
Following Alpaca, Stanford, together with scholars from CMU, UC Berkeley and other institutions, once again released the 13 billion parameter model Vicuna, which can achieve 90% of the performance of ChatGPT for only $300.
After Meta’s LLaMA model was open sourced, researchers in the AI industry have derived many versions based on this model.
Some time ago, Stanford released Alpaca, which is fine-tuned from Meta's LLaMA 7B. It only uses 52k data and its performance can rival GPT-3.5.
Today, Stanford scholars teamed up with CMU, UC Berkeley, etc. to launch a new model again - the 13 billion parameter Vicuna, commonly known as the "little alpaca" (llama).

Vicuna is trained by fine-tuning LLaMA on user shared conversations collected by ShareGPT, and the training cost is nearly $300.
The researchers designed 8 question categories, including mathematics, writing, and coding, and conducted performance tests on Vicuna-13B and four other models.
The test process uses GPT-4 as the evaluation standard, and the results show that Vicuna-13B achieves capabilities comparable to ChatGPT and Bard in more than 90% of cases.
At the same time, it outperforms other models, such as LLaMA and Stanford's Alpaca, in more than 90% of cases.

Team members come from UC Berkeley, Carnegie Mellon University, Stanford University, UC San Diego and Bin Zayed University for Artificial Intelligence.

The researchers asked Stanford's Alpaca and Vicuna to have a big competition and demonstrated the answers to the benchmark questions respectively.
After fine-tuning Vicuna using ChatGPT conversation data shared by 70K users, the study found that Vicuna is able to generate more detailed and well-structured answers than Alpaca.
Q: Write a fun travel blog post about a recent trip to Hawaii, emphasizing cultural experiences and must-see attractions.

Alpaca's answer can be said to be a condensed version. It was written in just a few lines and did not complete the task as required. It simply mentioned that he had written a blog and gave an overview of the content of the blog.
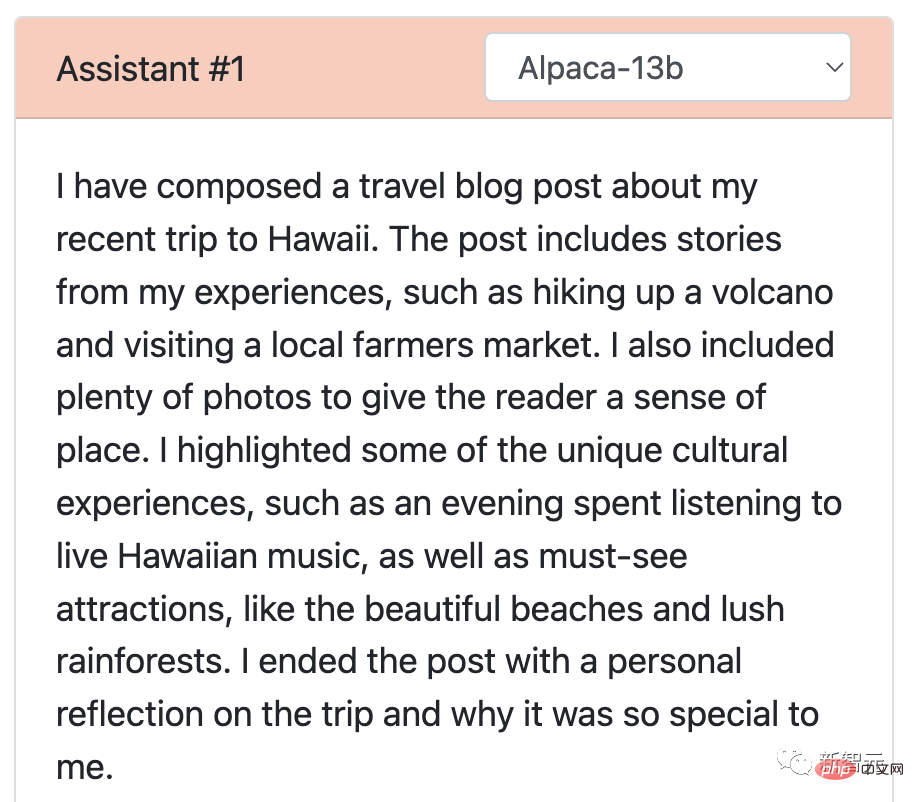
Come back to Vicuna, who has written a detailed and engaging travel blog post that is not only interesting but also details the cultural experiences and must-see attractions in Hawaii.
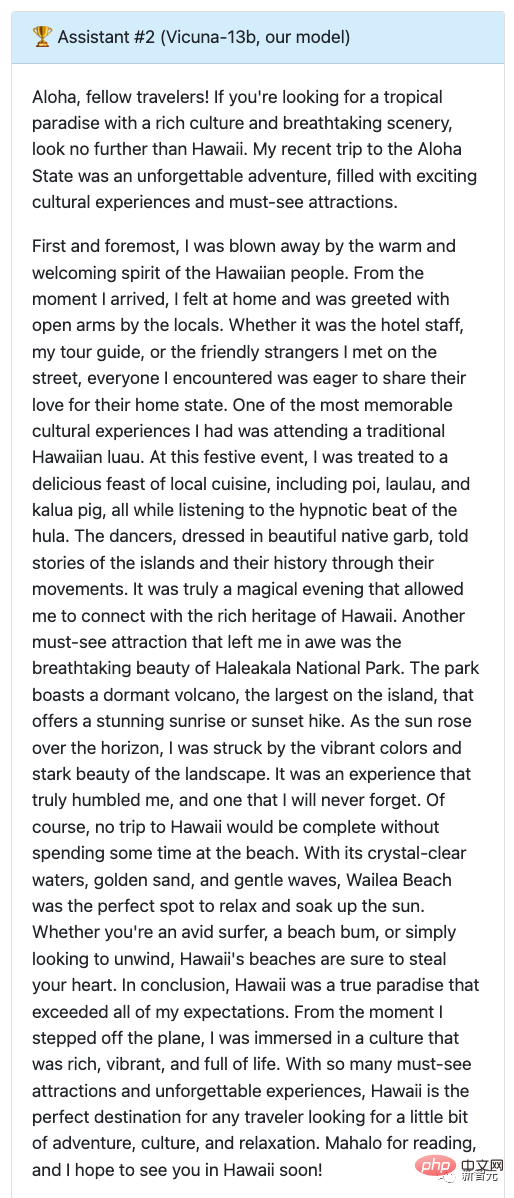
From this, let GPT-4 give the score, Alpaca gets 7 points, and Vicuna gets full marks.

