Installing LUA on Mac is very simple, just use the brew related commands directly;
brew install lua
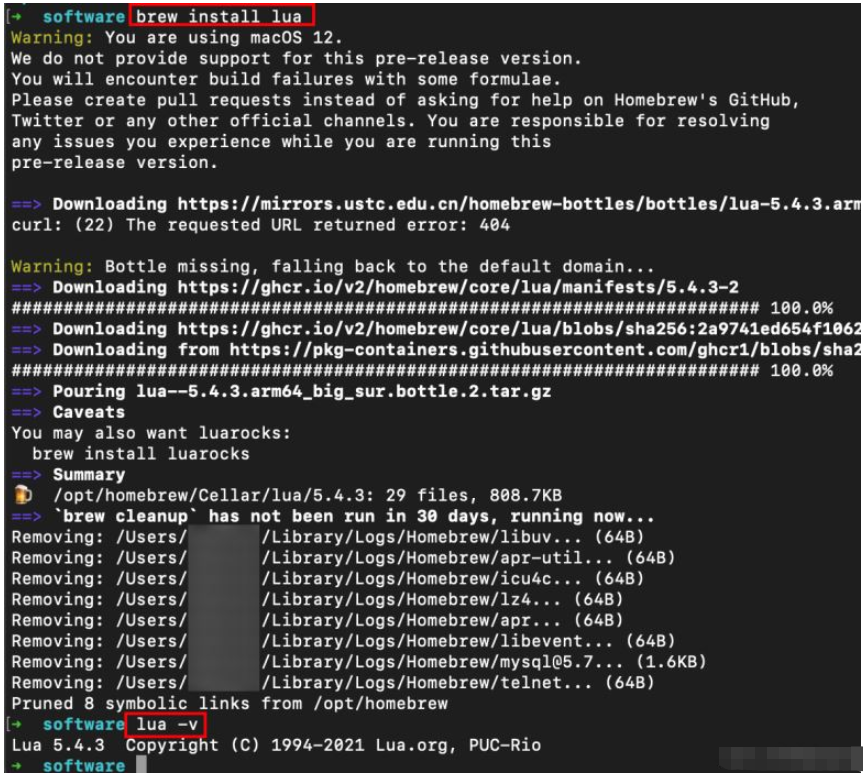
lua -vCommand you can see that lua has been installed.

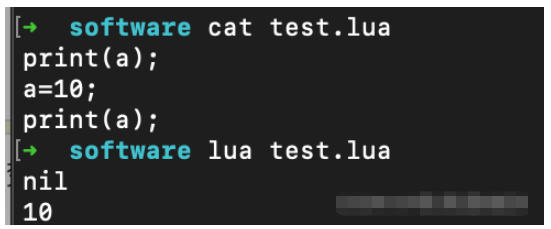
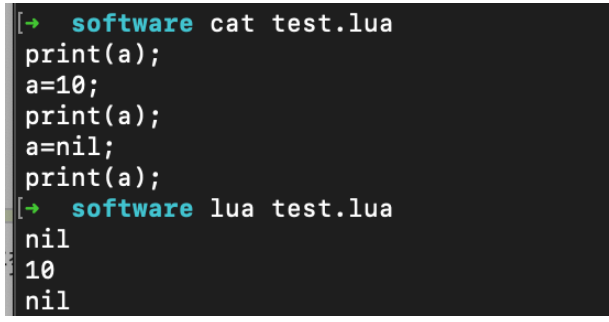
Execute the command:
lua test.lua
The output is:

--
--[[ 多行注释 多行注释 --]]
local;
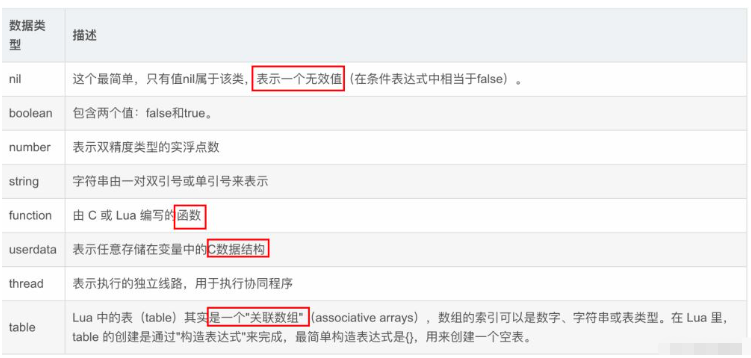
In addition, names that generally start with an underscore followed by a string of uppercase letters (such as _VERSION) are reserved for Lua internal global variables.
