
How to operate the database in Thinkphp5 and perform addition, deletion, modification and query? The following article will give you a detailed understanding of the methods of adding, deleting, modifying and querying the database in Thinkphp5. I hope it will be helpful to you!

##[Related tutorial recommendations:thinkphp standard data table design:
Create time field: create_time
Update time field :update_time
Delete time field: delete_time
Select int as the type, as shown below:
thinkphp framework】
1. Create a model folder Create a new folder named model in the secondary object directory under the application folder. This folder is the same as The corresponding controller and view directories are at the same level, as shown below: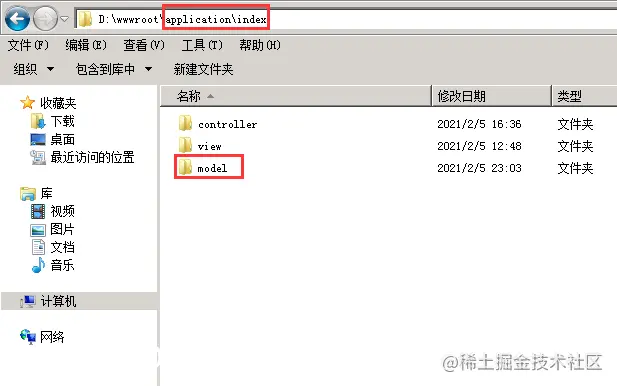
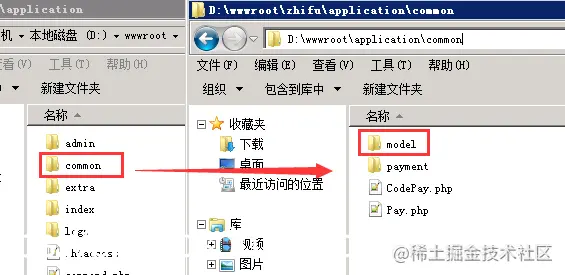
表名 pre_user ---------------> 模型名 User.php 表名 pre_user_info ---------------> 模型名 UserInfo.php
//导入定义的数据模型类 use \app\index\model\User; //方法一: $res = User::get(1); //方法二: $user = new User; $res = $user::get(1); //方法三: use think\Loader; $user = Loader::model("User"); $res = $user::get(1); //方法四: $user = model("User"); $res = $user::get(1);
get Get a record
$res = User::get(1);
all Get multiple records
1. No parameters are passed$result = User::all(); //查询出所有记录
$result = User::all(1); //查询出id为1的记录
$result = User::all('7, 8, 9, 10'); //查询出id为7、8、9、10的4条记录
$result = User::all([7, 8, 9, 10]); //查询出id为7、8、9、10的4条记录
find Query a certain item
$res = User::where('id','1')->field('name')->find();
Not equal to ->where('id','neq',1)##select multiple queries
$res = User::where('id','1')->field('name')->limit(2)->order('id DESC')->select();
$res = User::where('id','1')->value('name');
$res = $res->toArray();
//查询总条数 $res = User::count(); //按条件统计条数 $res = User::where('id','>',3)->count();
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'today')->select(); //也可以简化为下面方式 db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'd')->select();
2. Get yesterday’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'yesterday')->select();
3. Get this Weekly information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'week')->select(); //也可以简化为下面方式 db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'w')->select();
4. Get this month’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'month')->select(); //也可以简化为下面方式 db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'm')->select();
5. Get last month’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time','last month')->select();
6. Get this year’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'year')->select(); //也可以简化为下面方式 db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'y')->select();
7. Get last year’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time','last year')->select();
8. Date interval query
//根据时间戳查询今天到后天 db('table')->whereTime('time', 'between', [strtotime(date('Y-m-d')), strtotime(date('Y-m-d', strtotime('+2 day')))])->select(); 根据日期查询今天到后天 db('table')->whereTime('time', 'between', ['2020-3-28', '2020-3-30'])->select();
5. Add operation
$res = User::create([ 'name' => '安阳', 'age' => 23, 'sex' => 1, 'password' => '123456' ]);
2. Add data and return the added primary key
$uid=UserModel::create([ 'name' => '安阳', 'age' => 23, 'sex' => 1, 'password' => '123456' ])->id;
You can also use the insertGetId method of the DB class, as follows:
$uid = User::insertGetId([ 'name' => '安阳', 'age' => 23, 'sex' => 1, 'password' => '123456' ]);
3. Add by instantiation
$user = new User; $user->name = '安阳'; $user->age = 23; $user->save();
4 , Filter the inserted fields by instantiation and return the number of inserted rows
$user = new User; $data = [ 'name' => '安阳', 'age' => 23, 'email' => '123456@qq.com' ]; //只有name和age字段会写入 $res = $user->allowField(['name', 'age'])->save($data);
5. The model uses allowField() to filter the data of non-data table fields
