

Many people say that the algorithm is the core of the program. The key to whether a program is better than worse is the quality of the program's algorithm. As a junior PHPer, although I have little exposure to algorithmic things. However, you still need to master basic algorithms such as bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, quick sort, and merge sort.
Requirements: Use bubble sort, quick sort, selection sort, insertion sort, and merge sort to sort the values in the following array from small to large.
$arr=array(11,3,56, 62,21,66,32,78,36,76,39,88,34);
#1. Bubble sort
Introduction:
Bubble Sort is a simple sorting algorithm. It repeatedly walks through the sequence to be sorted, comparing the two elements in turn, and swapping them if they are in the wrong order. The work of visiting the array is repeated until no more exchanges are needed, which means that the array has been sorted. The name of this algorithm comes from the fact that smaller elements will slowly "float" to the top of the array through swapping.Steps:
1. Compare adjacent elements. If the first one is bigger than the second one, swap them both. 2. Do the same work for each pair of adjacent elements, from the first pair at the beginning to the last pair at the end. At this point, the last element should be the largest number. 3. Repeat the above steps for all elements except the last one. 4. Continue to repeat the above steps for fewer and fewer elements each time until there are no pairs of numbers to compare.Code:
##
<?php $arr = [1, 43, 54, 62, 21, 66, 32, 78, 36, 76, 39, 2];
//Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge
function bubbleSort($arr) {
$len = count($arr);
//该层循环控制 需要冒泡的轮数
for ($i = 1; $i < $len; $i++) {
//该层循环用来控制每轮 冒出一个数 需要比较的次数
for ($k = 0; $k < $len - $i; $k++) {
if ($arr[$k] > $arr[$k + 1]) { //从小到大
$tmp = $arr[$k + 1]; // 声明一个临时变量
$arr[$k + 1] = $arr[$k];
$arr[$k] = $tmp;
}
}
}
return $arr;
}
$arr = bubbleSort($arr);
print_r($arr);
2. Selection sort
Introduction:Selection sort is a simple and intuitive sorting algorithm. Here's how it works. First, find the smallest element in the unsorted sequence and store it at the beginning of the sorted sequence. Then, continue to find the smallest element from the remaining unsorted elements, and then put it at the end of the sorted sequence. And so on until all elements are sorted.
Code:##
<?php $arr = [1, 43, 54, 62, 21, 66, 32, 78, 36, 76, 39, 2];
//Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge
//实现思路 双重循环完成,外层控制轮数,当前的最小值。内层控制比较次数
function selectSort($arr) {
$len = count($arr);
//$i 当前最小值的位置, 需要参与比较的元素
for ($i = 0; $i < $len - 1; $i++) {
//先假设最小的值的位置
$p = $i;
//$j 当前都需要和哪些元素比较,$i 后边的。
for ($j = $i + 1; $j < $len; $j++) {
//$arr[$p] 是 当前已知的最小值
//比较,发现更小的,记录下最小值的位置;并且在下次比较时,应该采用已知的最小值进行比较。
$p = ($arr[$p] <= $arr[$j]) ? $p : $j;
}
//已经确定了当前的最小值的位置,保存到$p中。
//如果发现 最小值的位置与当前假设的位置$i不同,则位置互换即可
if ($p != $i) {
$tmp = $arr[$p];
$arr[$p] = $arr[$i];
$arr[$i] = $tmp;
}
}
//返回最终结果
return $arr;
}
$arr = selectSort($arr);
print_r($arr);
Introduction:
The algorithm description of Insertion Sort is a simple and intuitive sorting algorithm. It works by constructing an ordered sequence. For unsorted data, it scans from back to front in the sorted sequence, finds the corresponding position and inserts it. In the implementation of insertion sort, in-place sorting is usually used (that is, sorting that only uses O(1) extra space). Therefore, during the scanning process from back to front, it is necessary to repeatedly and gradually shift the sorted elements backward. , providing insertion space for the latest element.