2) Local variables-- 局部变量赋值 local b=2
.. Connect two strings;
string.sub() is used to intercept strings;
string.sub(s, i [, j])
string.find() Used for string search
string.find (str, substr, [init, [plain]])
init Specifies the starting position of the search, the default is 1, it can be a negative number, indicating the number of characters from back to front.
#plain Indicates whether to use simple mode, the default is false, true only does a simple search for substrings, false indicates using regular pattern matching.
then, and the flow control ends with end.
if(xxx) then
print("xxx")
else if(xx) then
print("xx")
else
print("x")
endSyntax format:
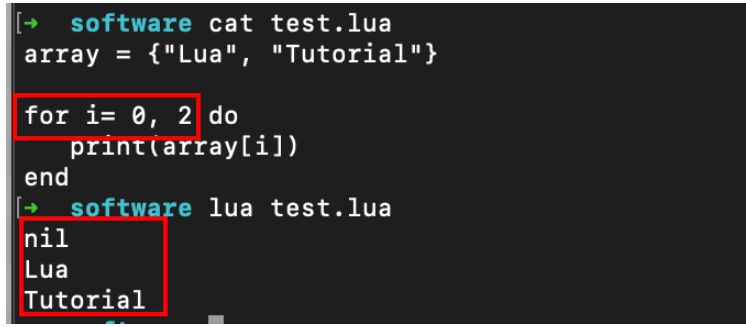
for var=exp1,exp2,exp3 do
<执行体>
end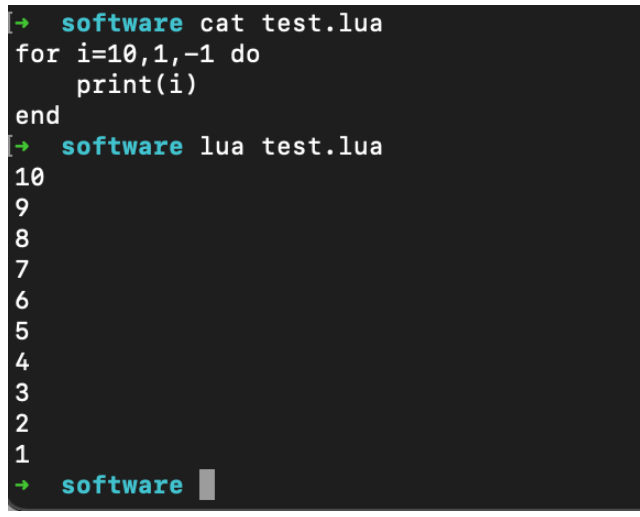
2> 泛型for循环
通过一个迭代器函数来遍历所有值,类似 java 中的 foreach 语句;
语法格式:
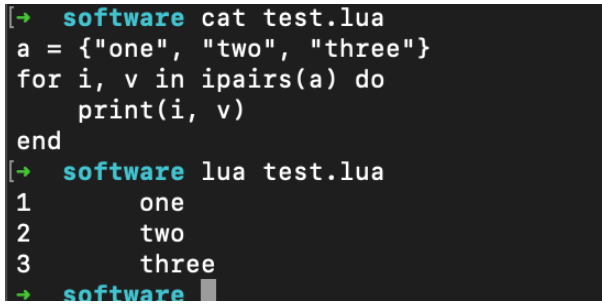
--打印数组a的所有值
a = {"one", "two", "three"}
for i, v in ipairs(a) do
print(i, v)
endi 是数组索引值,v 是对应索引的数组元素值。
ipairs是Lua提供的一个迭代器函数,用来迭代数组。
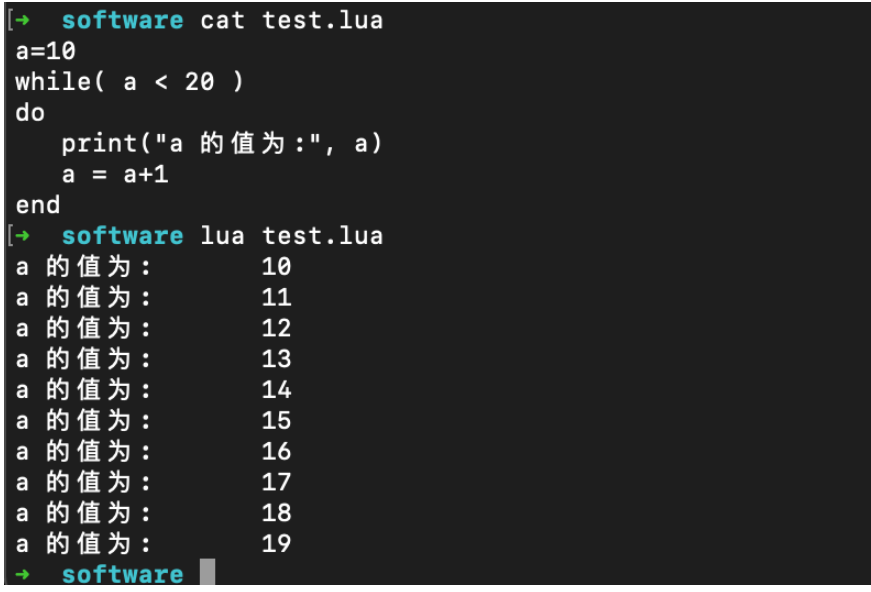
while 循环语句在判断条件为 true 时会重复执行循环体语句。
语法格式:
while(condition) do statements end
