
As an important part of react, setState queues changes to component state and notifies React that it needs to re-render this component and its subcomponents using the updated state. The following article will take you through the setState mechanism in React. I hope it will be helpful to you!

state is an important concept in React. We know that React manages components through state management. So, how does React control the state of components, and how does it use state to manage components? [Related recommendations: Redis Video Tutorial]
We all know that React accesses state through this.state , update the state through the this.setState() method. When this.setState() is called, React will re-call the render method to re-render UI.
setState is already a API that we are very familiar with, but do you really understand it? Below we will decrypt the update mechanism of setState.
When everyone first starts writing React, they usually write code like this.state.value = 1, This is completely wrong.
Note: Never modify this.state directly. Not only is this an inefficient approach, but it is also likely to be replaced by subsequent operations.
setStatestate is updated through a queue mechanism. When setState is executed, the state that needs to be updated will be merged and put into the state queue, and this.state will not be updated immediately. The queue mechanism can be efficient Update state in batches. If the value of this.state is modified directly without setState, then the state will not be put into the state queue, and the next time is called When setState is used to merge the state queues, the state that was directly modified before will be ignored, causing unpredictable errors.
Therefore, the setState method should be used to update state, and React also uses the state queue mechanism to implement setState Asynchronous updates to avoid frequent repeated updates of state. The relevant code is as follows:
// 将新的state合并到状态更新队列中 var nextState = this._processPendingState(nextProps, nextContext); // 根据更新队列和 shouldComponentUpdate 的状态来判断是否需要更新组件 var shouldUpdate = this._pendingForceUpdte || !inst.shouldCompoonentUpdate || inst.shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext0;
When setState is called, the enqueueSetState method will actually be executed, and partialState and _pendingStateQueue update the queue for merge operations, and the final operation enqueueSetState performs state update.
The performUpdateIfNecessary method will obtain _pendingElement, _pendingStateQueue, _pendingForceUpdate, and call the receiveComponent and updateComponent methods to update components .
If setState is called in the shouldComponetUpdate or componentWillUpdate method, then this._pendingStateQueue != null, then The performUpateIfNecessary method will call the updateComponent method to update the component, but the updateComponent method will call shouldComponentUpdate and componentWillUpdate method, thus causing a loop call, causing the browser to crash after the memory is full.
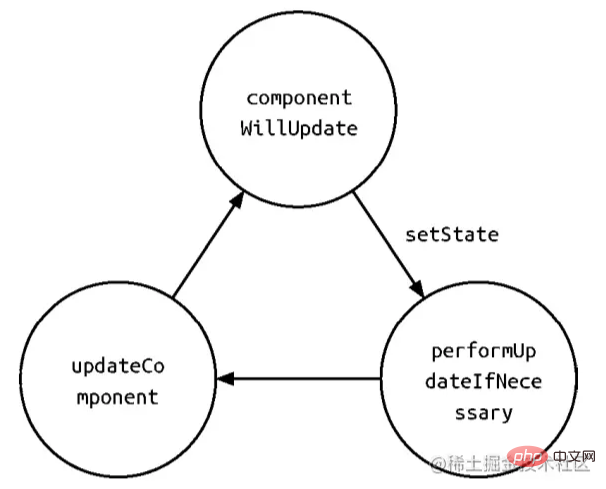
Since setState is ultimately executed through enqueueUpate state Update, then how does enqueueUpdate update state?
First of all, take a look at the following question. Can you answer it correctly?
import React, { Component } from 'react'
class Example extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
val: 0
}
}
componentDidMount() {
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1})
console.log(this.state.val)
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1})
console.log(this.state.val)
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1})
console.log(this.state.val)
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1})
console.log(this.state.val)
},0)
}
render() {
return null
}
}In the above code, the val printed out by console.log four times are: 0, 0, 2, 3.
If the result is not exactly the same as the answer in your mind, then do you want to know what enqueueUpdate actually does?
The figure below is a simplified setState call stack. Pay attention to the core state judgment.
