
The object can obtain its class through reflection, and the class can obtain all methods (including Private) Through the reflection mechanism in the java language, bytecode files can be operated, and bytecode files can be read and modified.
You only need to know the class name, and the instance code will be used when loading JDBC
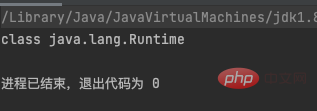
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class name = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
Use .class to get the object
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> name = Runtime.class;
System.out.println(name);
}
}getClass to get the bytecode object, you must be clear about the specific class, and then create the object
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
Class<?> name = rt.getClass();
System.out.println(name);
}
}This method is similar to forName, as long as there is a class name, but the difference is that the static JVM of forName The class will be loaded and the code in static() will be executed
public class getSystemClassLoader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> name = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass("java.lang.Runtime");
System.out.println(name);
}
}Returns all methods declared by the class or interface, including public , protected, private and default methods, but does not include inherited methods
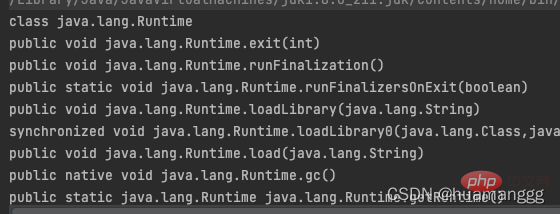
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class getDeclaredMethods {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> name = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
System.out.println(name);
Method[] m = name.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method x:m)
System.out.println(x);
}
}
Gets a specific method, the first parameter is the method name. The second parameter is the class object corresponding to the parameter of the method. For example, the exec method parameter of Runtime here is a String, so the second parameter here is String.class
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class getDeclaredMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class<?> name = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Method m = name.getDeclaredMethod("exec",String.class);
System.out.println(m);
}
}Return all public methods of a class, including public methods of inherited classes
The parameters are the same as getDeclaredMethod
Similar to the methods of Method
Gets all variable arrays of members of the class, but does not include those of the parent class
Get specific, the parameter is the name of the desired method
Similarly, you can only get public, But it includes the parent class
Similarly, the parameter is the name of the desired method
Constructor[] getConstructors(): Returns only public constructors
Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors(): Returns all constructors
Constructor<> getConstructor(class... parameterTypes): matches the public constructor that matches the parameter type