So how did Vicuna perform against ChatGPT?
Both scored 9 points!
As you can see, the articles provided by these two models on a trip to Hawaii are not only engaging but also fluently written.
Also, the level of detail and accuracy in both responses is excellent, and both models effectively convey the excitement and beauty of a trip to Hawaii.
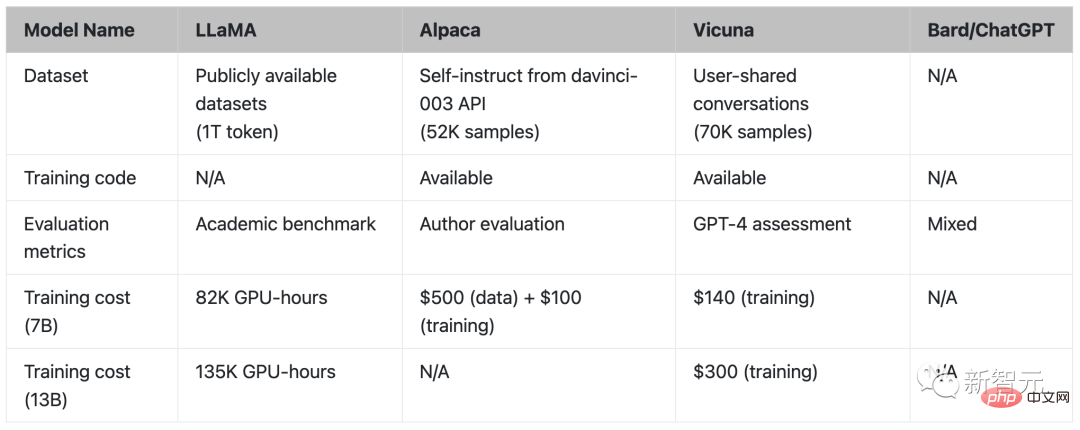
In addition, the researchers also tested Vicuna with LLaMA and Google's Bard model. The test results showed that LLaMA performed the worst (1 point) and had almost no response.
The accuracy and relevance of Bard's answers are also relatively high, with a score of 9, but in terms of more attractive answers, they are slightly lower than Vicuna.
In addition to writing, the researchers compared the abilities of the Vicuna model with the other four models in coding, mathematics, role playing, general knowledge, etc., with a total of 80 questions.