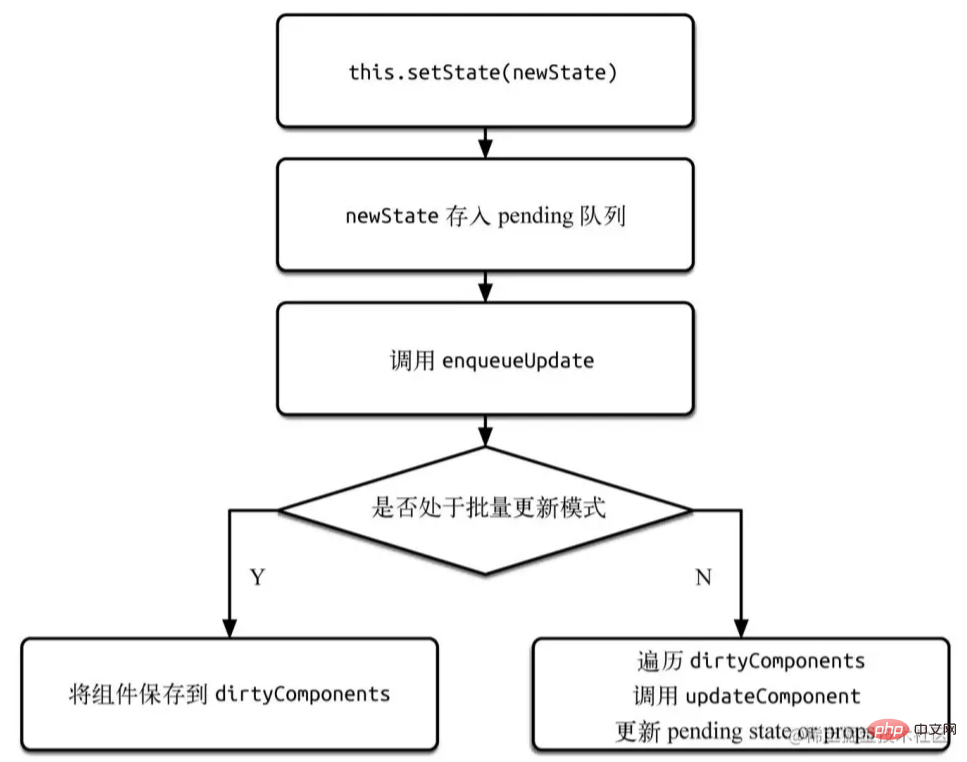
setStateSimplify the call stack
What causes itsetState What about the various manifestations of ?
我们先要了解事务跟 setState 的不同表现有什么关系。首先,我们把4次 setState 简单归类,前两次属于一类,因为他们在同一次调用栈中执行,setTimeout 中的两次 setState 属于另一类,因为他们也是在同一次调用栈中执行。我们分析一下这两类 setState 的调用栈。
在 componentDidMount 中直接调用的两次 setState,其调用栈更加复杂;而setTimeout 中调用的两次 setState,其调用栈则简单很多。下面我们重点看看第一类 setState 的调用栈,我们发现了 batchedUpdates 方法,原来早在 setState 调用前,已经处于batchedUpdates执行的事务中了。
那batchedUpdates方法,又是谁调用的呢?我们再往前追溯一层,原来是 ReactMount.js 中的 _renderNewRootComponent方法。也就是说,整个将React组件渲染到DOM中的过程就处于一个大的事务中。
接下来的解释就顺理成章了,因为在componentDidMount中调用setState时,batchingStrategy 的 isBatchingUpdates 已经被设为true,所以两次setState的结果并没有立即生效,而是被放到了dirtyComponents中。这也解释了两次打印 this.state.val 都是 0 的原因,因为新的 state 还没有被应用到组件中。

componentDidMount中setState的调用栈
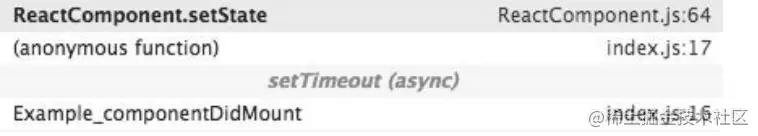
setTimeout中setState的调用栈
再反观 setTimeout 中的两次setState,因为没有前置的 batchedUpdate 调用,所以 batchingStrategy 的 isBatchingUpates 标志位是false,也就导致了新的 state 马上生效,没有走到 dirtyComponents 分支。也就是说,setTimeout 中第一次执行 setState 时,this.state.val 为 1, 而 setState 完成打印后打印时 this.state.val 变成了2。第二次的 setState 同理。
前面介绍事务时,也提到了其在 React 源码中的多处应用,像 initialize、perform、close、closeAll、motifyAll 等方法出现在调用栈中,都说明当前处于一个事务中。
既然事务这么有用,我们写应用代码时能使用它吗?很可惜,答案是不能。尽管React不建议我们直接使用事务,但在 React 15.0 之前的版本中还是为开发者提供了 batchedUpdates 方法,它可以解决针对一开始例子中setTimeout 里的两次 setState 导致两次 render 的情况:
import ReactDOM, { unstable_batchedUpates } from 'teact-dom'
unstable_batchedUpates(() => {
this.setState(val: this.state.val + 1)
this.setState(val: this.state.val + 1)
})在 React 15.0 以及之后版本中,已经彻底将 batchUpdates 这个 API 移除了,因此不再建议开发者使用它。
在使用React的setState的过程中,了解setState的实现原理,对setState异步更新、setState循环调用风险、setState调用栈等进行更加全面的了解,才能让我们在遇到相关问题的时候更加游刃有余。
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
The above is the detailed content of In-depth understanding of the update mechanism of setState in React. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 String array assignment method
String array assignment method
 Why disabling automatic updates in Windows 11 is invalid
Why disabling automatic updates in Windows 11 is invalid
 How to embed CSS styles in HTML
How to embed CSS styles in HTML
 The difference between official replacement phone and brand new phone
The difference between official replacement phone and brand new phone
 Can't open app store
Can't open app store
 The role of parseint function
The role of parseint function
 Android desktop software recommendations
Android desktop software recommendations
 Ethereum today's market price
Ethereum today's market price