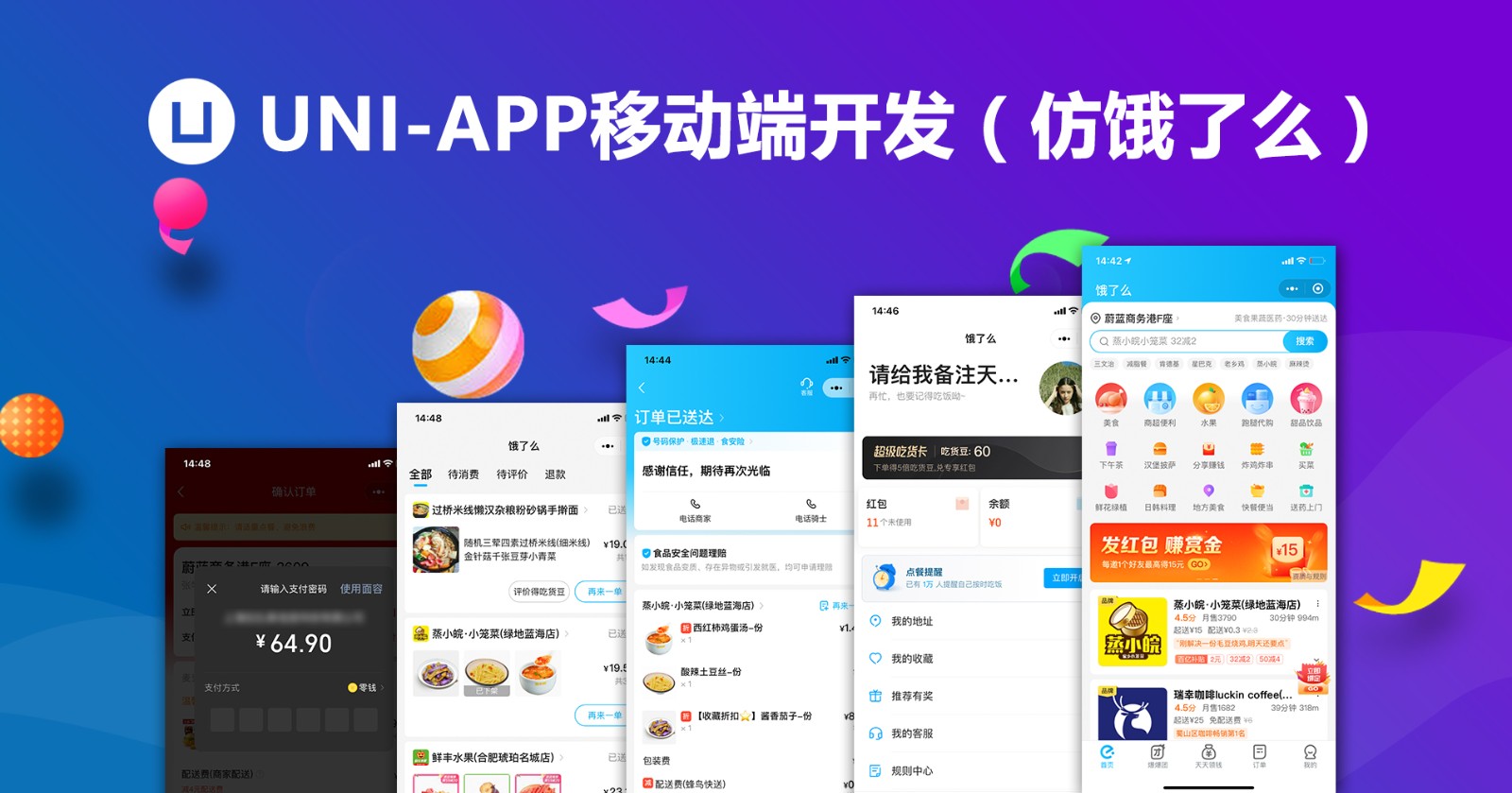
磁盘分区形式有两种:1、MBR(主启动记录)形式,它是存在于磁盘驱动器开始部分的一个特殊的启动扇区;2、GPT(GUID分区表)形式,它是一种使用UEFI启动的磁盘组织方式。

本教程操作环境:windows7系统、Dell G3电脑。
磁盘分区形式有两种MBR和GPT。
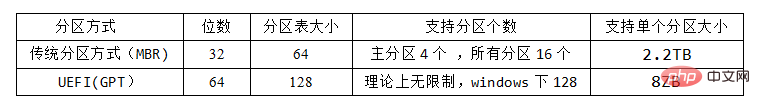
新买一块硬盘,设置分区时,系统会询问你是想要使用MBR分区形式还是GPT分区形式(有些硬盘出厂的时候就默认给你设定了分区形式)。MBR是以前的分区形式,GPT是一种新的分区形式,现在逐渐取代MBR分区形式。
MBR分区
MBR的意思是“主引导记录”,是IBM公司早年间提出的。它是存在于磁盘驱动器开始部分的一个特殊的启动扇区。这个扇区包含了已安装的操作系统系统信息,并用一小段代码来启动系统。如果你安装了Windows,其启动信息就放在这一段代码中——如果MBR的信息损坏或误删就不能正常启动Windows,这时候你就需要找一个引导修复软件工具来修复它就可以了。Linux系统中MBR通常会是GRUB加载器。MBR。当一台电脑启动时,它会先启动主板自带的BIOS系统,bios加载MBR,MBR再启动Windows,这就是mbr的启动过程。
GPT分区
GPT的意思是GUID Partition Table,即“全局唯一标识磁盘分区表”。他是另外一种更加先进新颖的磁盘组织方式,一种使用UEFI启动的磁盘组织方式。最开始是为了更好的兼容性,后来因为其更大的支持内存(mbr分区最多支持2T的磁盘),更多的兼容而被广泛使用,特别是苹果的MAC系统全部使用gpt分区。gtp不在有分区的概念,所有CDEF盘都在一段信息中存储。可以简单的理解为更先进但是使用不够广泛的技术。
GPT带来了很多新特性,但MBR仍然拥有最好的兼容性。GPT并不是Windows专用的新标准—— Mac OS X,Linux,及其他操作系统同样使用GPT。在使用新磁盘之前,你必须对其进行分区。MBR(Master Boot Record)和GPT(GUID Partition Table)是在磁盘上存储分区信息的两种不同方式。这些分区信息包含了分区从哪里开始,这样操作系统才知道哪个扇区是属于哪个分区的,以及哪个分区是可以启动的。在磁盘上创建分区时,你必须在MBR和GPT之间做出选择。目前有且只有这两种分区形式。
