This article brings you relevant knowledge aboutRedis, which mainly introduces how to ensure the consistency of the redis cache and the database, including updating the cache and updating the database, etc. I hope everyone has to help.

Recommended learning:Redis learning tutorial
Want to ensure caching Consistent with the double writing of the database, there are 4 ways, that is, 4 synchronization strategies:
From these four synchronization strategies, what we need to compare is:
Which method is more appropriate to update the cache or delete the cache? Should the database be operated first or the cache first?
Next, let’s analyze whether we should update the cache or delete the cache.
Advantages:The cache is updated in time every time the data changes, so misses are less likely to occur during queries.
Disadvantages:Updating the cache consumes a lot of money. If the data needs to undergo complex calculations before being written to the cache, frequent updates to the cache will affect the performance of the server. If it is a business scenario where data is written frequently, there may be no business reading the data when the cache is frequently updated.
Advantages:The operation is simple. No matter whether the update operation is complicated or not, the data in the cache will be deleted directly.
Disadvantages:After deleting the cache, the next query cache will miss, and the database needs to be read again. From the above comparison, in general, deleting the cache is a better solution.
Next, let’s analyze whether the database or the cache should be operated first.
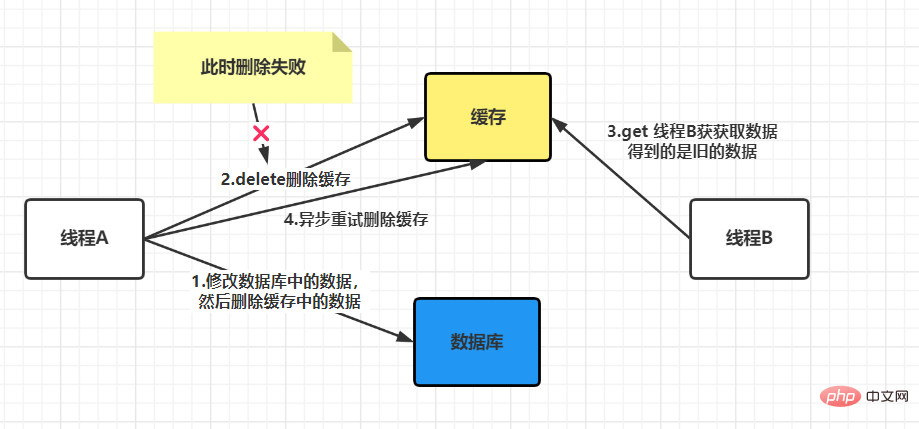
First, we will delete the cache first and update the database first, and make a comparison whenfailureoccurs:

As shown above, the cache is deleted first and then the database is updated. Problems that may occur when failure occurs:
 As shown above, the database is updated first and then the cache is deleted. Problems that may occur when
As shown above, the database is updated first and then the cache is deleted. Problems that may occur when
fails:
failureoccurs, it is impossible to clearly distinguish which method is better: deleting the cache first or updating the database first, thinking that they are both better. There is a problem. We will further compare these two methods later, but here we first discuss how to solve the problems that arise in the above scenarios?
use a retry mechanism to solve the problem, in the above two pictures Already painted.
