

According to news on November 14, Nvidia officially released the new H200 GPU at the "Supercomputing 23" conference on the morning of the 13th local time, and updated the GH200 product line
Among them, H200 is still built on the existing Hopper H100 architecture, but adds more high-bandwidth memory (HBM3e) to better handle the large data sets required to develop and implement artificial intelligence, making it easier to run The overall performance of the large model is improved by 60% to 90% compared to the previous generation H100. The updated GH200 will also power the next generation of AI supercomputers. More than 200 exaflops of AI computing power will come online in 2024.
H200: HBM capacity increased by 76%, performance of large models improved by 90%
Specifically, the new H200 offers up to 141GB of HBM3e memory, effectively running at approximately 6.25 Gbps, for a total bandwidth of 4.8 TB/s per GPU in the six HBM3e stacks. This is a huge improvement compared to the previous generation H100 (with 80GB HBM3 and 3.35 TB/s bandwidth), with more than 76% increase in HBM capacity. According to official data, when running large models, H200 will bring an improvement of 60% (GPT3 175B) to 90% (Llama 2 70B) compared to H100

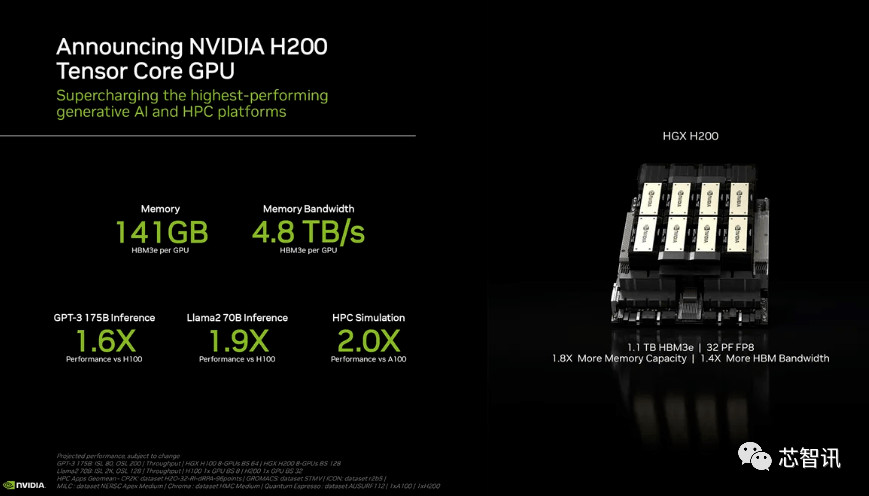
While some configurations of the H100 do offer more memory, such as the H100 NVL which pairs the two boards and offers a total of 188GB of memory (94GB per GPU), even compared to the H100 SXM variant, the new The H200 SXM also offers 76% more memory capacity and 43% more bandwidth.
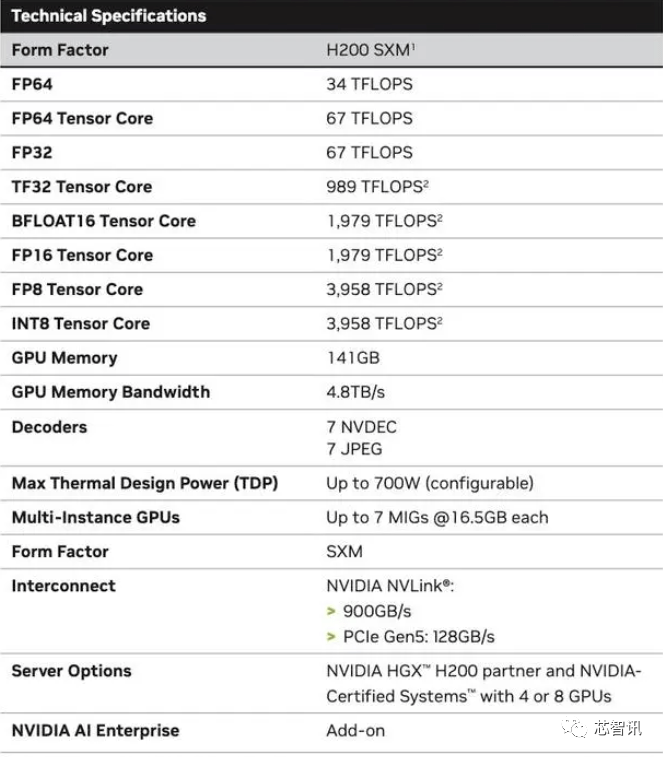
It should be pointed out that the raw computing performance of H200 does not seem to have changed much. The only slide Nvidia showed that reflected compute performance was based on an HGX 200 configuration using eight GPUs, with a total performance of "32 PFLOPS FP8." While the original H100 provided 3,958 teraflops of FP8 computing power, eight such GPUs also provide approximately 32 PFLOPS of FP8 computing power
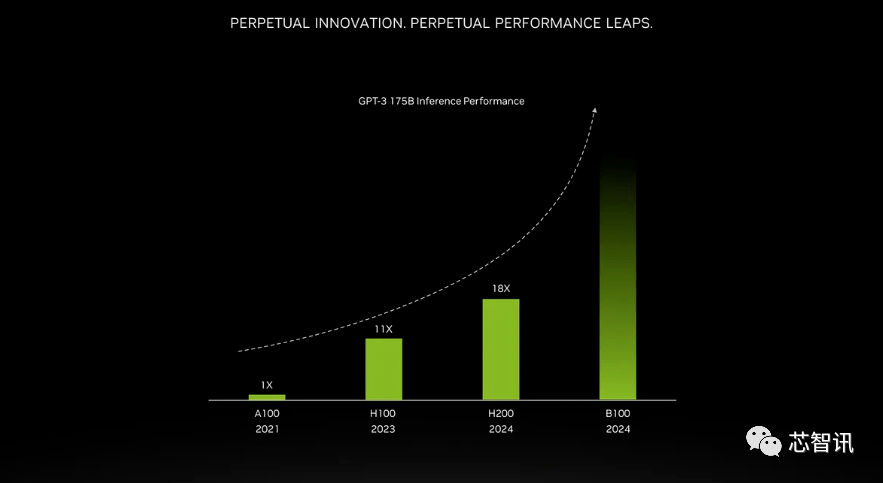
The improvement brought by higher bandwidth memory depends on the workload. Large models (such as GPT-3) will greatly benefit from the increase in HBM memory capacity. According to Nvidia, the H200 will perform 18 times better than the original A100 when running GPT-3 and approximately 11 times faster than the H100. Additionally, a teaser for the upcoming Blackwell B100 shows that it contains a taller bar that fades to black, roughly twice as long as the H200's.
