
In Linux, the full name of d is "directory", which means "directory". It is an attribute that specifies the file type in file permissions; if the first attribute of a file is represented by "d", it means that the file is a directory file.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, Dell G3 computer.
Linux system is a typical multi-user system. Different users are in different positions and have different permissions.
In order to protect the security of the system, the Linux system has different regulations on the permissions of different users to access the same file (including directory files).
In Linux, we usually use the following two commands to modify the user and permissions of a file or directory:
chown (change owner): Modify the user and group to which it belongs. .
chmod (change mode): Modify user permissions.
In the figure below, chown is used to authorize the user, and chmod is used to set the permissions for the user to open the door.

In Linux we can use the ll or ls -l command to display the attributes of a file and the user and group to which the file belongs, such as:
[root@www /]# ls -l total 64 dr-xr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 14 2012 bin dr-xr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Apr 19 2012 boot ……
In the example, the first attribute of the bin file is represented by d. d In Linux, it means that the file is a directory file.
In Linux, the first character indicates whether the file is a directory, file, link file, etc.
When it is d, it is a directory
When it is -, it is a file ;
If it is l, it is represented as a link file;
If it is b It is represented as a storable interface device (random access device) in the installation file;
If it is c, it is represented as a serial port in the installation file Devices such as keyboard, mouse (disposable reading device).
The following characters are grouped into groups of three, and they are all combinations of the three parameters of rwx. Among them, r represents readable (read), w represents writable (write), and x represents executable (execute). It should be noted that the positions of these three permissions will not change. If there is no permission, the minus sign - will appear.
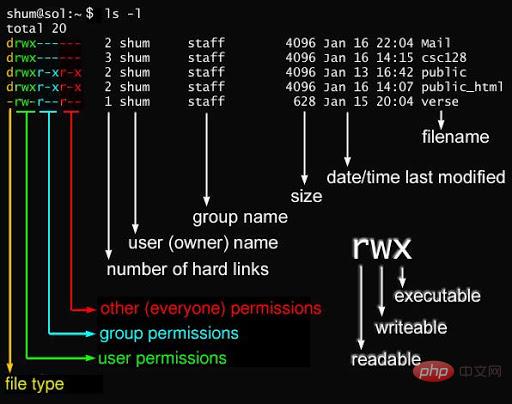
#The attributes of each file are determined by the 10 characters in the first part on the left (as shown below).

The numbers 0-9 are represented from left to right. The
bits 0 determine the file type, and the 1-3 bits determine the owner (the owner of the file) has the permissions of the file.
The 4-6 bits determine that the group (users in the same group of the owner) has the permissions of the file, and the 7-9 bits determine that other users have the permissions of the file. File permissions.
Among them, the 1, 4, and 7 bits represent read permission. If it is represented by r characters, it has read permission. If it is represented by -## If represented by the # character, there is no read permission; the
bits represent write permission. If it is represented by the w character, there is write permission. If Use - characters to indicate that there is no write permission; bits 3, 6, and 9 indicate executable permission. If it is expressed with x characters, it means there is execution permission. If it is expressed with - characters indicate that there is no execution permission. Related recommendations: "
The above is the detailed content of What does linux d mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!