 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What is the statement to modify permissions in Linux?
What is the statement to modify permissions in Linux?
What is the statement to modify permissions in Linux?
The statement to modify permissions in Linux is "chmod [-R] permission value file or directory name"; this statement can modify the permissions of the specified file. The chmod command is a command to control the user's permissions on the file. The setting of permissions Methods can use text or numerical codes; file calling permissions can be divided into file owners, user groups and other users.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is the statement to modify permissions in Linux
Linux chmod (full English spelling: change mode) command is a command to control user permissions on files
Linux/Unix files The calling permissions are divided into three levels: file owner (Owner), user group (Group), and other users (Other Users).
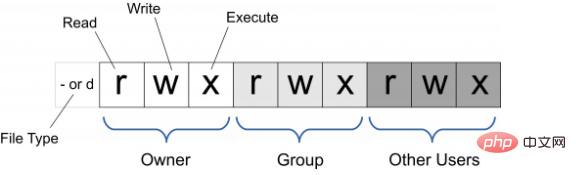
Only the file owner and superuser can modify the permissions of a file or directory. You can use absolute mode (octal number mode) and symbolic mode to specify file permissions.
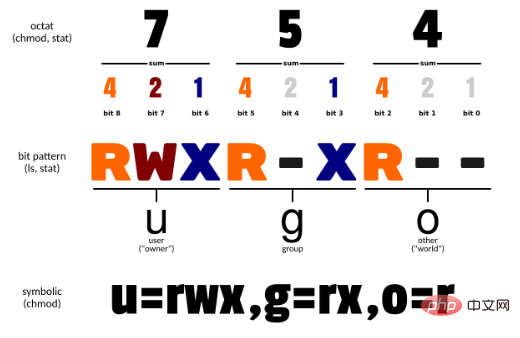
Usage permissions: all users
Syntax
chmod [-cfvR] [--help] [--version] mode file...
Parameter description
mode: permission setting string , the format is as follows:
[ugoa...][[ -=][rwxX]...][,...]
where:
u means The owner of the file, g represents the person who belongs to the same group as the owner of the file, o represents other people, and a represents all three.
means adding permissions, - means canceling permissions, = means setting only permissions.
r means readable, w means writable, x means executable, and X means only when the file is a subdirectory or the file has been set to be executable.
Other parameter descriptions:
-c: If the file permissions have indeed been changed, the change action will be displayed
-f: If the file permissions cannot be changed, do not Display error message
-v: Display detailed information about permission changes
-R: Make the same permission changes to all files and subdirectories in the current directory (that is, change them one by one recursively) )
--help: Display auxiliary instructions
--version: Display version
The example is as follows:
Set the file file1.txt to everyone Readable by all:
chmod ugo+r file1.txt
Set the file file1.txt to be readable by everyone:
chmod a+r file1.txt
Set the files file1.txt and file2.txt as the owner of the file, and with them People who belong to the same group can write, but others cannot write:
chmod ug+w,o-w file1.txt file2.txt
Recommended learning: Linux video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of What is the statement to modify permissions in Linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to install software on Linux using the terminal?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:58 PM
How to install software on Linux using the terminal?
Aug 02, 2025 pm 12:58 PM
There are three main ways to install software on Linux: 1. Use a package manager, such as apt, dnf or pacman, and then execute the install command after updating the source, such as sudoaptininstallcurl; 2. For .deb or .rpm files, use dpkg or rpm commands to install, and repair dependencies when needed; 3. Use snap or flatpak to install applications across platforms, such as sudosnapinstall software name, which is suitable for users who are pursuing version updates. It is recommended to use the system's own package manager for better compatibility and performance.
 The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Gaming on Linux
Aug 03, 2025 am 05:51 AM
The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Gaming on Linux
Aug 03, 2025 am 05:51 AM
ChoosePop!_OS,Ubuntu,NobaraLinux,orArchLinuxforoptimalgamingperformancewithminimaloverhead.2.InstallofficialNVIDIAproprietarydriversforNVIDIAGPUs,ensureup-to-dateMesaandkernelversionsforAMDandIntelGPUs.3.EnabletheperformanceCPUgovernor,usealow-latenc
 What are the main pros and cons of Linux vs. Windows?
Aug 03, 2025 am 02:56 AM
What are the main pros and cons of Linux vs. Windows?
Aug 03, 2025 am 02:56 AM
Linux is suitable for old hardware, has high security and is customizable, but has weak software compatibility; Windows software is rich and easy to use, but has high resource utilization. 1. In terms of performance, Linux is lightweight and efficient, suitable for old devices; Windows has high hardware requirements. 2. In terms of software, Windows has wider compatibility, especially professional tools and games; Linux needs to use tools to run some software. 3. In terms of security, Linux permission management is stricter and updates are convenient; although Windows is protected, it is still vulnerable to attacks. 4. In terms of difficulty of use, the Linux learning curve is steep; Windows operation is intuitive. Choose according to requirements: choose Linux with performance and security, and choose Windows with compatibility and ease of use.
 Understanding RAID Configurations on a Linux Server
Aug 05, 2025 am 11:50 AM
Understanding RAID Configurations on a Linux Server
Aug 05, 2025 am 11:50 AM
RAIDimprovesstorageperformanceandreliabilityonLinuxserversthroughvariousconfigurations;RAID0offersspeedbutnoredundancy;RAID1providesmirroringforcriticaldatawith50�pacityloss;RAID5supportssingle-drivefailuretoleranceusingparityandrequiresatleastthre
 Linux how to enable and disable services at boot
Aug 08, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Linux how to enable and disable services at boot
Aug 08, 2025 am 10:23 AM
To manage the startup of Linux services, use the systemctl command. 1. Check the service status: systemctlstatus can check whether the service is running, enabled or disabled. 2. Enable the service startup: sudosystemctlenable, such as sudosystemctlenablenginx. If it is started at the same time, use sudosystemctlenable--nownginx. 3. Disable the service startup: sudosystemctldisable, such as sudosystemctldisablecups. If it is stopped at the same time, use sudosystemctldisabl
 Linux how to list all running processes
Aug 08, 2025 am 06:42 AM
Linux how to list all running processes
Aug 08, 2025 am 06:42 AM
Usepsauxforacompletesnapshotofallrunningprocesses,showingdetailedinformationlikeUSER,PID,CPU,andmemoryusage.2.Usetoporhtopforreal-timemonitoringofprocesseswithdynamicupdates,wherehtopoffersamoreintuitiveinterface.3.UsepgreporpidoftoquicklyfindthePIDs
 How to clean up your Linux system
Aug 22, 2025 am 07:42 AM
How to clean up your Linux system
Aug 22, 2025 am 07:42 AM
Removeunusedpackagesanddependencieswithsudoaptautoremove,cleanpackagecacheusingsudoaptcleanorautoclean,andremoveoldkernelsviasudoaptautoremove--purge.2.Clearsystemlogswithsudojournalctl--vacuum-time=7d,deletearchivedlogsin/var/log,andempty/tmpand/var
 Linux how to view the contents of a file
Aug 19, 2025 pm 06:44 PM
Linux how to view the contents of a file
Aug 19, 2025 pm 06:44 PM
ToviewfilecontentsinLinux,usedifferentcommandsbasedonyourneeds:1.Forsmallfiles,usecattodisplaytheentirecontentatonce,withcat-ntoshowlinenumbers.2.Forlargefiles,uselesstoscrollpagebypageorlinebyline,searchwith/search_term,andquitwithq.3.Usemoreforbasi






