

[Related topic recommendations:react interview questions(2020)]
Theme: React
Difficulty: ⭐
Virtual DOM (VDOM)is an in-memory representation of the real DOM. The representation of the UI is kept in memory and synchronized with the actual DOM. This is a step that occurs between the rendering function being called and the element being displayed on the screen. The entire process is calledreconciliation.
Theme: React
Difficulty: ⭐⭐
and lifecycle hooks.and renders it to the page, it is a stateless component and is a functional component. It is also called a dumb component or a display component.Theme: React
Difficulty: ⭐⭐
RefsProvides a way to access the DOM created in therendermethod Methods of nodes or React elements. In a typical data flow,propsis the only way for parent and child components to interact. If you want to modify a child component, you need to re-render it with a newpros. There are exceptions to everything. In some cases, we need to force modification of children outside of the typical data flow. In this case,Refscan be used.
We can add arefattribute to the component to use. The value of this attribute is a callback function that receives the underlying DOM element or the mounted instance of the component as its first parameter.
class UnControlledForm extends Component { handleSubmit = () => { console.log("Input Value: ", this.input.value) } render () { return ( ) } }
Please note that theinputelement has arefattribute whose value is a function. This function receives the actual DOM element of the input and then places it on the instance so that it can be accessed inside thehandleSubmitfunction.
It is often misunderstood thatrefscan only be used within class components, butrefscan also be used with function components by leveraging closures in JS.
function CustomForm ({handleSubmit}) { let inputElement return ( ) }
Topic: React
Difficulty: ⭐⭐
In order to solve cross-browser issues Compatibility issue,SyntheticEventinstance will be passed to your event handler function,SyntheticEventis React's cross-browser browser native event wrapper, it also has browser native events The same interface, includingstopPropagation()andpreventDefault().
What’s interesting is that React doesn’t actually attach events to the child nodes themselves. React uses a single event listener to listen to all events at the top level. This is good for performance and means React doesn't need to track event listeners when updating the DOM.
Theme: React
Difficulty: ⭐⭐
propsandstateare ordinary JS objects. Although they both contain information that affects rendered output, their functionality in terms of components is different. That is,
stateis the component’s own data management, control of its own state, and is variable;propsis the data passed in from the outside. Parameters, immutable;stateare called stateless components, and those withstateare called stateful components;props more, use lessstate, that is, write more stateless components.Theme: React
Difficulty: ⭐⭐
Refs are created usingReact .createRef()Created and attached to the React element via therefattribute. When constructing a component, you typically assignRefsto instance properties so that they can be referenced throughout the component.
class MyComponent extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.myRef = React.createRef(); } render() { return ; } }
Or use it like this:
class UserForm extends Component { handleSubmit = () => { console.log("Input Value is: ", this.input.value) } render () { return ( ) } }
Theme: React
Difficulty: ⭐⭐
Higher Order Component (HOC)is a function that accepts a component and returns a new component. Basically, this is a pattern derived from the composition feature of React, calledPure Componentsbecause they can accept any dynamically provided subcomponent, but do not modify or copy the input component any behavior in.
const EnhancedComponent = higherOrderComponent(WrappedComponent);
HOC can be used for many of the following use cases
superin the constructor and passingpropsas a parameter?Topic: React
Difficulty: ⭐⭐
The subclass constructor cannot be used until thesuper()method is calledthisQuotes, the same goes for ES6 subclasses. The main reason for passingpropsparameters to thesuper()call is to be able to obtain the incomingprops throughthis.propsin the child constructor.
Passing props
class MyComponent extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); console.log(this.props); // { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 } } }
Not passing props
class MyComponent extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(); console.log(this.props); // undefined // 但是 Props 参数仍然可用 console.log(props); // Prints { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 } } render() { // 构造函数外部不受影响 console.log(this.props) // { name: 'sudheer',age: 30 } } }
The above example reveals something. The behavior ofpropsis different only inside the constructor, it is the same outside the constructor.
Theme: React
Difficulty: ⭐⭐⭐
In HTML, form elements such as,usually maintain their own state and update based on user input. When the user submits the form, the values from the above elements will be sent with the form.
而 React 的工作方式则不同。包含表单的组件将跟踪其状态中的输入值,并在每次回调函数(例如onChange)触发时重新渲染组件,因为状态被更新。以这种方式由 React 控制其值的输入表单元素称为受控组件。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
问题:
const element = (Hello, world!