Steps:
1. Starting from the first element, the element can be considered to have been sorted
2. Take out the next element, in Scan the sorted element sequence from back to front3. If the element (sorted) is larger than the new element, move the element to the next position4. Repeat step 3. Until you find the position where the sorted element is less than or equal to the new element5, insert the new element into the position6, repeat step 2code :
<?php $arr = [1, 43, 54, 62, 21, 66, 32, 78, 36, 76, 39,2];
//插入排序
function insert_sort($arr)
{
$len=count($arr);
for($i=1; $i<$len; $i++) {
//获得当前需要比较的元素值
$tmp = $arr[$i];
//内层循环控制 比较 并 插入
for($j=$i-1; $j>=0; $j--) {
//$arr[$i];需要插入的元素
//$arr[$j];需要比较的元素
if($tmp
{
//发现插入的元素要小,交换位置
//将后边的元素与前面的元素互换
$arr[$j+1] = $arr[$j];
//将前面的数设置为 当前需要交换的数
$arr[$j] = $tmp;
} else {
//如果碰到不需要移动的元素
//由于是已经排序好是数组,则前面的就不需要再次比较了。
break;
}
}
}
//将这个元素 插入到已经排序好的序列内。
//返回
return $arr;
}
$arr = insert_sort($arr);
print_r($arr);Introduction:
Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge是由东尼·霍尔所发展的一种排序算法。在平均状况下,排序 n 个项目要Ο(n log n)次比较。在最坏状况下则需要Ο(n2)次比较,但这种状况并不常见。事实上,Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge通常明显比其他Ο(n log n) 算法更快,因为它的内部循环(inner loop)可以在大部分的架构上很有效率地被实现出来,且在大部分真实世界的数据,可以决定设计的选择,减少所需时间的二次方项之可能性。
