项发生了一些变化,例如不再能侦测一个点操作符之外的字符串形式的表达式; reactivity API中新出现了watch、watchEffect可以完全替代目前的watch选项,且功能更加强大。
可能追问
watch会不会立即执行?
watch 和 watchEffect有什么差异
知其所以然
computed的实现
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/reactivity/src/computed.ts#L79-L80
ComputedRefImpl
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/reactivity/src/computed.ts#L26-L27
缓存性
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/reactivity/src/computed.ts#L59-L60
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/reactivity/src/computed.ts#L45-L46
watch的实现
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/apiWatch.ts#L158-L159
这题考查大家对创建过程的理解程度。
思路分析
给结论
阐述理由
回答范例
创建过程自上而下,挂载过程自下而上;即:
之所以会这样是因为Vue创建过程是一个递归过程,先创建父组件,有子组件就会创建子组件,因此创建时先有父组件再有子组件;子组件首次创建时会添加mounted钩子到队列,等到patch结束再执行它们,可见子组件的mounted钩子是先进入到队列中的,因此等到patch结束执行这些钩子时也先执行。
知其所以然
观察beforeCreated和created钩子的处理
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/componentOptions.ts#L554-L555
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/componentOptions.ts#L741-L742
观察beforeMount和mounted钩子的处理
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts#L1310-L1311
测试代码,test-v3.html
缓存组件使用keep-alive组件,这是一个非常常见且有用的优化手段,vue3中keep-alive有比较大的更新,能说的点比较多。
思路
缓存用keep-alive,它的作用与用法
使用细节,例如缓存指定/排除、结合router和transition
组件缓存后更新可以利用activated或者beforeRouteEnter
原理阐述
回答范例
开发中缓存组件使用keep-alive组件,keep-alive是vue内置组件,keep-alive包裹动态组件component时,会缓存不活动的组件实例,而不是销毁它们,这样在组件切换过程中将状态保留在内存中,防止重复渲染DOM。
<keep-alive> <component :is="view"></component> </keep-alive>
结合属性include和exclude可以明确指定缓存哪些组件或排除缓存指定组件。vue3中结合vue-router时变化较大,之前是keep-alive包裹router-view,现在需要反过来用router-view包裹keep-alive:
<router-view v-slot="{ Component }">
<keep-alive>
<component :is="Component"></component>
</keep-alive>
</router-view>缓存后如果要获取数据,解决方案可以有以下两种:
beforeRouteEnter:在有vue-router的项目,每次进入路由的时候,都会执行beforeRouteEnter
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next){
next(vm=>{
console.log(vm)
// 每次进入路由执行
vm.getData() // 获取数据
})
},actived:在keep-alive缓存的组件被激活的时候,都会执行actived钩子
activated(){
this.getData() // 获取数据
},keep-alive是一个通用组件,它内部定义了一个map,缓存创建过的组件实例,它返回的渲染函数内部会查找内嵌的component组件对应组件的vnode,如果该组件在map中存在就直接返回它。由于component的is属性是个响应式数据,因此只要它变化,keep-alive的render函数就会重新执行。
知其所以然
KeepAlive定义
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/components/KeepAlive.ts#L73-L74
缓存定义
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/components/KeepAlive.ts#L102-L103
缓存组件
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/components/KeepAlive.ts#L215-L216
获取缓存组件
https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/components/KeepAlive.ts#L241-L242
测试缓存特性,test-v3.html
综合实践类题目,考查实战能力。没有什么绝对的正确答案,把平时工作的重点有条理的描述一下即可。
思路
构建项目,创建项目基本结构
引入必要的插件:
代码规范:prettier,eslint
提交规范:husky,lint-staged
其他常用:svg-loader,vueuse,nprogress
常见目录结构
回答范例
从0创建一个项目我大致会做以下事情:项目构建、引入必要插件、代码规范、提交规范、常用库和组件
目前vue3项目我会用vite或者create-vue创建项目
接下来引入必要插件:路由插件vue-router、状态管理vuex/pinia、ui库我比较喜欢element-plus和antd-vue、http工具我会选axios
其他比较常用的库有vueuse,nprogress,图标可以使用vite-svg-loader
下面是代码规范:结合prettier和eslint即可
最后是提交规范,可以使用husky,lint-staged,commitlint
目录结构我有如下习惯:.vscode:用来放项目中的 vscode 配置
plugins:用来放 vite 插件的 plugin 配置