Constructor<> getDeclaredConstructor(class... parameterTypes ): Match the constructor that matches the parameter type
The parameters of the latter two methods are class objects of the type of the method parameters, similar to the one of Method, for example String.class
You can generate instantiated objects through reflection. Generally, we use newInstance()# of the Class object. ##Method to create a class object
Class c = Class.forName("com.reflect.MethodTest"); // 创建Class对象
Object m1 = c.newInstance(); // 创建类对象public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
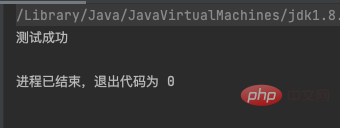
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Invoke {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
Class c = Class.forName("Invoke");
Object o = c.newInstance();
Method m = c.getMethod("test");
m.invoke(o);
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("测试成功");
}
}
Method.invoke (class or class object)First forName gets the Class, then newInstance gets the class object, then getMethod gets the method, and then calls Runtime rce example (access restriction breakthrough)There is an exec method in the Runtime class, which can execute the command
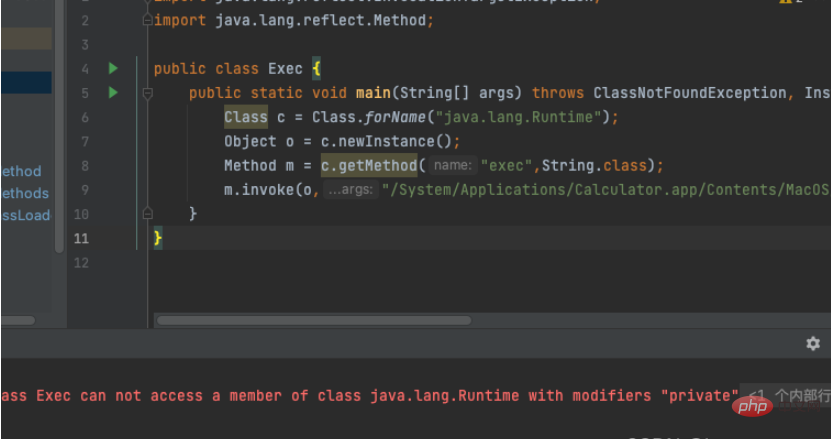
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Exec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Object o = c.newInstance();
Method m = c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
m.invoke(o,"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator");
}
}
setAccessible(true);, use this to break through access restrictions
Java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject类是Field,Method和Constructor类对象的基类,可以提供将反射对象标记为使用它抑制摸人Java访问控制检查的功能,同时上述的反射类中的Field,Method和Constructor继承自AccessibleObject。所以我们在这些类方法基础上调用setAccessible()方法,既可对这些私有字段进行操作
简单来说,私有的属性、方法、构造方法,可以通过这个去突破限制,xxx.setAccessible(true) 可以看到Runtime的构造方法是private的
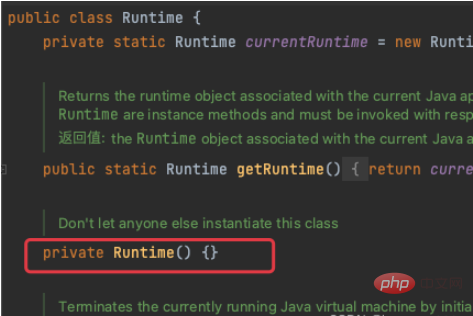
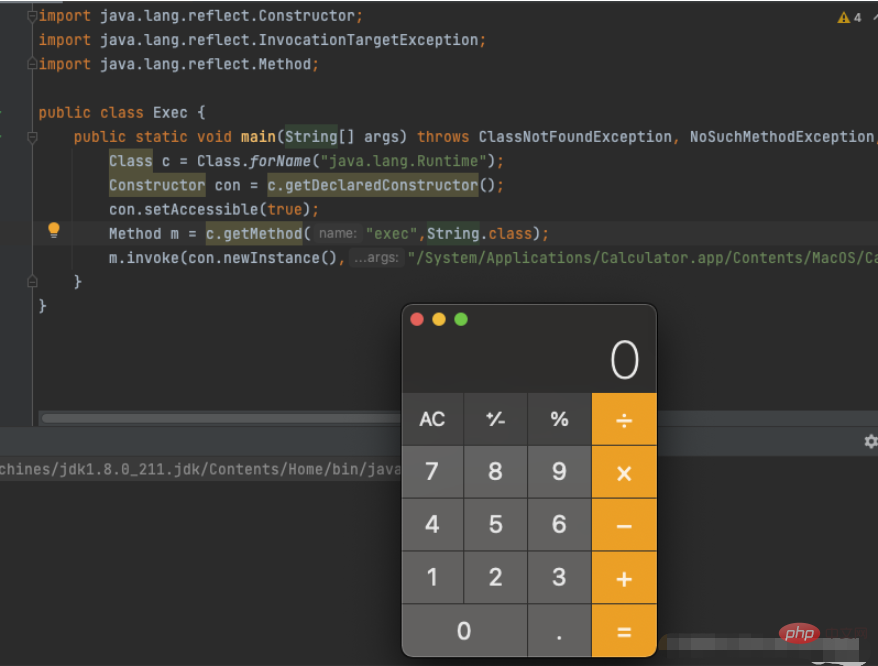
那么这里我们就可以这么去突破限制 先获取构造方法,然后setAccessible获取访问权限 然后再最后invoke里面,第一个参数写成con.newInstance()
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Exec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Constructor con = c.getDeclaredConstructor();
con.setAccessible(true);
Method m = c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
m.invoke(con.newInstance(),"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator");
}
}
这里有一个疑问,如果把con.newInstance单独提取出来,他打开计算器不会显示出来,但是后台的确是启动了,不知道啥原因
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Exec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Class c = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Constructor con = c.getDeclaredConstructor();
con.setAccessible(true);
Object o = con.newInstance();
Method m = c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
m.invoke(o,"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator");
}
}反射中常用的几个重要方法:
获取类的⽅法: forName
实例化类对象的⽅法: newInstance
获取函数的⽅法: getMethod
执⾏函数的⽅法: invoke
限制突破方法:setAccessible
The above is the detailed content of How to use Java reflection and analysis of examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