)
上述代码如何使用React.createElement来实现:
const element = React.createElement( 'h1', {className: 'greeting'}, 'Hello, world!' );
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
当Facebook第一次发布 React 时,他们还引入了一种新的 JS 方言JSX,将原始 HTML 模板嵌入到 JS 代码中。JSX 代码本身不能被浏览器读取,必须使用Babel和webpack等工具将其转换为传统的JS。很多开发人员就能无意识使用 JSX,因为它已经与 React 结合在一直了。
class MyComponent extends React.Component { render() { let props = this.props; return ( ); } }
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
请看下面的代码:
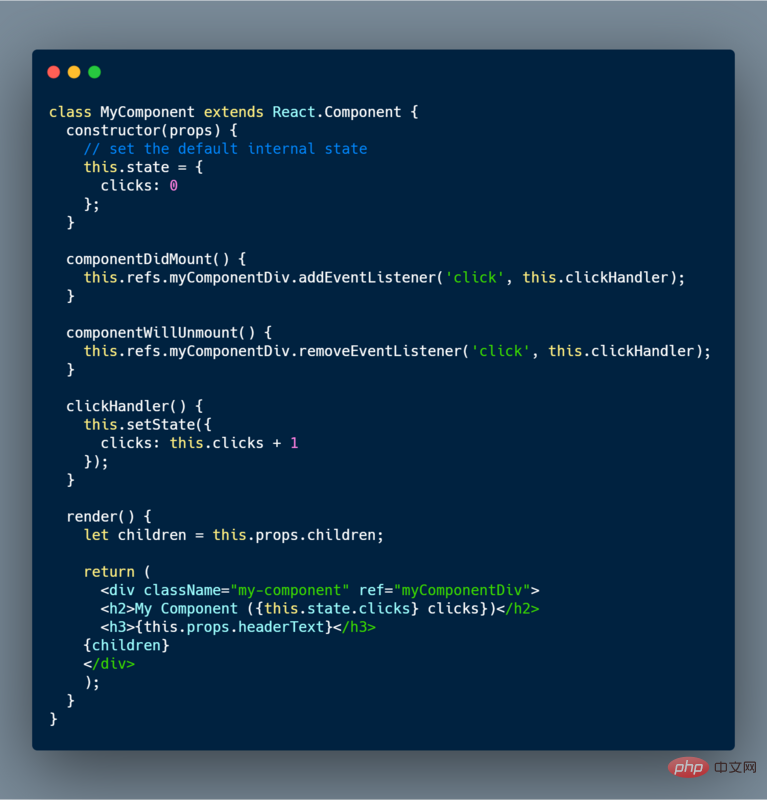
答案:
1.在构造函数没有将props传递给super,它应该包括以下行
constructor(props) { super(props); // ... }
2.事件监听器(通过addEventListener()分配时)的作用域不正确,因为 ES6 不提供自动绑定。因此,开发人员可以在构造函数中重新分配clickHandler来包含正确的绑定:
constructor(props) { super(props); this.clickHandler = this.clickHandler.bind(this); // ... }
state呢 ?主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
如果试图直接更新state,则不会重新渲染组件。
// 错误 This.state.message = 'Hello world';
需要使用setState()方法来更新state。它调度对组件state对象的更新。当state改变时,组件通过重新渲染来响应:
// 正确做法 This.setState({message: ‘Hello World’});
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
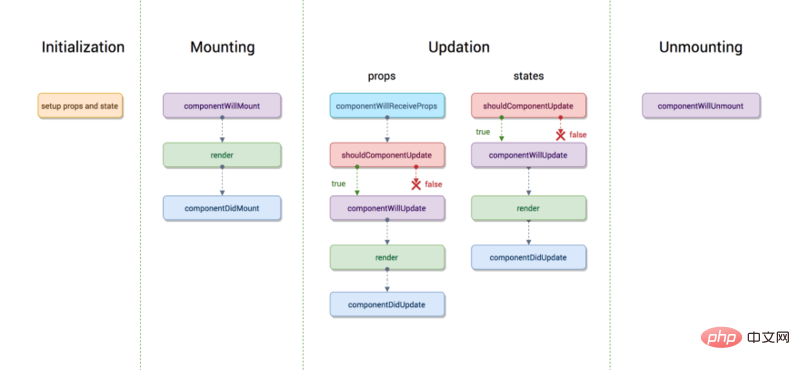
在组件生命周期中有四个不同的阶段:
componentWillMount和componentDidMount生命周期方法。shouldComponentUpdate、componentWillUpdate和componentDidUpdate生命周期方法。componentWillUnmount生命周期方法。除以上四个常用生命周期外,还有一个错误处理的阶段:
Error Handling:在这个阶段,不论在渲染的过程中,还是在生命周期方法中或是在任何子组件的构造函数中发生错误,该组件都会被调用。这个阶段包含了componentDidCatch生命周期方法。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
componentWillMount:在渲染之前执行,用于根组件中的 App 级配置。componentDidMount:在第一次渲染之后执行,可以在这里做AJAX请求,DOM 的操作或状态更新以及设置事件监听器。componentWillReceiveProps:在初始化render的时候不会执行,它会在组件接受到新的状态(Props)时被触发,一般用于父组件状态更新时子组件的重新渲染shouldComponentUpdate:确定是否更新组件。默认情况下,它返回true。如果确定在state或props更新后组件不需要在重新渲染,则可以返回false,这是一个提高性能的方法。componentWillUpdate:在shouldComponentUpdate返回true确定要更新组件之前件之前执行。componentDidUpdate:它主要用于更新DOM以响应props或state更改。componentWillUnmount:它用于取消任何的网络请求,或删除与组件关联的所有事件监听器。主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
...在React(使用JSX)代码中做什么?它叫什么?
