
This time I will bring you how to use the CSS position attribute. What are the precautions when using the CSS position attribute. Here is a practical case, let’s take a look.
At present, almost all mainstream browsers support the position attribute (except "inherit", "inherit" does not support all browsers including IE8 and previous versions of IE, and IE9 and IE10 have not been tested). The following is w3school Explanation of the five values of position:
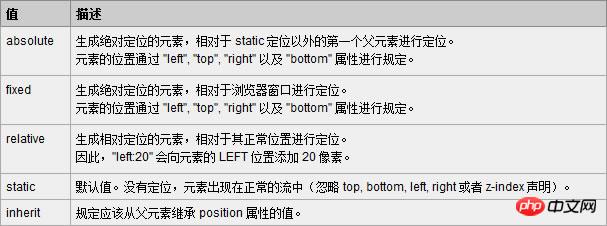
Absolute and relative are the most commonly used, and fixed is also used more frequently (IE6 does not support fixed).
1. Absolute (Absolute positioning)
##Absolute is an element that generates visual positioning and is separated from the text flow. (That is, it no longer occupies a position in the document), refer to the upper left corner of the browser for positioning through top, right, bottom, left (TRBL for short). You can select a positioned parent object (the combination of relative and absolute will be discussed below) or the body coordinate origin for positioning, or you can perform hierarchical classification through z-index. When the TRBL value is not set, absolute uses the coordinates of the parent object as the starting point. When the TRBL value is set, the upper left corner of the browser is used as the original point. The specific case is as follows:<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>position:absolute定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
.center{
margin:30px;
border:#999999 solid 10px;
width:400px;
height:300px;
}
.p1{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:#0099FF;
/*设定TRBL*/
position:absolute;
left:0px;
top:0px;
}
.p2{
width:400px;
height:300px;
font-size:30px;
font-weight:bold;
color:#fff;
background:#FF0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="center">
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2">position:absolute定位测试</p>
</p>
</body>
</html>
This is the effect after setting TRBL (setting TRBL uses the upper left corner of the browser as the origin). When TRBL is not set (when TRBL is not set, the coordinates of the parent object are used as the origin), change p1 to the following When coding
.p1{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:#0099FF;
/*没有设定TRBL*/
position:absolute;
}, the effect is as follows:

2. Relative (relative positioning)
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>position:relative定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
.center{
margin:30px;
border:#999999 solid 10px;
width:400px;
height:300px;
background:#FFFF00;
}
.p1{
width:200px;
height:150px;
background:#0099FF;
position:relative;
top:-20px;
left:0px;
}
.p2{
width:400px;
height:150px;
font-size:30px;
font-weight:bold;
color:#fff;
background:#FF0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="center">
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2">position:relative定位测试</p>
</p>
</body>
</html>
3. The combination of relative and absolute
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<style type="text/css">
html,body,p,ul,li,a{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
}
a, a:hover{
color:#000;
border:0;
text-decoration:none;
}
#warp,#head,#main,#foot
{
width: 962px;
}
/*设置居中*/
#warp{
margin: 0 auto;
}
#head{
height:132px;
position:relative;
}
.logo{
position:absolute;
top:17px;
}
.head_pic{
position:absolute;
top:17px;
left:420px;
}
.sc{
position:absolute;
right:5px;
top:12px;
}
.sc a{
padding-left:20px;
color:#666;
}
.nav{
width:960px;
height:42px;
line-height:42px;
position:absolute;
bottom:0px;
background:url(img/nav_bj.jpg) no-repeat center;
}
.nav ul{
float:left;
padding:0 10px;
}
.nav li{
float:left;
background:url(img/li_bj.jpg) no-repeat right center;
padding-right:40px;
padding-left:20px;
text-align:center;
display:inline;
}
.nav li a{
font-size:14px;
font-family:Microsoft YaHei !important;
white-space:nowrap;
}
.nav li a:hover{
color:#FBECB7;
}
</style>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="warp">
<p id="head">
<p class="logo"><img src="img/logo.jpg" /></p>
<p class="head_pic"><img src="img/head_pic.jpg" /></p>
<p class="sc">
<a href=""><img src="img/sc_btn.jpg" /></a>
<a href=""><img src="img/sy_btn.jpg" /></a>
<a href=""><img src="img/kf_btn.jpg" /></a>
</p>
<p class="nav">
<ul>
<li><a href="">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="">关于我们</a></li>
<li><a href="">团队文化</a></li>
<li><a href="">公司动态</a></li>
<li><a href="">资讯参考</a></li>
<li><a href="">业务中心</a></li>
<li><a href="">合作银行</a></li>
<li><a href="">联系我们</a></li>
</ul>
</p>
</p>
<p id="main"></p>
<p id="foot"></p>
</p>
</body>
</html>
In the above In the code, the relative positioning is first set for the head. Then you can see that all the child elements inside will be positioned relative to the head instead of relative to the body after setting absolute. This is much simpler and more convenient than using floating, and there is no need to worry about compatibility issues.
Detailed explanation of BFC mode
What are the differences between href and src, link and @import
How can the absolute positioning of css be compatible with all resolutions
The above is the detailed content of How to use CSS position property. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




