
What is Clean Architecture? This article will take you through Clean Architecture and talk about how to implement Clean Architecture using Node.js. I hope it will be helpful to you!

Clean Architecture is a software architecture pattern proposed by Robert C. Martin to divide the system into layer to achieve separation of concerns, making the system easier to understand, maintain and expand. This architecture divides the system into four levels, from inside to outside: entity layer, use case layer, presentation layer, infrastructure (repository, framework, etc.).
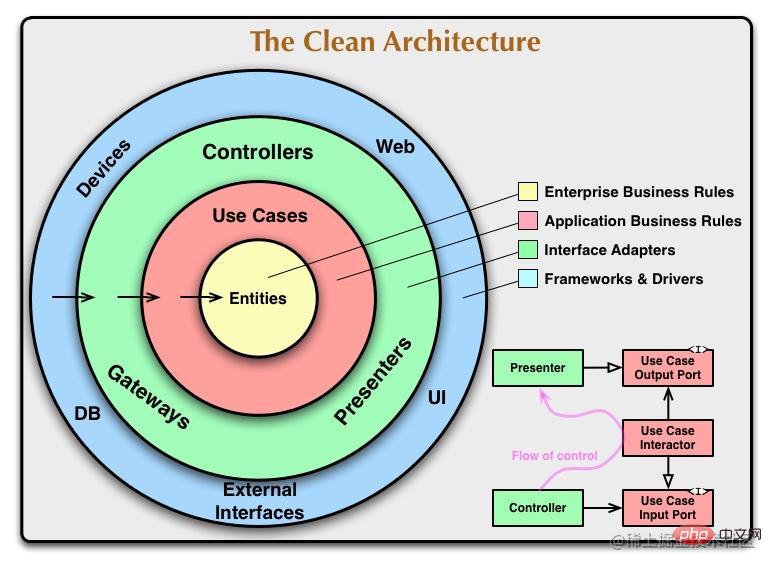
In this article, we will introduce how to implement Clean Architecture using Node.js and provide some sample code to demonstrate the key concepts of the architecture.
Next we will use the TypeScript project example (github.com/lulusir/cle…). The project uses a Monorepo structure and is managed using Rush.js. The server folder contains three sub-projects, namely core, koa and nestjs-app. Core is the core business logic, koa uses koa prisma as the underlying framework web project, and nestjs-app uses nestjs typeorm as the underlying framework. s project. The purpose is to demonstrate how the same business logic can bridge different frameworks. [Related tutorial recommendations: nodejs video tutorial, Programming teaching]
In this project, the entity layer contains entity objects and related business rules and logic, and the use case layer Contains the use cases and business logic of the system, the repository layer is responsible for saving and retrieving data, and the presentation layer is the http interface exposed to the outside.
Realize a post publishing and browsing function
User creation and query
Publish, edit, query, delete posts
├── server │ ├── core // 核心业务逻辑 │ │ └── src │ │ ├── domain │ │ ├── repository │ │ └── useCase │ ├── koa │ │ └── src │ │ ├── post │ │ └── user │ └── nestjs-app │ ├── src │ ├── post │ │ ├── dto │ │ └── entities │ └── user │ └── entities └── web
core: core is the code of the core business logic
At the koa/nestjs-app level, we have actual consumers at the core level. They implement specific routers and repositories based on the interfaces provided by the core layer. One of the main advantages of using Clean Architecture is that it separates business logic from technical implementation. This means you can easily switch between different frameworks and libraries without changing the core business logic. In our example, we can switch between koa and nestjs-app while keeping the same core business logic.
Code implementation// server/core/src/domain/post.ts
import { User } from "./user";
export class Post {
author: User | null = null;
content: string = "";
updateAt: Date = new Date(); // timestamp;
createdAt: Date = new Date(); // timestamp;
title: string = "";
id: number = -1;
}
// server/core/src/domain/user.ts
export class User {
name: string = ''
email: string = ''
id: number = -1
}import { Post } from "../domain/post";
export interface IPostRepository {
create(post: Post): Promise<boolean>;
find(id: number): Promise<Post>;
update(post: Post): Promise<boolean>;
delete(post: Post): Promise<boolean>;
findMany(options: { authorId: number }): Promise<Post[]>;
}
...
import { User } from "../domain/user";
export interface IUserRepository {
create(user: User): Promise<boolean>;
find(id: number): Promise<User>;
}import { User } from "../domain/user";
import { IUserRepository } from "../repository/user";
export class UCUser {
constructor(public userRepo: IUserRepository) {}
find(id: number) {
return this.userRepo.find(id);
}
create(name: string, email: string) {
if (email.includes("@test.com")) {
const user = new User();
user.email = email;
user.name = name;
return this.userRepo.create(user);
}
throw Error("Please use legal email");
}
}// server/koa/src/user/user.repo.ts
import { PrismaClient } from "@prisma/client";
import { IUserRepository, User } from "core";
export class UserRepository implements IUserRepository {
prisma = new PrismaClient();
async create(user: User): Promise<boolean> {
const d = await this.prisma.user_orm_entity.create({
data: {
email: user.email,
name: user.name,
},
});
return !!d;
}
async find(id: number): Promise<User> {
const d = await this.prisma.user_orm_entity.findFirst({
where: {
id: id,
},
});
if (d) {
const u = new User();
u.email = d?.email;
u.id = d?.id;
u.name = d?.name;
return u;
}
throw Error("user id " + id + "not found");
}
}// server/koa/src/user/user.controller.ts
import Router from "@koa/router";
import { UCUser } from "core";
import { UserRepository } from "./user.repo";
export const userRouter = new Router({
prefix: "/user",
});
userRouter.get("/:id", async (ctx, next) => {
try {
const service = new UCUser(new UserRepository());
if (ctx.params.id) {
const u = await service.find(+ctx.params.id);
ctx.response.body = JSON.stringify(u);
}
} catch (e) {
ctx.throw(400, "some error on get user", e.message);
}
await next();
});I won’t post the code here Please note that in the actual project, we will not put the core business logic in a separate warehouse (i.e. core), this is just to demonstrate the performance under different frameworks Use the same business logic By decoupling business logic from the framework, you can easily switch between different frameworks and libraries without changing the core business logic. If you want to build scalable and maintainable applications, Clean Architecture is definitely worth considering. If you want to demonstrate how to connect to other frameworks, you can put forward the project address in the comment area (github.com/lulusir/cle... I think it’s a good idea, You can give a star, thank you For more node-related knowledge, please visit:nodejs tutorial!Finally
The above is the detailed content of What is Clean Architecture? How to implement it with Node?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!