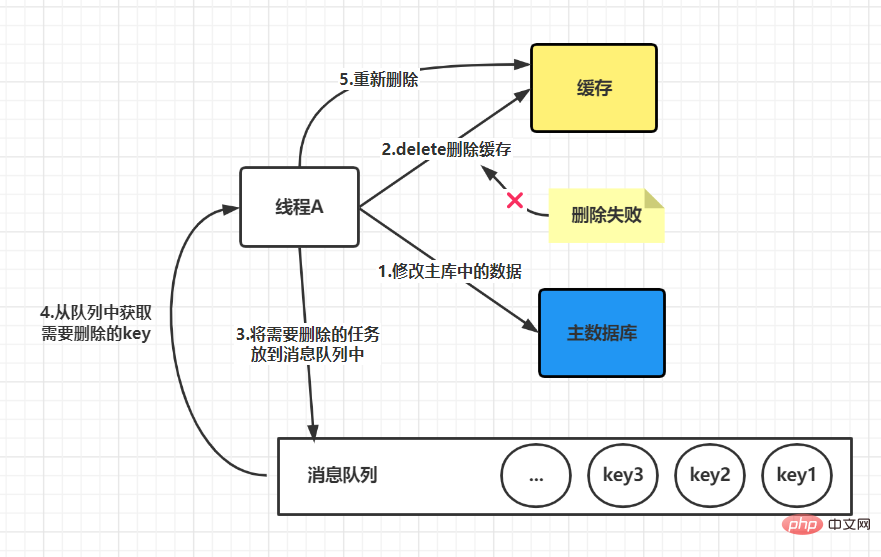
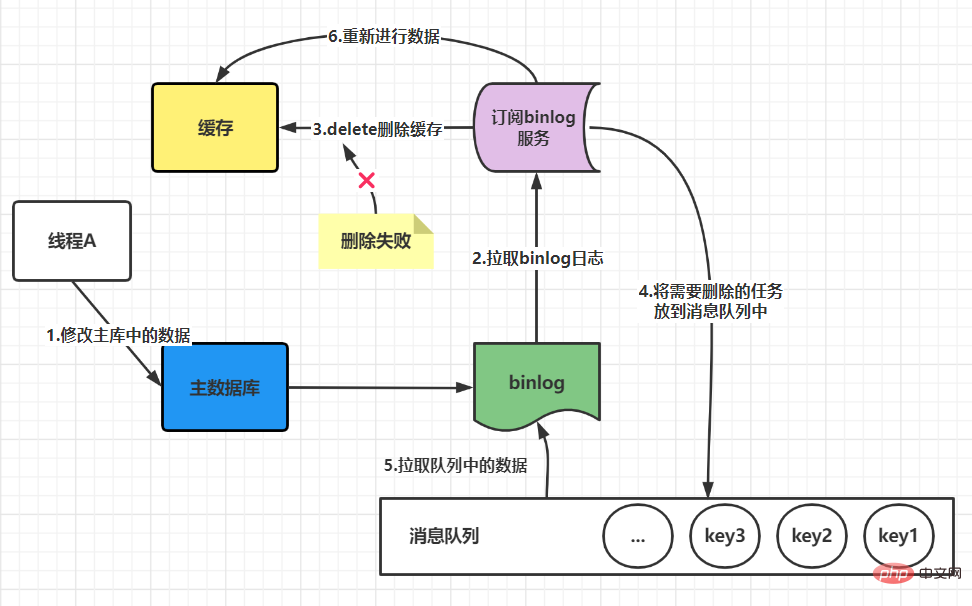
when there is no failure: It can be seen that the two steps of process A were successful, but due to concurrency, process B accessed the cache between the two steps. The end result is that the old data is stored in the cache, and the new data is stored in the database, and the two data are inconsistent. It can be seen thatthe final cache is consistent with the data in the database, and both are the latest data. But thread B read the old data during this process. There may be other threads like thread B that read the old data in the cache between these two steps, but because the execution speed of these two steps will be faster, So the impact is not big. After these two steps, when other processes read cached data, problems similar to process B will not occur. Final conclusion: After comparison, you will find that updating the database first and then deleting the cache is a solution with less impact. If the second step fails, a retry mechanism can be used to solve the problem. We mentioned above thatif the cache is deleted first and then the database is updated, it may cause a problem when there is no failure. Data inconsistency. If in actual applications, we need to choose this method due to certain considerations, is there a way to solve this problem? The answer is yes, that is to adopt the strategy of delayed double deletion.The basic idea of delayed double deletion is as follows: After blocking for a period of time, delete the cache again to delete the inconsistent data in the cache. As for the specific time, you need to evaluate the approximate time of your business and set it according to this time. If the database adopts a read-write separation architecture, then new problems will arise, as shown below: The solution at this time is that if Redis is used to query the database for filling data, then it must be forced to point to the main database for query. What should I do if the deletion fails? If the deletion still fails, you can increase the number of retries, but this number must be limited. When it exceeds a certain number, measures such as reporting errors, recording logs, and sending email reminders must be taken. Update the database first, then