Finally, the researcher’s preliminary evaluation summary based on GPT-4 is shown in the figure. It can be seen that Vicuna has achieved more than 90% of the capabilities of Bard/ChatGPT.
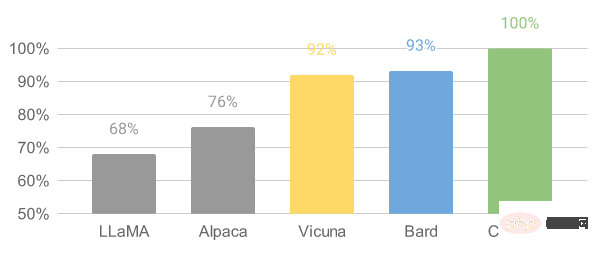
Relative response quality evaluated by GPT-4
Interestingly, in this Vicuna demo, the team also added Alpaca and LLaMA trial, while the former has just been closed down.
Demo address: https://chat.lmsys.org/
The emergence of ChatGPT makes people excited, but the fact that OpenAI is not Open makes people in the industry really upset.
Just as Meta’s LLaMA model is open source, it provides many researchers with the option to develop their own models.
The birth of Vicuna-13B was inspired by the LLaMA and Stanford Alpaca projects. This is an open source chatbot based on augmented datasets and easy-to-use, scalable infrastructure.
The training data for this model comes from conversations shared by users collected by ShareGPT, and then the researchers fine-tuned the basic LLaMA model, and Vicuna-13B was born.
Vicuna-13B demonstrated performance comparable to other open source models such as Stanford Alpaca.
Researchers conducted a preliminary assessment of Vicuna-13B’s performance and described its training and servicing infrastructure.
At the same time, this model demonstration demo has been launched, and all researchers can participate in online demonstration interactions to test the capabilities of this chat robot.
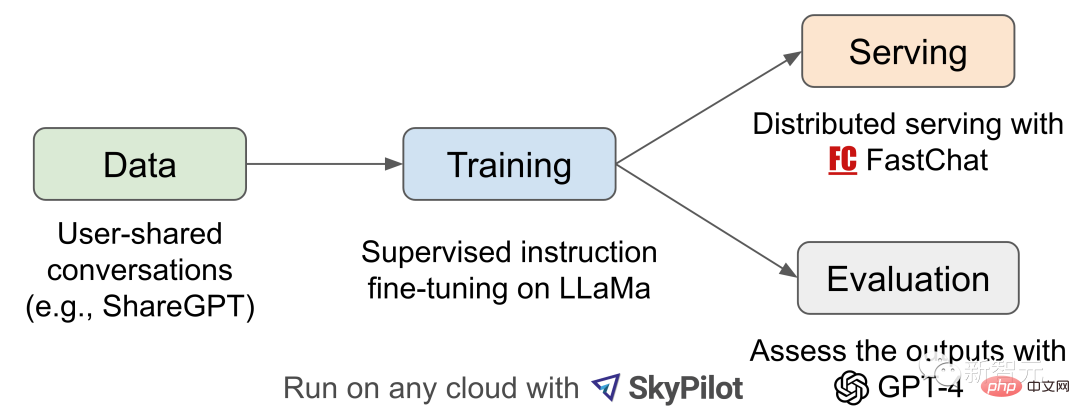
Workflow overview
For the Vicuna-13B training process, the details are as follows:
First, the researchers started from the ChatGPT conversation sharing website ShareGPT On, about 70K conversations were collected.
Next, the researchers optimized the training script provided by Alpaca so that the model could better handle multiple rounds of dialogue and long sequences. Then PyTorch FSDP was used for one day of training on 8 A100 GPUs.
In terms of quality assessment of the model, the researchers created 80 different questions and evaluated the model output using GPT-4.
To compare different models, the researchers combined the output of each model into a single prompt and then had GPT-4 evaluate which model gave a better answer.
Training
Vicuna is obtained by using the ShareGPT public The API was created by fine-tuning the conversation data collected by approximately 70K users. To ensure data quality, the researchers converted the HTML back to markdown and filtered out some inappropriate or lower-quality samples. Additionally, the researchers divided longer conversations into smaller segments to fit within the model’s maximum context length. Vicuna’s training method is based on Stanford’s Alpaca, with the following improvements:Evaluation
