
Method: 1. Use wget to download the tar.gz file of php, the syntax is "wget http://br2.php.net/get/php-7.2.2.tar.gz"; 2. Use tar Command to decompress the PHP tar.gz file, the syntax is "tar zxvf php compressed file"; 3. Create a new PHP-related folder, then enter the decompressed PHP installation package folder, and use the command to configure; 4. Configure PHP-related files; 5. Start php and confirm whether the installation is successful.

The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, PHP7.2.2 version, DELL G3 computer
Check whether Installed php
1) yum installation check: yum list installed | grep php
2) rpm installation check: rpm -qa | grep php
3) There are many ways to query if you compile and install it yourself, such as finding the executable program of php, or checking the process ps -ef | grep php and other methods.
Check If php is not installed, you can prepare the initial software before php installation. Use yum install xxxx to install it. Of course, you can compile and install it yourself if you don't mind the trouble. I won't go into details here.
1) zlib and zlib-devel zlib provides a data compression function library and is also the front-end software of nginx. Since zlib needs to compile the zlib extension of php, the zlib.h header will need to be used during compilation. Files and header files are in zlib-devel, so zlib-devel also needs to be downloaded.
2) libxml2 and libxml-devel libxml2 is a c language xml library that can simply perform various operations on xml, and supports xpath query, and partially supports xslt conversion and other functions.
3) If libxslt and libxslt-devel are not installed, you will be prompted to find the xslt.config file. xslt is an extension for converting xml to other formats.

3) openssl and openssl-devel security proprietary layer password library
4) jpeg IJG's jpeg library, PHP's gd library required.
5) libpng is a cross-platform library for relatively complex pngpng files written in C language. It can help easily read and replace each line of pngpng files, which is required by the gd library of PHP.
6) Freetype and freetype-devel are free, open source and portable font engines that provide a unified interface to access multiple font formats. Both of these are dependent software of the gd library, so if they are not installed, or The version is too low. When installing phptime, the setting is to install the gd library and insert an error. In addition, if -devel is not installed, an error will be reported because the ft2build.h file will be generated when compiling the extension. The error is reported as shown below.

7) gd gd is an extension library for PHP to process graphics
8) curl, because the version in my yum is too low, so I directly use it myself Compiled and installed, the installation method is very simple, that is, wget curl downloads the address and decompresses the tar, creates a new /usr/local/curl folder, and then enters the curl decompressed folder to configure. /configure--prefix=/usr/local/curl immediately, and finally make and make install are installed.
Note: xxx-devel is the development package of xxx software, including header files, static libraries and even source code.
Download and install php in linux
1) Use wget to download the tar.gz file of php: wget <span class="invisible">http: //<span class="visible">br2.php.net/get/php-7.2<span class="invisible">.2.tar.gz</span></span></span>
2) Unzip the tar.gz file :tar zxvf php-7.2.2.tar.gz
3) Create a new folder where php will be installed later: mkdir/usr/local/php, and then enter the decompressed php In the installation package folder, configure:
./configure --prefix = / usr / local / php --with-curl = / usr / local / curl --with-freetype-dir --with-gd --with-gettext --with-iconv-dir- -with-kerberos --with-libdir = lib64 --with-libxml-dir --with-mysqli --with-openssl --with-pcre-regex --with-pdo-mysql --with-pdo-sqlite- -with-pear --with-png-dir --with-xmlrpc --with-xsl --with-zlib --enable-fpm --enable-bcmath --enable-libxml --enable-inline-optimization- enable-mbregex --enable-mbstring --enable-opcache --enable-pcntl --enable-shmop --enable-soap --enable-sockets --enable-sysvsem --enable-xml --enable-zip
Note:
--prefix =installation directory
--with-use package name[=package directory]
--enable-Features that need to be activated
Configure php related files
1) Configure php.ini, which is the php configuration file: cp /home /myload/php-7.2.2/php.ini-development /usr/local/php/lib/php.ini
2) Configure php-fpm.conf, this is the php-fpm configuration file: cp /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf.default /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf
3) Configure www.conf and configure the user’s file: cp etc /php-fpm.d/www.conf.default etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
4) Copy the php-fpm startup file to the init.d folder to conveniently start php: cp -R sbin / php-fpm /etc/init.d/php-fpm
Start php and confirm whether the installation is successful
Execute the command /etc/init. d/php-fpm immediately
Check whether it is started: ps -ef | grep php You can see that php has started some progress
After successful installation, configure nginx to support php
1) Change the php.ini file, vim /usr/local/php/lib/php.ini
By searching for the configuration cgi.fix_pathinfo = 1, deleting the comment, and replacing cgi.fix_pathinfo = 0, this is not related to nginx’s support for php configuration, or is a security vulnerability specific to php under nginx. If this is narrowed down 1. Users can upload Trojans by uploading images, and then access the image address through the URL, and add /xxx.php after the address to run the image as a PHP file. This is a problem that only exists in nginx, apache and iis None of them have this problem
The above questions can be directly thought of Brother Niao’s blog, which is written in quite detail: http://http://www.laruence.com/2010/05/20 /1495.html
2) Configure web-specific groups and users
Add www user group: groupadd www
Add the user www under the www user group: useradd -g www www
3) Change the php-fpm.conf configuration
Remove the comment user = nobody, add nobody and change it to the configuration above www user
Remove the comment of group = nobody, add nobody and change it to the www user group configured above
Finally check whether the last value contained in php-fpm.conf is correct www. conf directory address, if incorrect, replace it with the correct directory address.
4) Change the www.conf configuration
Remove the comment of user = nobody, add nobody and change it to the www user configured above
Remove the comment of group = nobody, Join nobody and change to the www user group configured above
5) Change the nginx.conf file /etc/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
Remove the comment and replace #user = nobody user = www
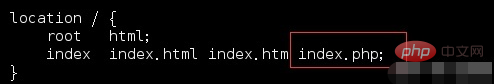
Delete the comments of this code at location ~\.php ${...}, and replace $document_root
PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to install php in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!