
This article will take you to understand the events inNode, and talk about the event driver and EventEmitter class. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

Almost every API in Node.js supports callback functions.
Node.js Basically all event mechanisms are implemented using the observer pattern in the design pattern.
Node.js single thread is similar to entering a while(true) event loop until no event observer exits. Each asynchronous event generates an event observer. If an event occurs, the callback function is called.
Node.js uses the event-driven model. When the web server receives a request, it closes it, processes it, and then serves it. Next web request.
When the request is completed, it is put back into the processing queue, and when the beginning of the queue is reached, the result is returned to the user.
This model is very efficient and scalable because the webserver always accepts requests without waiting for any read or write operations. (This is also called non-blocking IO or event-driven IO)
In the event-driven model, a main loop is generated to listen for events, and a callback function is triggered when an event is detected.
Node.js has multiple built-in events. We can bind and listen to events by introducing the events module and instantiating the EventEmitter class, as shown in the following example:
// 引入 events 模块 var events = require('events'); // 创建 eventEmitter 对象 var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
The following program binds Event handler:
// 绑定事件及事件的处理程序 eventEmitter.on('eventName', eventHandler);
We can trigger events through the program:
// 触发事件 eventEmitter.emit('eventName');
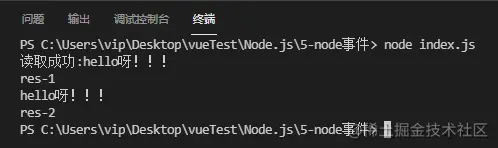
Createindex.jsfile, The code looks like this:
//引入 fs 模块 var fs = require("fs"); // 引入 events 模块 var events = require('events'); // 创建对象 var ee = new events.EventEmitter(); // 绑定事件及事件的处理程序 ee.on('res', function (data) { console.log('res-1'); console.log(data); }); ee.on('res', function () { console.log('res-2'); }); fs.readFile('hello.txt',{flag:'r',encoding:'utf-8'},function(err,data){ if(err){ console.log("读取出错:"+err); }else{ console.log("读取成功:"+data); // 触发res事件 ee.emit('res',data); } })
Next let us execute the above code:
eventsThe module only provides one object:events.EventEmitter. The core ofEventEmitteris the encapsulation of event triggering and event listener functions.
// 引入 events 模块 var events = require('events'); // 创建 eventEmitter 对象 var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
//event.js 文件 var EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter; var event = new EventEmitter(); event.on('some_event', function() { console.log('some_event 事件触发'); }); setTimeout(function() { event.emit('some_event'); }, 1000);
after 1 second 'some_event event triggers'. The principle is that the event object registers a listener for the event some_event, and then we use setTimeout to send the event some_event to the event object after 1000 milliseconds. At this time, the listener for some_event will be called.
$ node event.js some_event 事件触发
EventEmitterEach event consists of an event name and several parameters. The event name is a string, which usually expresses certain semantics. For each event,EventEmittersupports several event listeners.
//event.js 文件 var events = require('events'); var emitter = new events.EventEmitter(); emitter.on('someEvent', function(arg1, arg2) { console.log('listener1', arg1, arg2); }); emitter.on('someEvent', function(arg1, arg2) { console.log('listener2', arg1, arg2); }); emitter.emit('someEvent', 'arg1 参数', 'arg2 参数');
$ node event.js listener1 arg1 参数 arg2 参数 listener2 arg1 参数 arg2 参数
emitterTwo event listeners were registered for the eventsomeEvent, and then thesomeEventevent was triggered.
EventEmitter.
EventEmitterprovides several properties such asonandemit. Theonfunction is used to bind the event function, and theemitattribute is used to trigger an event.
nodejs tutorial! !
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about event drivers and EventEmitter class in Node.js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!