statements(循环体语句) 可以是一条或多条语句,condition(条件) 可以是任意表达式;
在 condition(条件) 为 true 时执行循环体语句。
和Java中的break一个作用,用于退出当前循环或语句;
在Lua中,函数是对语句和表达式进行抽象的主要方法。类似于Java中的方法。
Lua 函数主要有两种用途:
完成指定的任务,这种情况下函数作为调用语句使用;
计算并返回值,这种情况下函数作为赋值语句的表达式使用;
函数的编写方式如下:
--[[ 函数返回两个值的最大值 --]]
function max(num1, num2)
if (num1 > num2) then
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
end
return result;
end
-- 调用函数
print("两值比较最大值为 ",max(10,4))
print("两值比较最大值为 ",max(5,6))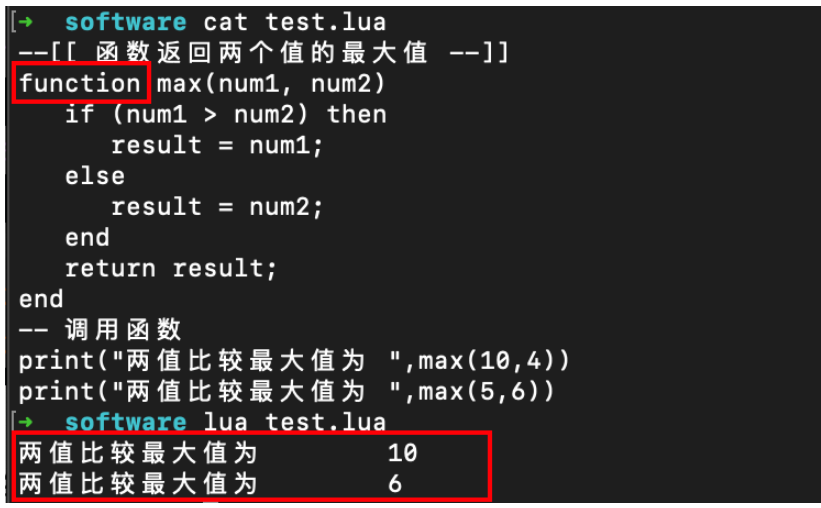
Java中执行Lua脚本有两种方式:字符串的方式、文件的方式;
Java中想要执行LUA脚本,首先需要在pom中引入相关依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.luaj</groupId>
<artifactId>luaj-jse</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>对于简单的lua脚本,可以直接用java字符串写;
package com.saint.base.lua;
import org.luaj.vm2.Globals;
import org.luaj.vm2.LuaValue;
import org.luaj.vm2.lib.jse.JsePlatform;
public class LuaString {
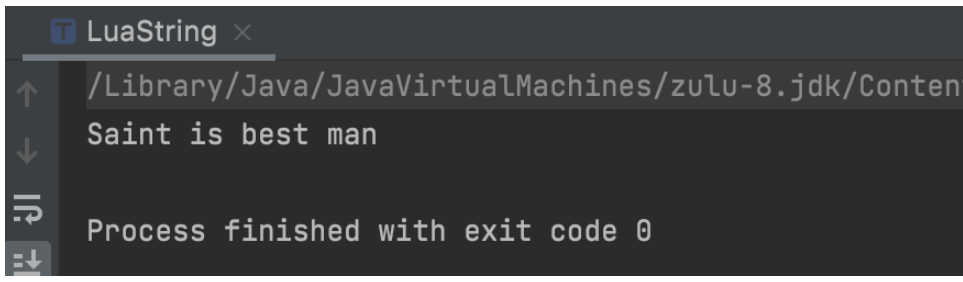
public static void main(String[] args) {
String luaStr = "print 'Saint is best man'";
Globals globals = JsePlatform.standardGlobals();
LuaValue luaValue = globals.load(luaStr);
luaValue.call();
}
}控制台输出:
对于一些比较常用的、复杂的脚本可以选择存放在文件中,在Java中再调用lua文件;
package com.saint.base.lua;