Nvidia said that by launching new products, they hope to keep up with the growth in the size of data sets used to create artificial intelligence models and services. The enhanced memory capabilities will make the H200 faster in the process of feeding data to software, a process that helps train artificial intelligence to perform tasks such as recognizing images and speech.
"Integrating faster and larger HBM memory can help improve performance for computationally demanding tasks, including generative AI models and high-performance computing applications, while optimizing GPU usage and efficiency." NVIDIA High said Ian Buck, vice president of performance computing products.
Dion Harris, head of data center products at Nvidia, said: “When you look at the trends in the market, model sizes are increasing rapidly. This is our continued introduction of the latest and greatest technology. Model.”
Mainframe computer manufacturers and cloud service providers are expected to begin using the H200 in the second quarter of 2024. NVIDIA server manufacturing partners (including Evergreen, ASUS, Dell, Eviden, Gigabyte, HPE, Hongbai, Lenovo, Wenda, MetaVision, Wistron and Wiwing) can use the H200 to update existing systems, while Amazon , Google, Microsoft, Oracle, etc. will become the first cloud service providers to adopt H200.
Given the current strong market demand for Nvidia AI chips and the new H200 adding more expensive HBM3e memory, the price of H200 will definitely be more expensive. Nvidia doesn't list a price, but the previous generation H100 cost $25,000 to $40,000.
Nvidia spokesperson Kristin Uchiyama said final pricing will be determined by Nvidia’s manufacturing partners
Regarding whether the launch of H200 will affect the production of H100, Kristin Uchiyama said: "We expect the total supply throughout the year to increase."
Nvidia’s high-end AI chips have always been regarded as the best choice for processing large amounts of data and training large language models and AI generation tools. However, when the H200 chip was launched, AI companies were still desperately seeking A100/H100 chips in the market. The market's focus remains on whether Nvidia can provide enough supply to meet market demand. Therefore, NVIDIA has not given an answer to whether H200 chips will be in short supply like H100 chips
However, next year may be a more favorable period for GPU buyers. According to a report in the Financial Times in August, NVIDIA plans to triple H100 production in 2024, and the production target will increase from approximately 2023 to approximately 500,000 to 2 million in 2024. But generative AI is still booming, and demand is likely to be greater in the future.