public:用来放一些诸如 页头icon 之类的公共文件,会被打包到dist根目录下
src:用来放项目代码文件
api:用来放http的一些接口配置
assets:用来放一些 CSS 之类的静态资源
components:用来放项目通用组件
layout:用来放项目的布局
router:用来放项目的路由配置
store:用来放状态管理Pinia的配置
utils:用来放项目中的工具方法类
views:用来放项目的页面文件
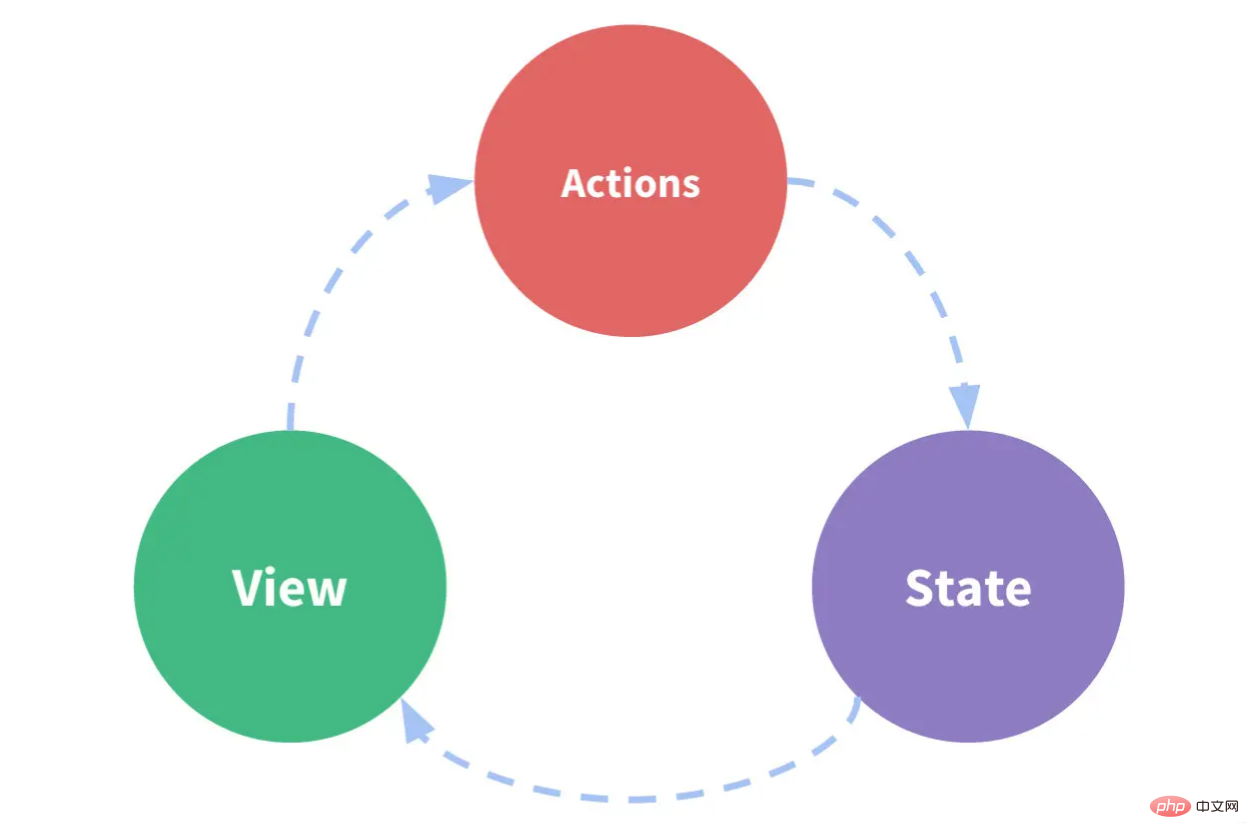
看到这样的题目,可以用以下图片来回答:
思路
查看vue官方文档:
风格指南:https://vuejs.org/style-guide/
性能:https://vuejs.org/guide/best-practices/performance.html#overview
安全:https://vuejs.org/guide/best-practices/security.html
访问性:https://vuejs.org/guide/best-practices/accessibility.html
发布:https://vuejs.org/guide/best-practices/production-deployment.html
回答范例
我从编码风格、性能、安全等方面说几条:
编码风格方面:
性能方面:
安全:
template: <div> + userProvidedString + </div>
etc.. ....
##Thoughts
Example
State management pattern library. It uses centralized storage to manage the status of all components of the application, and uses corresponding rules to ensure that the status changes in a predictable way.
multiple components sharing state, for example: multiple views depend on the same state or behaviors from different views need to change the same state. The simplicity of one-way data flow can easily be broken at this point. Therefore, it is necessary for us to extract the shared state of the component and manage it in a global singleton mode. By defining and isolating the various concepts in state management and maintaining the independence between views and state by enforcing rules, our code will become more structured and maintainable. This is the necessity for the existence of vuex. It is the same concept as redux in the react ecosystem.
Possible questions
Analysis
Asking us about the process from template to render is actually asking about the working principle of vuecompiler.
Ideas
Answer examples
Know why
Peeping into the vue3 compilation process:Possible questions
AnalysisThe mounting process completes the two most important things:
Answer sample The mounting process refers to the app.mount() process. In this process, two things are done as a whole: Initialization and Establishing an update mechanism Initialization will create component instances, initialize component status, and create various responsive data This step of establishing an update mechanism will execute the component immediately The update function will execute the component rendering function for the first time and execute the patch to convert the previously obtained vnode into dom; at the same time, executing the rendering function for the first time will create a dependency between its internal responsive data and the component update function, which will cause future data changes. The corresponding update function will be executed. Know why Test code, test-v3.html
mount function definition https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/apiCreateApp.ts#L277-L278 First render process https://github1s.com/vuejs/core/blob/HEAD/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts#L2303-L2304 Possible questions How to create responsive data Dependencies How to establish Original address: https://juejin.cn/post/7097067108663558151 Author: Village Chief Yang (Learning video sharing: vue video tutorial)