这个叫扩展操作符号或者展开操作符,例如,如果this.props包含a:1和b:2,则
等价于下面内容:
扩展符号不仅适用于该用例,而且对于创建具有现有对象的大多数(或全部)属性的新对象非常方便,在更新state咱们就经常这么做:
this.setState(prevState => { return {foo: {...prevState.foo, a: "updated"}}; });
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
首先,Hooks 通常支持提取和重用跨多个组件通用的有状态逻辑,而无需承担高阶组件或渲染props的负担。Hooks可以轻松地操作函数组件的状态,而不需要将它们转换为类组件。
Hooks 在类中不起作用,通过使用它们,咱们可以完全避免使用生命周期方法,例如componentDidMount、componentDidUpdate、componentWillUnmount。相反,使用像useEffect这样的内置钩子。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
Hooks是 React 16.8 中的新添加内容。它们允许在不编写类的情况下使用state和其他 React 特性。使用 Hooks,可以从组件中提取有状态逻辑,这样就可以独立地测试和重用它。Hooks 允许咱们在不改变组件层次结构的情况下重用有状态逻辑,这样在许多组件之间或与社区共享 Hooks 变得很容易。
useState()是什么?主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
下面说明useState(0)的用途:
... const [count, setCounter] = useState(0); const [moreStuff, setMoreStuff] = useState(...); ... const setCount = () => { setCounter(count + 1); setMoreStuff(...); ... };
useState是一个内置的 React Hook。useState(0)返回一个元组,其中第一个参数count是计数器的当前状态,setCounter提供更新计数器状态的方法。
咱们可以在任何地方使用setCounter方法更新计数状态-在这种情况下,咱们在setCount函数内部使用它可以做更多的事情,使用 Hooks,能够使咱们的代码保持更多功能,还可以避免过多使用基于类的组件。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
React 的StrictMode是一种辅助组件,可以帮助咱们编写更好的 react 组件,可以使用
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
在 JS 中,this值会根据当前上下文变化。在 React 类组件方法中,开发人员通常希望this引用组件的当前实例,因此有必要将这些方法绑定到实例。通常这是在构造函数中完成的:
class SubmitButton extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { isFormSubmitted: false }; this.handleSubmit = this.handleSubmit.bind(this); } handleSubmit() { this.setState({ isFormSubmitted: true }); } render() { return ( ) } }
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
在构建 React 应用程序时,在多层嵌套组件来使用另一个嵌套组件提供的数据。最简单的方法是将一个prop从每个组件一层层的传递下去,从源组件传递到深层嵌套组件,这叫做prop drilling。
prop drilling的主要缺点是原本不需要数据的组件变得不必要地复杂,并且难以维护。
为了避免prop drilling,一种常用的方法是使用React Context。通过定义提供数据的Provider组件,并允许嵌套的组件通过Consumer组件或useContextHook 使用上下文数据。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
传统的 MVC 模式在分离数据(Model)、UI(View和逻辑(Controller)方面工作得很好,但是 MVC 架构经常遇到两个主要问题:
数据流不够清晰:跨视图发生的级联更新常常会导致混乱的事件网络,难于调试。
缺乏数据完整性:模型数据可以在任何地方发生突变,从而在整个UI中产生不可预测的结果。
使用 Flux 模式的复杂用户界面不再遭受级联更新,任何给定的React 组件都能够根据store提供的数据重建其状态。Flux 模式还通过限制对共享数据的直接访问来加强数据完整性。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐
尽管非受控组件通常更易于实现,因为只需使用refs即可从 DOM 中获取值,但通常建议优先选择受控制的组件,而不是非受控制的组件。
这样做的主要原因是受控组件支持即时字段验证,允许有条件地禁用/启用按钮,强制输入格式。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐
这段代码有什么问题:
this.setState((prevState, props) => { return { streak: prevState.streak + props.count } })
答案:
没有什么问题。这种方式很少被使用,咱们可以将一个函数传递给setState,该函数接收上一个state的值和当前的props,并返回一个新的状态,如果咱们需要根据以前的状态重新设置状态,推荐使用这种方式。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐
Context通过组件树提供了一个传递数据的方法,从而避免了在每一个层级手动的传递props属性。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐
Fiber是 React 16 中新的协调引擎或重新实现核心算法。它的主要目标是支持虚拟DOM的增量渲染。React Fiber的目标是提高其在动画、布局、手势、暂停、中止或重用等方面的适用性,并为不同类型的更新分配优先级,以及新的并发原语。
