
Usage of return in JavaScript: 1. Return function value, which can return any type of value including basic data types, objects, functions, etc.; 2. Use the return statement without a return value to terminate the execution of the function at any time .

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, javascript version 1.8.5, Dell G3 computer.
The JavaScript return statement has two functions in the function definition:
One is to return the function value;
Two Is to abort the execution of the function.
The return statement can return any type of value including basic data types, objects, functions, etc. Every function returns a value. When the return statement is not used, or when return is used but no return value is specified after it, the function will return an "undefined" value. If you need to return a value other than "undefined", you must use return and specify the returned value.
Once the function executes the return statement, it will immediately return the function value and terminate the execution of the function. At this time, the code after the return statement will not be executed. According to this characteristic of the return statement, when the execution of the function needs to be exited early, a return statement without a return value is often used to terminate the execution of the function at any time.
[Example 1] The return statement explicitly returns the function value.
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>return语句显式返回函数值</title>
<script>
function expressionCaculate(x){
if((x >= -10) && (x <= 10)){
return x * x - 1;
} else {
return 5 * x + 3;
}
}
console.log(expressionCaculate(6));
console.log(expressionCaculate(12));
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>expressionCaculate()'s return is followed by an expression. When the function executes the return statement, the value of the expression will first be calculated and then the value will be returned. When the function is called, the value of a different expression is returned depending on the value passed to x.
[Example 2] The return statement terminates the execution of the function.
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>return语句中止函数执行</title>
<script>
function add(a,b){
if(a > b){
console.log("a大于b");
return;
console.log("a+b=" + (a + b));
}
console.log("a+b=" + (a + b));
}
add(7,3);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>When the add(7,3) code is executed, the add() method will be called. At this time, the value of the first parameter is greater than the second parameter, and "a is greater than b" is output in the console. , then the function returns and stops execution, so that the two logs after the return statement will not be output. The running results are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The return statement aborts the function execution result
[Example 3] The return statement returns the function.
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>return语句返回函数</title>
<script>
function outerFunc(){
var b = 0;
return function(){ //返回匿名函数
b++;
console.log("内部函数中b=" + b);
}
}
var func = outerFunc();
func();
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Because the outerFunc() function returns an anonymous function, the calling expression of the outerFunc function becomes a function expression, so the variable func can be used to call the anonymous function. The running results are shown in Figure 2.
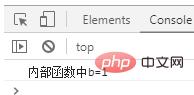
Figure 2: Anonymous function returned by calling return statement
[Related recommendation: javascript learning tutorial]
The above is the detailed content of What is the usage of return in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!