
In the previous article "JS Array Learning: Traverse the Array and Double the Element Value", we introduced the method of traversing the array and processing each element in the array. This time we will continue to talk about array traversal and introduce several methods to detect whether all array elements meet the specified conditions. Friends in need can learn about it~
So how to determine whether the elements in the array meet the specified conditions? For example, traverse an array and check whether all elements in the array are even numbers. How to do this?
Let's introduce 3 methods below, starting with the familiar for loop, and then introducing 2 built-in functions - see how to use them to detect.
Method 1: Use for loop
Implementation idea:
for(var i=0;i<a.length;i++){
}var a = [2,4,5,6,8],b=0;
for(var i=0;i<a.length;i++){
if (a[i] % 2 != 0) {
b=0
break;
}else{
b++;
}
}
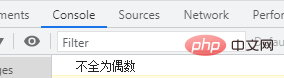
if (b) {
console.log("都是偶数");
} else {
console.log("不全为偶数");
}bAssign a value of 0. If the array element is an even number, b will increase by 1; when an array element is not an even number, the value of b will become 0 again, and use "break;" to exit the loop.
b>0, then they are all even numbers; if b=0 is not all even numbers.
Method 2: Use the some() method
some() method to detect whether there are elements that meet the conditions in the array. Thinking about it from another angle, it can also be used to detect whether all elements in the array do not meet the specified conditions. If they do not meet the specified conditions, it will return false. If one or more elements match, it will return true. (The same idea as the above code)array.some(function callbackfn(Value,index,array),thisValue)
function callbackfn(value,index,array): A callback function, which cannot be omitted, and can accept up to three parameters:
function f(value, index, ar) {
if (value % 2 != 0) {
return true;
}
}
var a = [2,4,6,8,10,12];
var b = a.some(f);
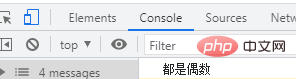
if (b) {
console.log("不全为偶数");
} else {
console.log("都是偶数");
}
Method 3: Use every() method
Every() method can detect whether all array elements meet the specified conditions. The syntax is as follows. For parameter values, please refer to the some() method abovearray.every(function callbackfn(Value,index,array),thisValue)
function f(value, index, ar) {
if (value % 2 == 0) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
var a = [2,4,6,8,10,11];
var b = a.every(f);
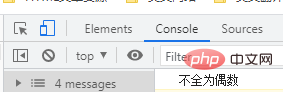
if (b) {
console.log("都是偶数");
} else {
console.log("不全为偶数");
}不全为偶数
The difference between every() and some() methods:
Every() returns true only when all elements in the array meet the conditions; as long as one element in the array meets the conditions, some( ) will return true. Okay, that’s all. If you need it, you can watch it:The above is the detailed content of JS array learning to determine whether array elements meet given conditions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!