
The constructor property of an object is used to return the function that created the object, which is what we often call the constructor. The following article will introduce you to the constructor property of JavaScript. I hope it will be helpful to you.

JavaScript constructor property
Function: The constructor property returns the creation of Object A reference to the instance object's constructor.
Note: In JavaScript, every object with a prototype will automatically obtain the constructor attribute. Except for some special objects such as arguments, Enumerator, Error, Global, Math, RegExp, Regular Expression, etc., all other JavaScript built-in objects have the constructor attribute. For example: Array, Boolean, Date, Function, Number, Object, String, etc.
Syntax:
object.constructor
Note: The value of the constructor attribute is a reference to the function itself, not a string containing the function name.
JavaScript constructor property usage example
Example 1:
<script type="text/javascript">
var test=new Array();
if (test.constructor==Array)
{
document.write("这是一个数组");
}
if (test.constructor==Boolean)
{
document.write("This is a Boolean");
}
if (test.constructor==Date)
{
document.write("This is a Date");
}
if (test.constructor==String)
{
document.write("这是一个字符串");
}
</script>Output:
This is an array
Example 2:
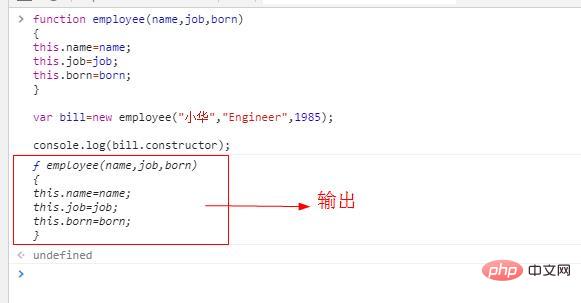
<script type="text/javascript">
function employee(name,job,born)
{
this.name=name;
this.job=job;
this.born=born;
}
var bill=new employee("小华","Engineer",1985);
console.log(bill.constructor);
</script>Rendering:
The above is the detailed content of How to use constructor attribute. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!