MBR的局限性
MBR的意思是“主引导记录”,最早在1983年在IBM PC DOS 2.0中提出。之所以叫“主引导记录”,是因为它是存在于驱动器开始部分的一个特殊的启动扇区。这个扇区包含了驱动器的分区信息(64个字节,大小固定,一个分区用16个字节记录)和已安装的操作系统的启动加载器(446字节)和2个字节的结束标志,所以这个扇区的大小是512个字节。。所谓启动加载器,是一小段代码,用于加载驱动器上其他分区上更大的加载器。如果你安装了Windows,Windows启动加载器的初始信息就放在这个区域里——如果MBR的信息被覆盖导致Windows不能启动,你就需要使用Windows的MBR修复功能来使其恢复正常。如果你安装了Linux,则位于MBR里的通常会是GRUB加载器。MBR支持最大2TB磁盘,它无法处理大于2TB容量的磁盘。MBR还只支持最多4个主分区——如果你想要更多分区,你需要创建所谓“扩展分区”,并在其中创建逻辑分区。MBR已经成为磁盘分区和启动的工业标准。
GPT的优势
GPT意为GUID分区表。(GUID意为全局唯一标识符)。这是一个正逐渐取代MBR的新标准。它和UEFI相辅相成——UEFI用于取代老旧的BIOS,而GPT则取代老旧的MBR。之所以叫作“GUID分区表”,是因为你的驱动器上的每个分区都有一个全局唯一的标识符(globally unique identifier,GUID)——这是一个随机生成的字符串,可以保证为地球上的每一个GPT分区都分配完全唯一的标识符。这个标准没有MBR的那些限制。磁盘驱动器容量可以大得多,大到操作系统和文件系统都没法支持。它同时还支持几乎无限个分区数量,限制只在于操作系统——Windows支持最多128个GPT分区,GPT硬盘上没有主分区、扩展分区的概念,所有的分区都是叫分区。在MBR磁盘上,分区和启动信息是保存在一起的。如果这部分数据被覆盖或破坏,事情就麻烦了。相对的,GPT在整个磁盘上保存多个这部分信息的副本,因此它更为健壮,并可以恢复被破坏的这部分信息。GPT还为这些信息保存了循环冗余校验码(CRC)以保证其完整和正确——如果数据被破坏,GPT会发觉这些破坏,并从磁盘上的其他地方进行恢复。而MBR则对这些问题无能为力——只有在问题出现后,你才会发现计算机无法启动,或者磁盘分区都不翼而飞了。
GPT的兼容性