React Fiber 的目标是增强其在动画、布局和手势等领域的适用性。它的主要特性是增量渲染:能够将渲染工作分割成块,并将其分散到多个帧中。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐
当应用程序在开发模式下运行时,React 将自动检查咱们在组件上设置的所有props,以确保它们具有正确的数据类型。对于不正确的类型,开发模式下会在控制台中生成警告消息,而在生产模式中由于性能影响而禁用它。强制的props用isRequired定义的。
下面是一组预定义的 prop 类型:
例如,咱们为用户组件定义了如下的propTypes
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'; class User extends React.Component { render() { return ( Welcome, {this.props.name}
Age, {this.props.age} ); } } User.propTypes = { name: PropTypes.string.isRequired, age: PropTypes.number.isRequired };
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐
构造函数和getInitialState之间的区别就是ES6和ES5本身的区别。在使用ES6类时,应该在构造函数中初始化state,并在使用React.createClass时定义getInitialState方法。
class MyComponent extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { /* initial state */ }; } }
等价于:
var MyComponent = React.createClass({ getInitialState() { return { /* initial state */ }; }, });
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐
对于某些属性,React 非常聪明,如果传递给它的值是虚值,可以省略该属性。例如:
var InputComponent = React.createClass({ render: function() { var required = true; var disabled = false; return ( ); } });
渲染结果:
另一种可能的方法是:
var condition = true; var component = ( );
render props和高阶组件吗?主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐
通常,render props和高阶组件仅渲染一个子组件。React团队认为,Hooks 是服务此用例的更简单方法。
这两种模式仍然有一席之地(例如,一个虚拟的scroller组件可能有一个renderItem prop,或者一个可视化的容器组件可能有它自己的 DOM 结构)。但在大多数情况下,Hooks 就足够了,可以帮助减少树中的嵌套。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐
React 中最常见的问题之一是组件不必要地重新渲染。React 提供了两个方法,在这些情况下非常有用:
React.memo():这可以防止不必要地重新渲染函数组件PureComponent:这可以防止不必要地重新渲染类组件这两种方法都依赖于对传递给组件的props的浅比较,如果props没有改变,那么组件将不会重新渲染。虽然这两种工具都非常有用,但是浅比较会带来额外的性能损失,因此如果使用不当,这两种方法都会对性能产生负面影响。
通过使用React Profiler,可以在使用这些方法前后对性能进行测量,从而确保通过进行给定的更改来实际改进性能。
主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
纯函数是不依赖并且不会在其作用域之外修改变量状态的函数。本质上,纯函数始终在给定相同参数的情况下返回相同结果。
setState时,Reactrender是如何工作的?主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
咱们可以将"render"分为两个步骤:
render方法被调用时,它返回一个新的组件的虚拟 DOM 结构。当调用setState()时,render会被再次调用,因为默认情况下shouldComponentUpdate总是返回true,所以默认情况下 React 是没有优化的。主题: React
难度: ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
有几种常用方法可以避免在 React 中绑定方法:
1.将事件处理程序定义为内联箭头函数
class SubmitButton extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { isFormSubmitted: false }; } render() { return ( ) } }
2.使用箭头函数来定义方法:
class SubmitButton extends React.Component { state = { isFormSubmitted: false } handleSubmit = () => { this.setState({ isFormSubmitted: true }); } render() { return ( ) } }
3.使用带有 Hooks 的函数组件
const SubmitButton = () => { const [isFormSubmitted, setIsFormSubmitted] = useState(false); return ( ) };
本文转载自:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000020912300
相关教程推荐:React视频教程
| Function component | Class component | |
|---|---|---|
this | No
Yes | |
| No | Yes | |
|
Yes |
The above is the detailed content of 35 interview questions you must know and master React. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!