
In Linux, x refers to "execution" permission. x permissions have different effects on files and directories: 1. For files, it means that the file can be run, especially shell script files, and has no effect on ordinary files; 2. For directories, it means that the user can enter the specified directory. Users granted x permissions can use the cd command to switch directories.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: CentOS 6 system, Dell G3 computer.
x refers to "execute" permission.
Linux system, there are three most common file permissions, namely read (represented by r), write (represented by w) and execute (represented by x, for executable files or directory) permissions.
x (execution) permissions have different effects on files and directories:
Function on files
| Execution permission (x) | indicates that the file has the permission to be executed by the system. In Windows systems, checking whether a file is an executable file is based on the extension (.exe, .bat, etc.), but in Linux systems, whether a file can be executed is determined by checking whether the file has x permissions. That is, as long as the file has x permissions, the file is executable. However, whether the file can run correctly depends on whether the code in the file is correct. |
Execution permission is mainly used for shell script files and has no effect on ordinary files.
The effect on the directory
| Execution permission (x) | The directory is If it cannot be run directly, granting x permissions to the directory means that the user can enter the directory. In other words, users or groups granted x permissions can use the cd command. |
Note:For a directory, if only r permission is granted, the directory cannot be used. It's very simple. For a directory with only r permissions, the user can only view the directory structure and cannot enter the directory at all (x permissions are required), let alone use it.
Note:
1. Read-only access to the directory does not allow using cd to enter the directory. You must have execution permissions to enter.
2. Only execution permissions can only enter the directory and cannot see the contents of the directory. If you want to see the file names and directory names in the directory, you need read permissions.
3. Whether a file can be deleted mainly depends on whether the directory where the file is located has write permission for the user. If the directory does not have write permission for the user, all files in the directory cannot be deleted. The file Except for the owner
4. The w permission of the directory is not set. Even if you have the w permission of a file in the directory, you cannot write to the file
The following is a detailed introduction:
1. File directory
For a file directory, the x permission is the permission to enter the directory
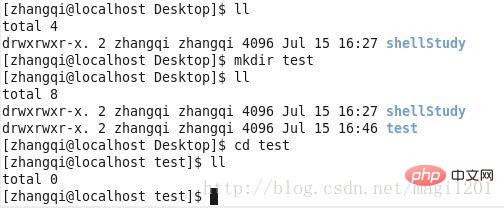
In the above picture, After creating the test directory, you can check that its permissions are drwxrwxr-x. Both the owner and the group have x permissions, so you can enter the test directory.
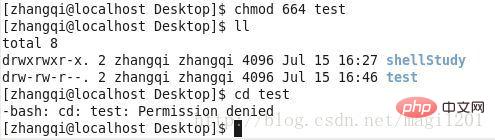
Next, we slightly modify the group permissions and only grant 664 permissions, that is, neither the owner nor the group has operation permissions. When trying to enter the test directory, permission problems will be reported
2. Ordinary files
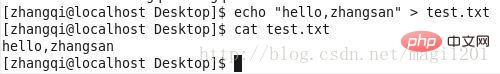
The executable permissions of ordinary files are of little significance at present, because there is no x permission and it does not affect the file. reading and writing.
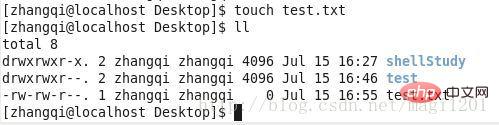
A test file test.txt is created here. You can see that the file does not have x permissions, but it does not affect file reading and writing
3. Shell script file
For shell scripts, without x permission, the script cannot be executed
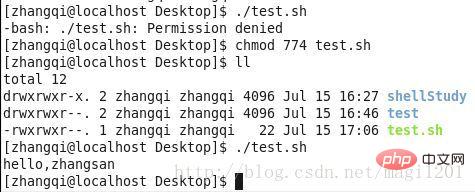
It should be noted here that there are other methods for script execution, which can be executed without x permissions, as follows
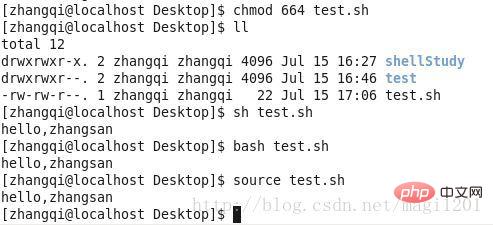
Related recommendations:《Linux video tutorial》
The above is the detailed content of What permissions are linux x. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!