可以看到,在GTP磁盘的第一个数据块中同样有一个与MBR(主引导记录)类似的标记,叫做PMBR(保护下MBR)。PMBR的作用是,当使用不支持GPT的分区工具时,整个硬盘将显示为一个受保护的分区,以防止分区表及硬盘数据遭到破坏。UEFI并不从PMBR中获取GPT磁盘的分区信息,它有自己的分区表,即GPT分区表。
主分区、扩展分区和逻辑分区
这几个名词是在MBR中才有的,因为GPT支持无限多个主分区。倘若你使用的是MBR的分区形式,那么你将最少拥有一个、最多只能有四个主分区;如果你想要有更多的分区,那么你将要建立扩展分区,然后在扩展分区里面在新建多个逻辑分区。且主分区+扩展分区的数量不超过四个;扩展分区可以没有,最多只能有一个;逻辑分区可以没有,也可以有多个。扩展分区不能包围在主分区之间。
激活的主分区是硬盘的启动分区,他是独立的,也是硬盘的第一个分区,正常分的话就是C驱。 分出主分区后,其余的部分可以分成扩展分区,一般是剩下的部分全部分成扩展分区,也可以不全分,那剩下的部分就浪费了。但扩展是不能直接用的,他是以逻辑分区的方式来使用的,所以说扩展分区可分成若干个逻辑分区。他们的关系是包含的关系,所有的逻辑分区都是扩展分区的一部分。 在linux中相当于hda分区。
硬盘的容量=主分区的容量+扩展分区的容量
扩展分区的容量=各个逻辑分区的容量之和
在MBR分区表中最多4个主分区或者3个主分区+1个扩展分区,也就是说扩展分区只能有一个,然后可以再细分为多个逻辑分区。
在Linux系统中,硬盘分区命名为 sda1~sda4 或者 hda1~hda4(sd表示SCSI硬盘,hd表示IDE硬盘,其中a表示硬盘编号,如果有多块硬盘,那就是b、c、d;1代表第一块分区,2代表第二块分区,以此类推)。在MBR硬盘中,分区号1-4是主分区(或者扩展分区),逻辑分区号只能从5开始
如图,磁盘1中F、G、H盘是主分区,I+K+J是扩展分区,I、K、J 是逻辑分区 。
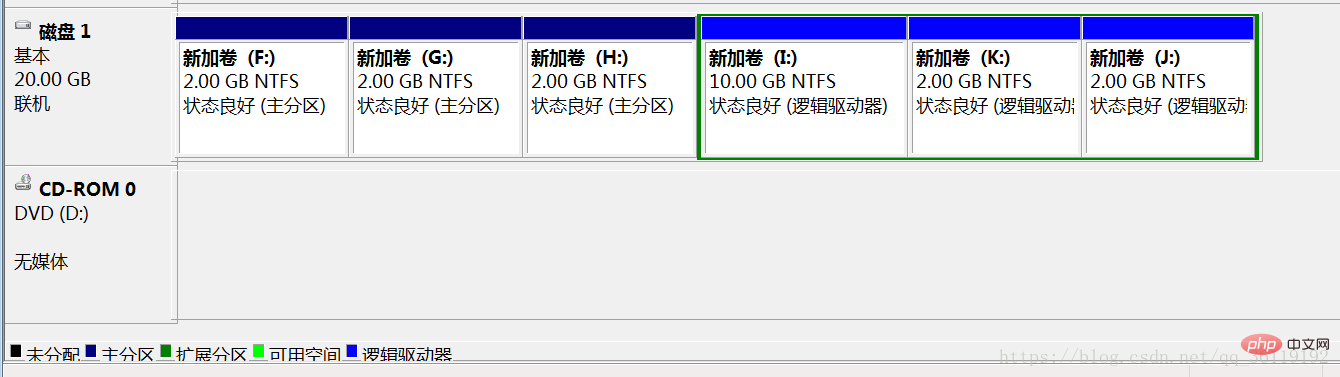
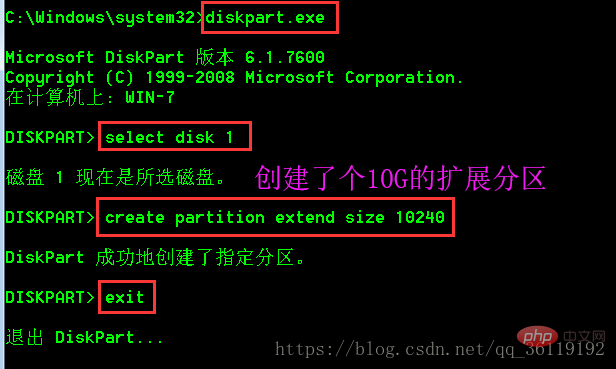
在windows中,默认只有你建立了3个主分区后,才会建立扩展分区。如果我们想直接建立扩展分区的话,可以使用命令
更多相关知识,请访问常见问题栏目!
以上就是磁盘分区形式有哪些的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系admin@php.cn核实处理。
- 上一篇:c/s架构和b/s架构的区别是什么
- 下一篇:mdf是什么文件格式