import org.luaj.vm2.Globals;
import org.luaj.vm2.LuaValue;
import org.luaj.vm2.lib.jse.JsePlatform;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class LuaFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// lua脚本的文件路径
String luaPath = "/xxxx/javaTest.lua";
Globals globals = JsePlatform.standardGlobals();
//加载脚本文件login.lua,并编译
globals.loadfile(luaPath).call();
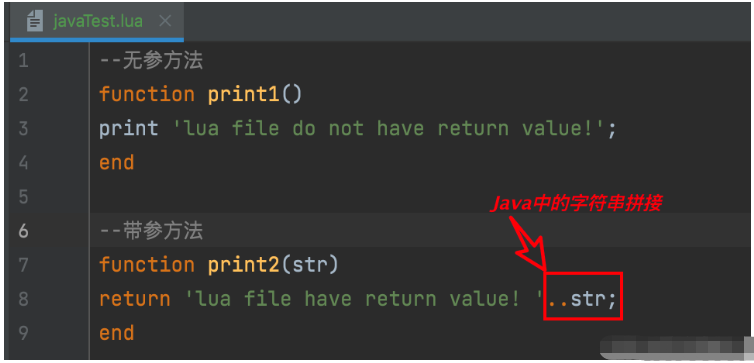
LuaValue func1 = globals.get(LuaValue.valueOf("print1"));
func1.call();
LuaValue func2 = globals.get(LuaValue.valueOf("print2"));
String luaResp = func2.call(LuaValue.valueOf("saint-input-param")).toString();
System.out.println("lua file return is : " + luaResp);
}
}lua脚本文件:
控制台输出:
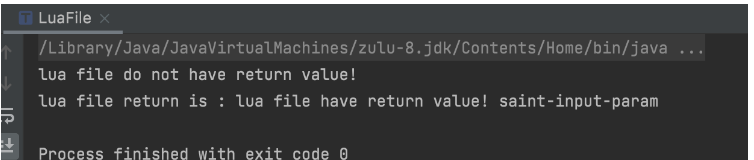
Luaj在包装执行具体的Lua代码时, 有三种不同的模式;
纯脚本解析执行(不选用任何Compiler)
To Lua字节码(LuaC, lua-to-lua-bytecode compiler)(默认选用)
To Java字节码(LuaJC, lua-to-java-bytecode compiler)
Luaj中的Globals对象不是线程安全的, 因此最佳实践是每个线程一个Globals对象。
事实上, 可以采用ThreadLocal的方式来存储该对象。
2)性能问题
Lua脚本在JAVA中运行,相比于直接运行Java代码会慢很多,大约1000倍。
在使用Redisson、Jedis+Lua时,我们可以通过redis客户端集成的、手写的LUA脚本来保证一系列命令在Redis中可以"原子执行"。
在redis执行lua脚本时,相当于一个redis级别的锁,不能执行其他操作,类似于原子操作,这也是redisson实现的一个关键点。