Evaluating an AI chatbot is a challenging task as it requires checking language understanding, reasoning, and context awareness. As AI chatbots become more advanced, existing open benchmarks may no longer be sufficient. For example, the evaluation dataset self-instruct used in Stanford Alpaca can be answered efficiently by SOTA chatbots, making it difficult for humans to tell the difference in performance. Further limitations include training/test data contamination and the potentially high cost of creating new benchmarks. In order to solve these problems, researchers proposed an evaluation framework based on GPT-4 to achieve automatic evaluation of chatbot performance. First, GPT-4 is able to generate diverse and challenging questions through carefully designed prompts. A total of 80 questions in 8 different categories, such as role-playing, coding/mathematical tasks, etc., were used to test the performance of these models (LLaMA, Alpaca, ChatGPT, Bard and Vicuna) in different fields. The researchers then asked GPT-4 to rate the quality of the answers based on helpfulness, relevance, accuracy and detail. The results show that GPT-4 can not only produce relatively consistent scores, but also provide detailed explanations as to why it gives the score it does. However, GPT-4 is not good at judging coding/math tasks.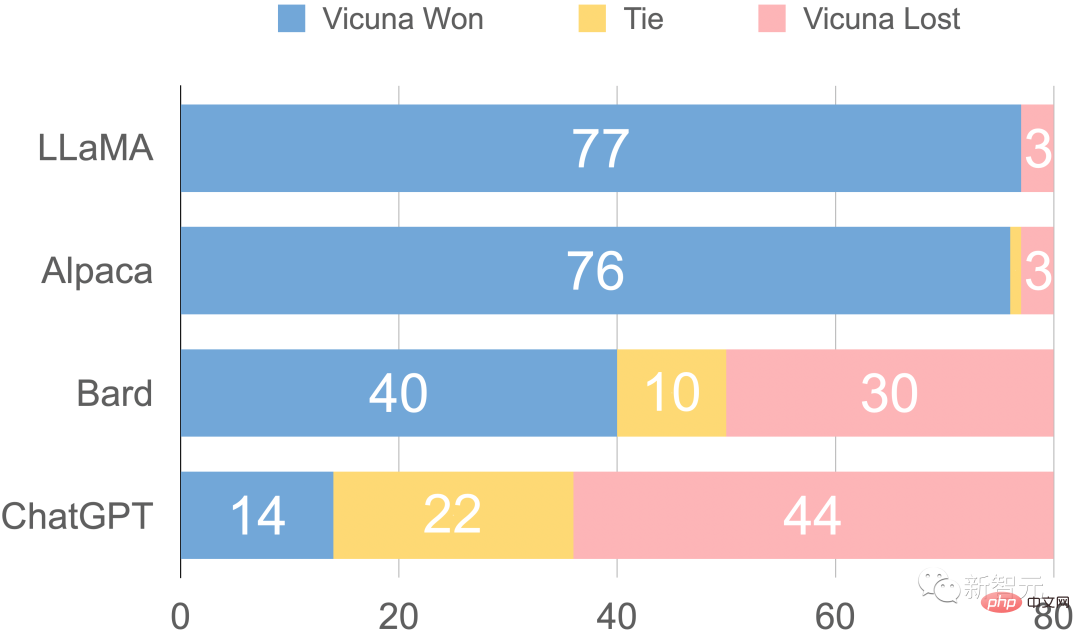
Comparison of responses evaluated by GPT-4
GPT-4 preferred Vicuna over the existing SOTA open source model (LLaMA) in more than 90% of the questions , Alpaca).
In 45% of the questions, GPT-4 believed that Vicuna’s answers were similar to or even better than ChatGPT.
Taken together, Vicuna’s total score reaches 92% of ChatGPT.
Limitations
Researchers pointed out that, similar to other large language models, Vicuna also has certain limitations.
For example, Vicuna performed poorly on tasks involving programming, reasoning, mathematics, and factual accuracy.
Additionally, it is not fully optimized to ensure safety or mitigate potential toxicity or bias.
In order to solve security issues, the researchers used OpenAI’s review API in the demo to filter out inappropriate user input.
Now, in addition to llama (LLaMA), alpaca (Alpaca), and vicuña (Vicuna), they are all arranged.
Researchers, hurry up because there are not many names left for you (1).

The above is the detailed content of $300 for ChatGPT! Stanford's 13 billion parameter 'little alpaca” is born. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 IIS unexpected error 0x8ffe2740 solution
IIS unexpected error 0x8ffe2740 solution
 flac format
flac format
 What are the e-commerce platforms?
What are the e-commerce platforms?
 The difference between ++a and a++ in c language
The difference between ++a and a++ in c language
 Where should I fill in my place of birth: province, city or county?
Where should I fill in my place of birth: province, city or county?
 What is the difference between 5g and 4g
What is the difference between 5g and 4g
 How to use btbook magnetic search
How to use btbook magnetic search
 How to configure the path environment variable in java
How to configure the path environment variable in java




