
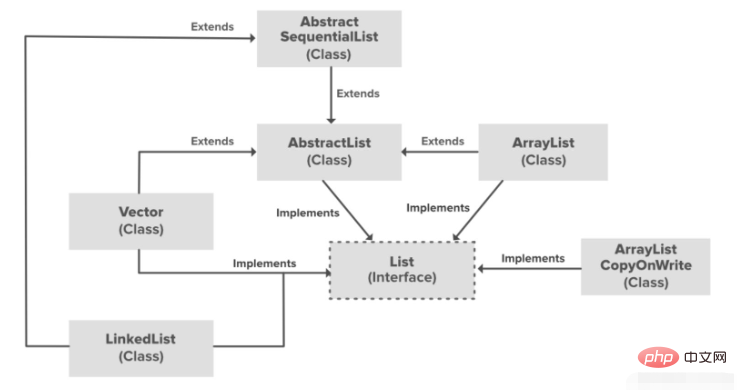
Linked List is part of the Collection framework in the java.util package.
The implementation of LinkedList data structure, which is a linear data structure in which elements are not stored in consecutive positions , and each element is a separate object, Has data part and address part.
Elements are linked using pointers and addresses. Each element is called a node
| Method | Description |
| add(int index, E element) | This method inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. |
| add(E e) | This method appends the specified element to the end of this list. |
| addAll(int index, Collection c) | This method inserts all elements in the specified collection into this list, starting at the specified position. |
| addAll(Collection c) | This method appends all elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order they are returned by the iterator of the specified collection . |
| addFirst(E e) | This method inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list. |
| addLast(E e) | This method appends the specified element to the end of this list. |
| clear() | This method removes all elements from this list. |
| clone() | This method returns a shallow copy of this LinkedList. |
| contains(Object o) | This method returns true if this list contains the specified element. |
| descendingIterator() | This method returns an iterator of the elements in this deque in reverse order. |
| element() | This method retrieves but does not remove the head (first element) of this list. |
| get(int index) | This method returns the element at the specified position in this list. |
| getFirst() | This method returns the first element in this list. |
| getLast() | This method returns the last element in this list. |
| indexOf(Object o) | This method returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element . |
| lastIndexOf(Object o) | This method returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. |
| listIterator(int index) | This method returns a list iterator of the elements in this list (in appropriate order), starting at the specified position in the list. |
| offer(E e) | This method adds the specified element to the tail (last element) of this list. |
| offerFirst(E e) | This method inserts the specified element at the front of this list. |
| offerLast(E e) | This method inserts the specified element at the end of this list. |
| peek() | This method retrieves but does not remove the head (first element) of this list. |
| peekFirst() | This method retrieves but does not delete the first element of this list, or returns null if this list is empty. |
| peekLast() | This method retrieves but does not delete the last element of this list, or returns null if this list is empty. |
| poll() | This method retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. |
| pollFirst() | This method retrieves and removes the first element of this list, or returns null if this list is empty. |
| pollLast() | This method retrieves and removes the last element of this list, or returns null if this list is empty. |
| pop() | This method pops an element from the stack represented by this list. |
| push(E e) | This method pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. |
| remove() | This method retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. |
| remove(int index) | This method removes the element at the specified position in this list. |
| remove(Object o) | This method removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, if it exists. |
| removeFirst() | This method removes and returns the first element from the list. |
| removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) | This method removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this list (when traversing the list from beginning to end). |
| removeLast() | This method removes and returns the last element from the list. |
| removeLastOccurrence(Object o) | This method removes the last occurrence of the specified element in this list (when the list is traversed from beginning to end). |
| set(int index, E element) | This method replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the specified element. |
| size() | This method returns the number of elements in this list. |
| spliterator() | This method creates a late-bound and fail-fast Spliterator on the elements in this list. |
| toArray() | This method returns an array containing all the elements in this list in correct order (from the first element to the last element). |
| toArray(T[] a) | This method returns an array containing this list in correct order (from first element to last element) all elements of the returned array; the runtime type of the returned array is the type of the specified array. |
| toString() | This method returns a string containing all the elements in this list in the correct order (from the first element to the last element) , each element is separated by commas, and the string is enclosed in square brackets. |
public class T1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> ll = new LinkedList<String>();
ll.add("B");
ll.addLast("C");
ll.addFirst("D");
ll.add(2, "E");
System.out.println(ll);
}
}[D, B, E, C]
The above is the detailed content of How to implement LinkedList data structure in Java?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