步骤:
1、从数列中挑出一个元素,称为 “基准”(pivot),
2、重新排序数列,所有元素比基准值小的摆放在基准前面,所有元素比基准值大的摆在基准的后面(相同的数可以到任一边)。在这个分区退出之后,该基准就处于数列的中间位置。这个称为分区(partition)操作。
3、递归地(recursive)把小于基准值元素的子数列和大于基准值元素的子数列排序。
代码:
<?php $arr = [1, 43, 54, 62, 21, 66, 32, 78, 36, 76, 39,2];
//Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge
function quick_sort($arr)
{
//判断参数是否是一个数组
if(!is_array($arr)) return false;
//递归出口:数组长度为1,直接返回数组
$length = count($arr);
if($length<=1) return $arr;
//数组元素有多个,则定义两个空数组
$left = $right = array();
//使用for循环进行遍历,把第一个元素当做比较的对象
for($i=1; $i<$length; $i++)
{
//判断当前元素的大小
if($arr[$i] < $arr[0]){ //从小到大 < || 从大到小 >
$left[]=$arr[$i];
}else{
$right[]=$arr[$i];
}
}
//递归调用
$left=quick_sort($left);
$right=quick_sort($right);
//将所有的结果合并
return array_merge($left,array($arr[0]),$right);
}
$arr = quick_sort($arr);
print_r($arr);排序效果:
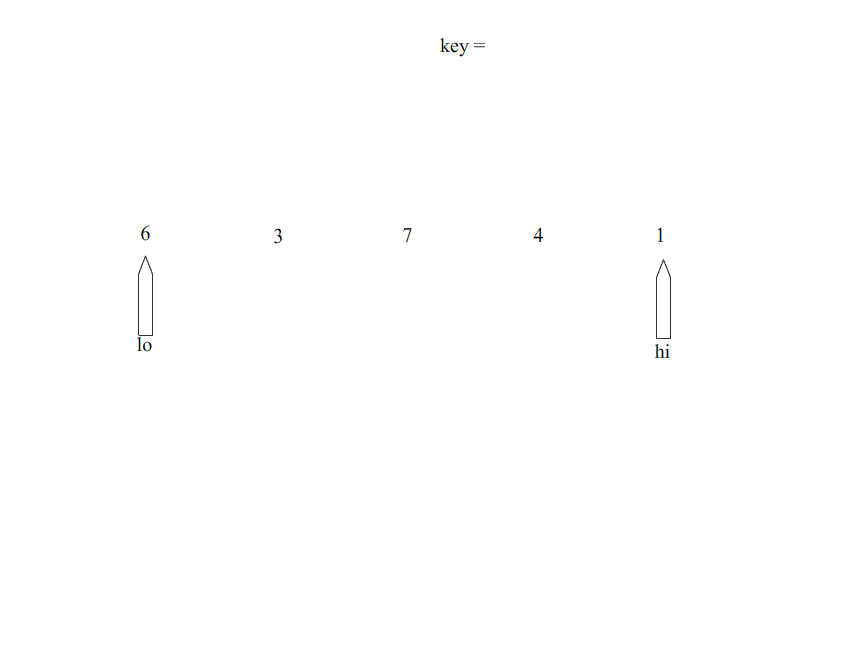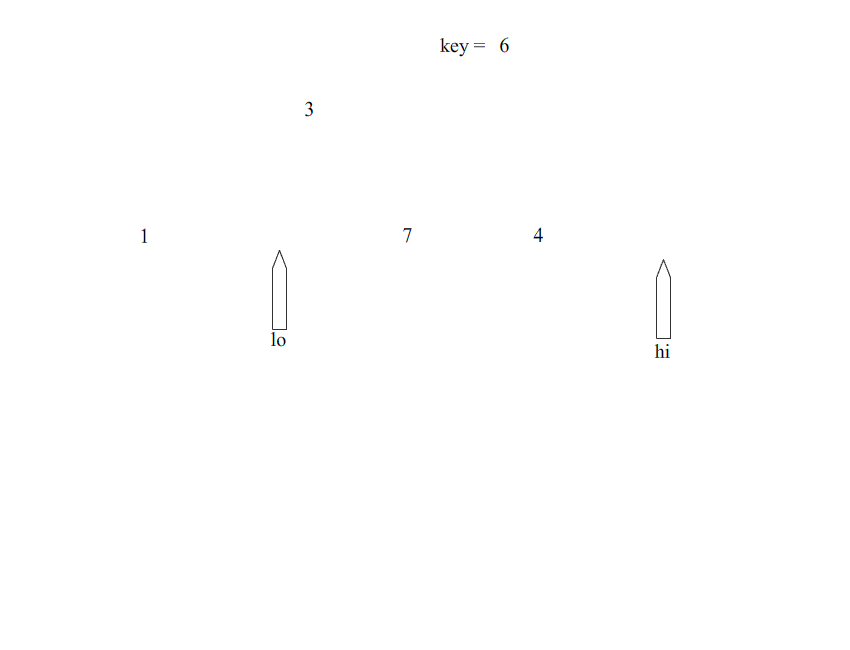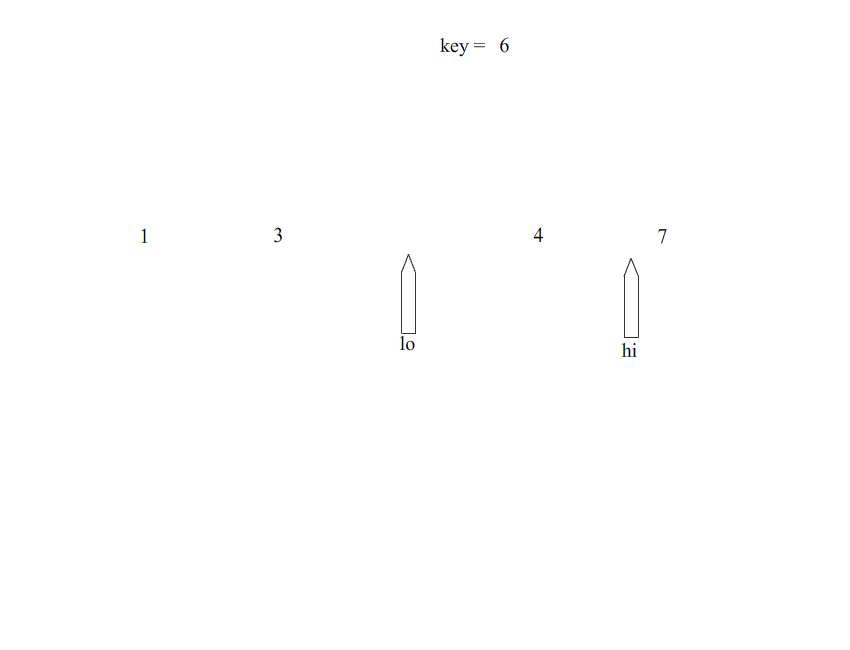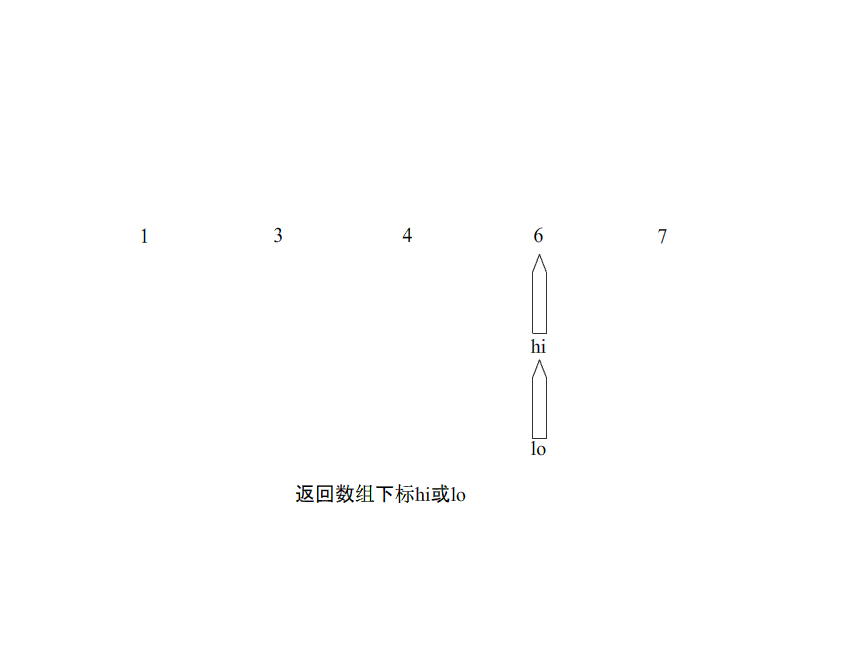
5、Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge
利用递归,先拆分、后合并、再排序。
步骤:
代码:
<?php $arr = [1, 43, 54, 62, 21, 66, 32, 78, 36, 76, 39,2];
// Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge主程序
function mergeSort($arr) {
$len = count($arr);
// 递归结束条件, 到达这步的时候, 数组就只剩下一个元素了, 也就是分离了数组
if ($len <= 1) {
return $arr;
}
$mid = intval($len / 2); // 取数组中间
$left = array_slice($arr, 0, $mid); // 拆分数组0-mid这部分给左边left
$right= array_slice($arr, $mid); // 拆分数组mid-末尾这部分给右边right
$left = mergeSort($left); // 左边拆分完后开始递归合并往上走
$right= mergeSort($right); // 右边拆分完毕开始递归往上走
$arr = merge($left, $right); // 合并两个数组,继续递归
return $arr;
}
// merge函数将指定的两个有序数组(arrA, arr)合并并且排序
function merge($arrA, $arrB) {
$arrC = array();
while (count($arrA) && count($arrB)) {
// 这里不断的判断哪个值小, 就将小的值给到arrC, 但是到最后肯定要剩下几个值,
// 不是剩下arrA里面的就是剩下arrB里面的而且这几个有序的值, 肯定比arrC里面所有的值都大所以使用
//从小到大 < || 从大到小 >
$arrC[] = $arrA[0] <p>排序效果:</p><p> </p><p><img src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/024/4059d12f5632ac9f990ed52b74747d4b-4.gif" alt="Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge" style="max-width:90%" style="max-width:90%"></p><p>相关推荐:<a href="//m.sbmmt.com/" target="_blank">PHP教程</a><br></p>The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of basic PHP algorithms: bubbling, selection, insertion, fast, merge. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!