For example, the newly launched GPT-4 is trained on approximately 10,000-25,000 blocks of A100. Meta’s large AI model requires approximately 21,000 A100 blocks for training. Stability AI uses approximately 5,000 A100s. Falcon-40B training requires 384 A100
According to Musk, GPT-5 may require 30,000-50,000 H100. Morgan Stanley's quote is 25,000 GPUs.
Sam Altman denied training GPT-5, but mentioned that "OpenAI has a serious shortage of GPUs, and the fewer people using our products, the better."
Of course, in addition to NVIDIA, AMD and Intel are also actively entering the AI market to compete with NVIDIA. The MI300X previously launched by AMD is equipped with 192GB HBM3 and 5.2TB/s memory bandwidth, which will make it far exceed the H200 in terms of capacity and bandwidth.
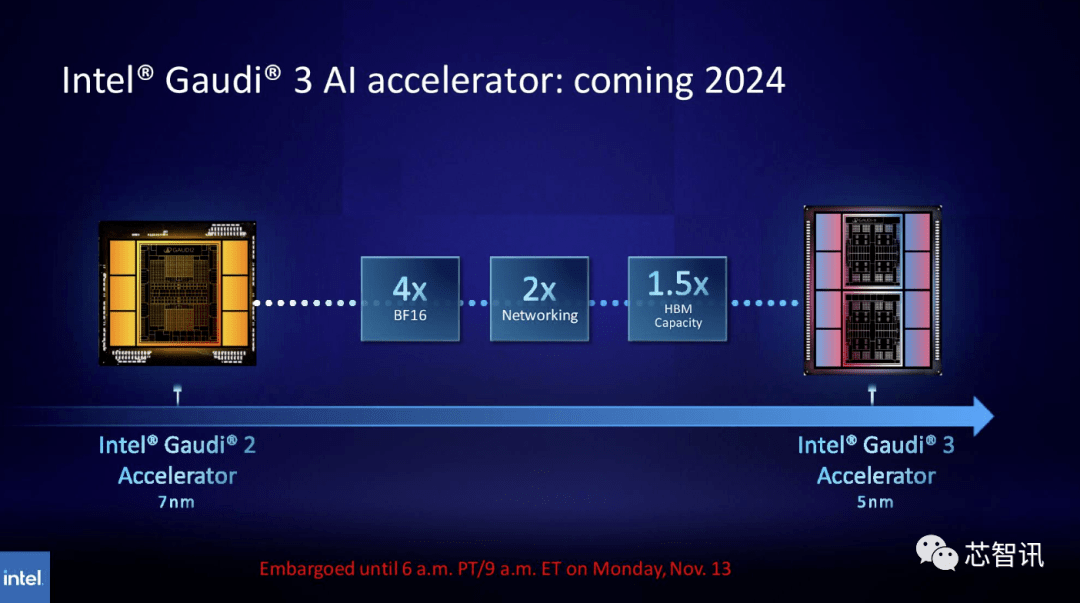
Similarly, Intel plans to increase the HBM capacity of Gaudi AI chips. According to the latest released information, Gaudi 3 uses a 5nm process, and its performance in BF16 workloads will be four times that of Gaudi 2, and its network performance will also be twice that of Gaudi 2 (Gaudi 2 has 24 built-in 100 GbE RoCE NICs ). Additionally, Gaudi 3 has 1.5 times the HBM capacity of Gaudi 2 (Gaudi 2 has a 96 GB HBM2E). As can be seen from the figure below, Gaudi 3 uses a chiplet-based design with two computing clusters, unlike Gaudi 2 which uses Intel’s single-chip solution
New GH200 super chip: Powering the next generation of AI supercomputers
In addition to releasing the new H200 GPU, Nvidia also launched an upgraded version of the GH200 super chip. This chip uses NVIDIA NVLink-C2C chip interconnect technology, combining the latest H200 GPU and Grace CPU (not sure if it is an upgraded version). Each GH200 super chip will also carry a total of 624GB of memory
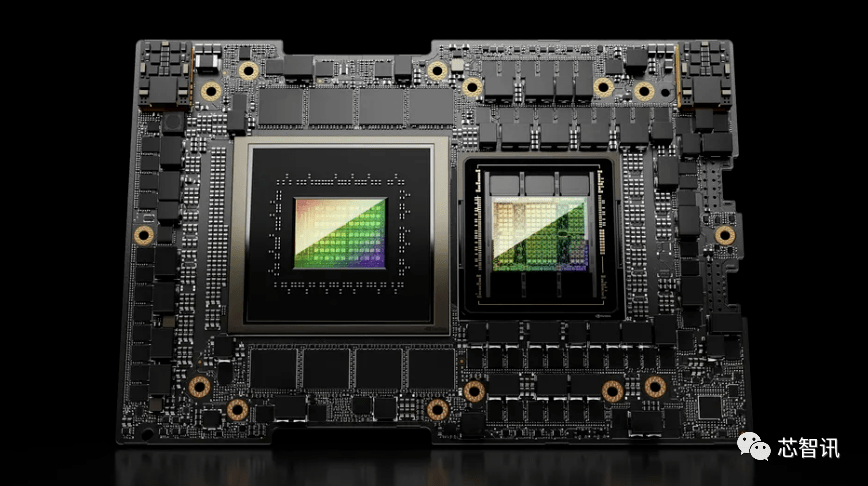
For comparison, the previous generation GH200 is based on the H100 GPU and the 72-core Grace CPU, providing 96GB of HBM3 and 512GB of LPDDR5X integrated in the same package.