比如Redisson中的lua脚本:
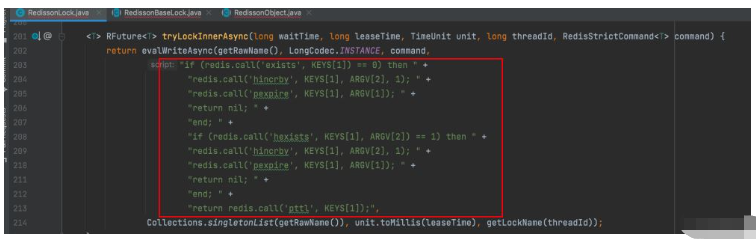
Redisson如何实现分布式锁,可以看文章:https://www.yisu.com/article/277312.htm
lua脚本中有如下几个概念:
redis.call():执行redis命令。
KEYS[n]:指脚本中第n个参数,比如KEYS[1]指脚本中的第一个参数。
ARGV[n]:指脚本中第n个参数的值,比如ARGV[1]指脚本中的第一个参数的值。
返回值中nil与false同一个意思。
redis2.6.0版本起 采用内置的Lua解释器 通过EVAL命令去执行脚本;
redis中的EVAL命令可以用于执行一段lua代码。命令格式如下:
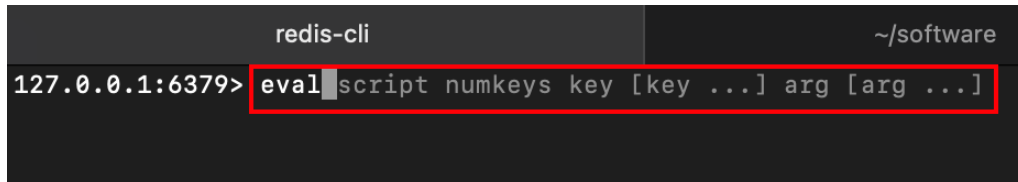
第一个参数script:表示lua脚本的内容;
第二参数numkeys:表示有多少个键值对。
其余参数:先把numkeys个key列出来,再把numkeys个arg列出来。
Lua脚本中可以使用2个函数调用redis命令;
redis.call()
redis.pcall()
redis.call()与redis.pcall()相似,二者唯一不同之处:
如果执行的redis命令执行失败,redis.call()将产生一个Lua error,从而迫使EVAL命令返回一个错误给命令的调用者;
然而redis.pcall()将会捕捉这个错误,并返回代表这个错误的Lua表。
有那么一段逻辑;
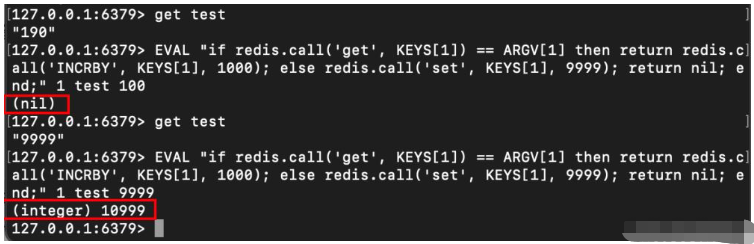
如果Redis某个key的整数值 和 某个value相等,则将key对应的整数值 + 1000;否则将key的值设置为9999;
lua脚本执行命令如下:
EVAL "if redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call('INCRBY', KEYS[1], 1000); else redis.call('set', KEYS[1], 9999); return nil; end;" 1 test 100
根据test值的不同,不同的执行结果如下:
The above is the detailed content of How to use Lua script in Java ecosystem/Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




