
Javascript supports variable length parameters. Two methods to implement variable-length parameters: 1. Use the arguments object. The length of the arguments object is determined by the number of actual parameters rather than the number of formal parameters; when both arguments and values exist, the two values are synchronized. , but for one of the null cases, the value will not be synchronized for this null case. 2. Rest parameter means accepting redundant parameters and putting them into an array. The syntax is "...variable name".

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, javascript version 1.8.5, Dell G3 computer.
Javascript supports variable length parameters.
Implementation of JS variable length parameters (variable parameters) 1: arguments
What are arguments? How to implement variable parameters?
arguments is an array-like object corresponding to the arguments passed to the function.
In ES5, you can use the arguments object to implement variable parameters.
The length of the arguments object is determined by the number of actual parameters rather than the number of formal parameters. Formal parameters are variables that are re-opened in memory space within the function, but they do not overlap with the memory space of the arguments object. When both arguments and values exist, the two values are synchronized, but when one of them has no value, the value will not be synchronized for this valueless case.
The parameters are not sure, so just don’t write them down.
You can write N multiple parameters when calling, or you can pass an array directly.
Execution effect:
Summary:
1. It can be seen from the function definition , if variable parameters arguments are used in the function, there is no need to write formal parameters
2. When calling a function, multiple actual parameters
arguments objects can be passed directly to the function are local variables available in all (non-arrow) functions. You can use the arguments object to reference a function's arguments within a function. This object contains each argument passed to the function, with the first argument at index 0. For example, if a function is passed three arguments, you can reference them like this:
arguments[0] arguments[1] arguments[2]
Parameters can also be set:
arguments[0] = 'value';
argumentsis an object,is not anArray. It is similar toArray, but does not have anyArrayproperties except the length attribute and the index element. For example, it has no pop method. But it can be converted to a realArray:
So you can often see code like this:
// 由于arguments不是 Array,所以无法使用 Array 的方法,所以通过这种方法转换为数组 var args = [].slice.call(arguments); // 方式一 var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments); // 方式二 // 下面是 es6 提供的语法 let args = Array.from(arguments) // 方式一 let args = [...arguments]; // 方式二
arguments# Properties on
rguments.callee())arguments combined with remaining parameters, default parameters and destructed assignment parameters
1) in strict In mode, the existence of remaining parameters, default parameters and destructed assignment parameters will not change the behavior of theargumentsobject, but it is different in non-strict mode
function func(a) { arguments[0] = 99; // 更新了arguments[0] 同样更新了a console.log(a); } func(10); // 99 // 并且 function func(a) { a = 99; // 更新了a 同样更新了arguments[0] console.log(arguments[0]); } func(10); // 99
do notcontain remaining parameters, default parameters, and destructuring assignments, then the value in theargumentsobjectwilltrack the value of the parameter (and vice versa) . Look at the following code:
function func(a = 55) { arguments[0] = 99; // updating arguments[0] does not also update a console.log(a); } func(10); // 10 // function func(a = 55) { a = 99; // updating a does not also update arguments[0] console.log(arguments[0]); } func(10); // 10 function func(a = 55) { console.log(arguments[0]); } func(); // undefined
...variable name) is introduced in to obtain the redundant parameters of the function. The variable matched with the rest parameter is an array, which puts the extra parameters into the array. Very suitable for dealing with variable length parameters.
Implementation syntax of variable parameters:
function f(a, b, ...theArgs) { // ... }
Note:There cannot be any other parameters after the rest parameter (that is, it can only be the last parameter), otherwise an error will be reported.
function f(arg1, ...rest, arg2) { // arg2 after ...rest ?! // error }
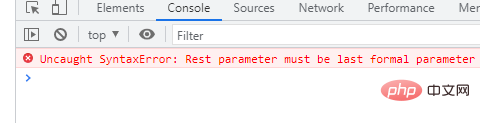
Distinguish between rest parameters and parameter (arguments) objects
rest参数不会为每个变量给一个单独的名称,参数对象包含所有参数传递给函数
参数对象不是真正的数组,rest参数是真实的数组实例。例如数组sort、map、forEach、pop的方法都可以直接使用
参数对象有他自己额外的特性(例如callee 属性)
Rest参数的引入减少样式代码
//以前函数 function f(a, b) { var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, f.length); // … } // 等效于现在 function f(a, b, ...args) { }
Rest参数可以被解构(通俗一点,将rest参数的数据解析后一一对应)不要忘记参数用[] 括起来,因为它数组嘛
function f(...[a, b, c]) { return a + b + c; } f(1) //NaN 因为只传递一个值,其实需要三个值 f(1, 2, 3) // 6 f(1, 2, 3, 4) // 6 (第四值没有与之对应的变量名)
示例
1、计算参数和
function sumAll(...args) { // args 是数组的名称 let sum = 0; for (let arg of args) sum += arg; return sum; } console.log( sumAll(1) ); // 1 console.log( sumAll(1, 2) ); // 3 console.log( sumAll(1, 2, 3) ); // 6
2、每个参数乘以2
function multiply(multiplier, ...theArgs) { return theArgs.map(function(element) { return multiplier * element; }); } var arr = multiply(2, 1, 2, 3); console.log(arr); // [2, 4, 6]
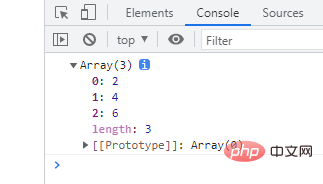
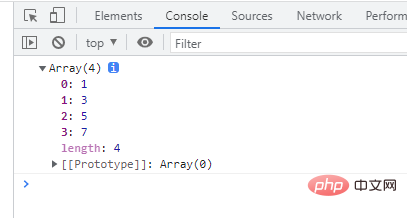
3、排序
function sortRestArgs(...theArgs) { var sortedArgs = theArgs.sort(); return sortedArgs; } //好像一位和两位混合不能进行排序,这需要看一下为甚?主要第一个为主 console.log(sortRestArgs(5, 3, 7, 1)); // shows 1, 3, 5, 7
对比:参数对象arguments不能排序
function sortArguments() { //arguments是参数对象不能直接使用sort()方法,因为不是数组实例,需要转换 var sortedArgs = arguments.sort(); return sortedArgs; // this will never happen } // 会抛出类型异常,arguments.sort不是函数 console.log(sortArguments(5, 3, 7, 1));
【相关推荐:javascript学习教程、编程视频】
The above is the detailed content of Does javascript support variable length parameters?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!