Although NVIDIA did not introduce the details of the Grace CPU in the GH200 super chip, NVIDIA provided some comparisons between GH200 and "modern dual-channel x86 CPUs." It can be seen that GH200 has brought an 8-fold improvement in ICON performance, and MILC, Quantum Fourier Transform, RAG LLM Inference, etc. have brought dozens or even hundreds of times improvement.
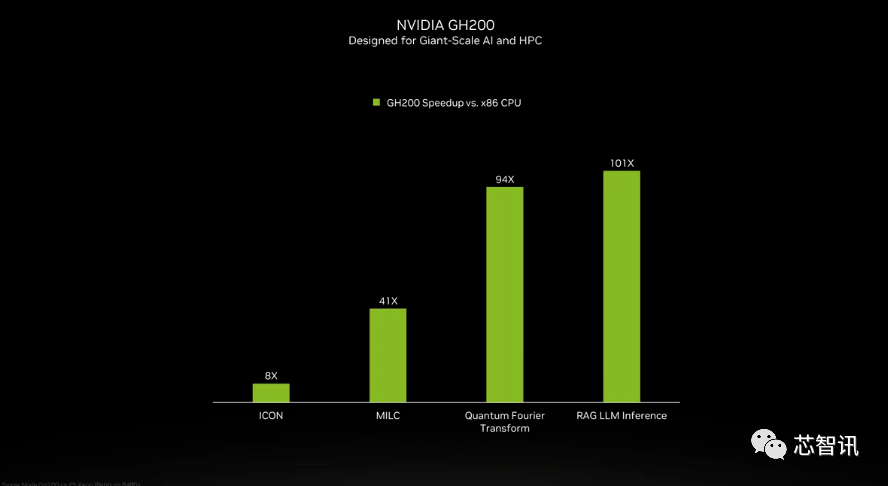
But it should be pointed out that accelerated and "non-accelerated systems" are mentioned. what does that mean? We can only assume that x86 servers are running code that is not fully optimized, especially considering that the world of artificial intelligence is evolving rapidly and new advances in optimization seem to be coming out on a regular basis.
The new GH200 will also be used in the new HGX H200 system. These are said to be "seamlessly compatible" with existing HGX H100 systems, meaning HGX H200s can be used in the same installation to increase performance and memory capacity without the need to redesign the infrastructure.
According to reports, the Alpine supercomputer of the Swiss National Supercomputing Center may be one of the first batch of GH100-based Grace Hopper supercomputers put into use next year. The first GH200 system to enter service in the United States will be the Venado supercomputer at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) Vista systems will also use the just-announced Grace CPU and Grace Hopper superchips, but it's unclear whether they will be based on the H100 or H200

Currently, the largest supercomputer to be installed is the Jupiter supercomputer at the Jϋlich Supercomputing Center. It will house "nearly" 24,000 GH200 superchips, totaling 93 exaflops of AI computing (presumably using FP8, although most AI still uses BF16 or FP16). It will also deliver 1 exaflop of traditional FP64 computing. It will use a "Quad GH200" board with four GH200 superchips.
Nvidia expects these new supercomputers to be installed in the next year or so to, collectively, achieve more than 200 exaflops of artificial intelligence computing power
If the original meaning does not need to be changed, the content needs to be rewritten into Chinese and the original sentence does not need to appear
The above is the detailed content of New title: NVIDIA H200 released: HBM capacity increased by 76%, the most powerful AI chip that significantly improves large model performance by 90%. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