delete the cacheThis situation will also cause problems. For example, the database is updated successfully, but If an error occurs during the cache deletion stage and the deletion is not successful, then when reading the cache again at this time, the data will be wrong every time. The solution at this time is to use the message queue to compensate for deletion. The specific business logic is described in the following language: But this solution will have a disadvantage, which is that it will cause a lot of intrusion into the business code and be deeply coupled together, so there will be an optimization method at this time. We know that the Mysql database is updated in the binlog after the operation. We can all find the corresponding operations, then we can subscribe to the binlog log of the Mysql database to operate the cache. Recommended learning:Redis tutorial The above is the detailed content of How to ensure the consistency between Redis cache and database. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
As shown above, the cache is deleted first and then the database is updated. When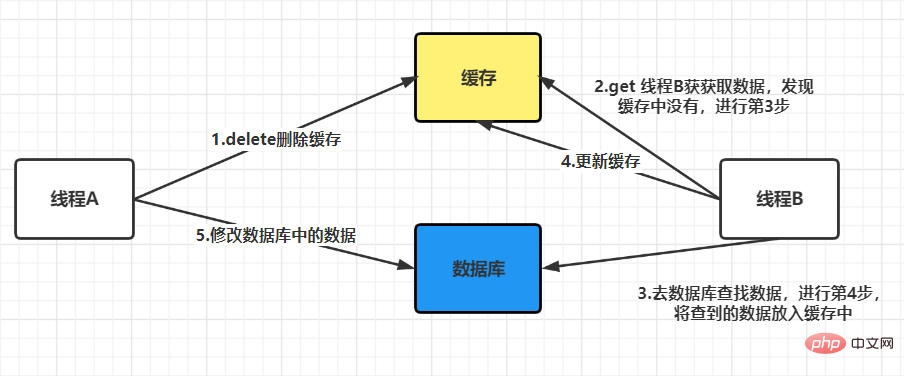 does not fail,
does not fail,
possible problems:

As shown above, the database is updated first and then the cache is deleted. When does not fail,possible problems:
4. Delayed double deletion
public void write(String key, Object data) { Redis.delKey(key); db.updateData(data); Thread.sleep(1000); Redis.delKey(key); }
4.1 What should we do if we adopt a read-write separation architecture?
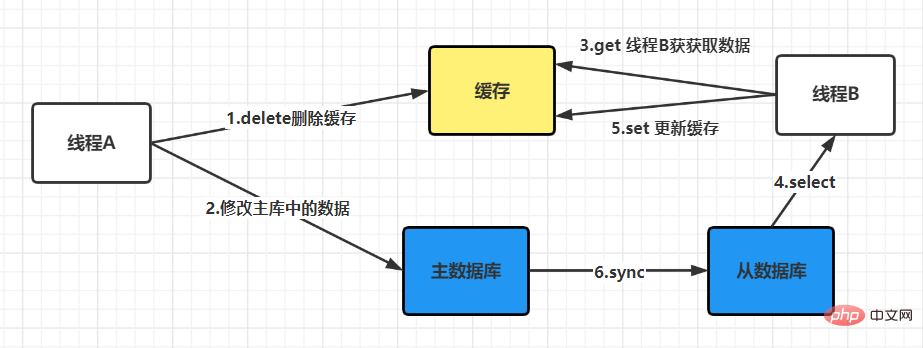
At this time, two requests came, requesting A (update operation ) and request B (query operation)
5. Use message queue to compensate for deletion
 Commonly used database software
Commonly used database software What are the in-memory databases?
What are the in-memory databases? Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis? How to use redis as a cache server
How to use redis as a cache server How redis solves data consistency
How redis solves data consistency How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency? What data does redis cache generally store?
What data does redis cache generally store? What are the 8 data types of redis
What are the 8 data types of redis