//定义模型对象,并传入post数据 $user = new User($_POST); //过滤post数组中的非数据表字段数据 $user->allowField(true)->save();
6. The model uses allowField() to specify certain Field writing
$user = new User; // post数组中只有name和email字段会写入 $user->allowField(['name','email'])->save($_POST, ['id' => 1]);
7. Use saveAll() for batch addition
user = new User; $list = [ ['name'=>'安阳','email'=>'thinkphp@qq.com'], ['name'=>'小柒','email'=>'12345678@qq.com'] ]; $user->saveAll($list);
You can also use the insertAll() method of the DB class to return the number of successfully added items
$res = User::insertAll([ 'name' => '安阳', 'age' => 23, 'sex' => 1, 'password' => '123456' ]);
Supplementary, other methods of filtering fields:1. In DB operations, you can use strict to turn off strict field checking
Db::name(‘user’)->strict(false)->insert($data);Copy after login2. Use php's unset( ) method destroys variables
6. saveAll adds multiple pieces of data and returns the object listunset($data[‘file’]);Copy after login
$user = new User; $data = [ [ 'name' => '安阳', 'age' => 20, 'email' => '123456@qq.com' ], [ 'name' => '小柒', 'age' => 25, 'email' => 'ap555@qq.com' ] ]; $res = $user->allowField(['name', 'age'])->saveAll($data);
6. Update operation
$res = User::where(['id'=>1])->update(['name'=>'安阳']);
2. setField updates a field individually
User::where('id',1)->setField('name','安阳');
3. setInc
//setInc('money',10)表示将money字段加上10 User::where(['id'=>1])->setInc('money', 10);
4. setDec
//setDec('money',10)表示将money字段减去10 User::where(['id'=>1])->setDec('money', 10);
5. Batch update requires the data to contain Primary key, return the update object list
$user = new User; $res = $user->saveAll([ ['id'=>1, 'name' => '安阳'], ['id'=>2, 'name' => '小柒'] ]);
7. Delete operation
$res = User::destroy(1);
2. Pass in the condition, return the number of affected rows
$res = User::destroy(['name'=>'安阳']);
3. Conditional deletion returns the number of affected rows
$res = User::where(['id'=>1])->delete();
8. Transaction
Db::transaction(function(){ Db::table('order')->where(['id'=>1])->delete(); Db::table('user')->where('id'=>1)->setInc('money',10); });
2. Manually control transaction
Db::startTrans();//启动事务 try { Order::where(['id'=>1])->delete(); User::where('id'=>1)->setInc('money',10); Db::commit();//提交事务 } catch (Exception $e) { Db::rollback(); //回滚 }
9. Model model getter
The naming convention of the reader is:->get the camel case name of the attribute name Attr
Additional explanation: strtotime() parses the date and time description of any English text into a Unix timestamp, and returns the timestamp if successful, otherwise it returns FALSE (before PHP 5.1.0, this function returned -1 on failure )
Copy after login
auto新增及更新的时候,自动完成的属性数组
insert仅新增的时候,自动完成的属性数组
update仅更新的时候,自动完成的属性数组
1、自动完成
Copy after login
2、添加数据时,自动完成
Copy after login
3、更新数据时,自动完成:
Copy after login
在数据库配置文件database.php中,有下列这项配置:
//自动写入时间戳字段 'auto_timestamp' => false, //如果开启(设置为true),则会自动完成所有表的时间戳,但是不建议这样,只在需要的地方设置更安全。
例如对用户表的时间戳自动完成,就在User的model中设置:
Copy after login
Thinkphp更新时,自动更新update_time字段时间戳的方法:
1、使用update
User::update(['name'=>'安阳'],['id'=>1]);Copy after loginThinkphp中update方法的源代码如下:
/** * 更新数据 * @access public * @param array $data 数据数组 * @param array $where 更新条件 * @param array|true $field 允许字段 * @return $this */ public static function update($data = [], $where = [], $field = null) { $model = new static(); if (!empty($field)) { $model->allowField($field); } $result = $model->isUpdate(true)->save($data, $where); return $model; }Copy after login2、使用save
$user=new User; $user->isUpdate(true)->save(['name'=>'安阳'],['id'=>1]);Copy after login
什么是软删除?
当删除某些记录时,有时我们需要假删除,只通过修改某个字段状态来标记该记录已删除,但实际上,数据库中还是存在这些记录的。假删除的应用场景还是比较多的,例如支付宝的收款记录,我们在APP上删除后,就不会再显示出来,你是不是以为真的删掉了,不会再留下任何痕迹?非也,非也,删除支付宝收款记录只是软删除,在支付宝的数据库中,实际上还保留有这些收款记录,如果你的收款涉嫌违规或者触犯法律,警方还是能通过支付宝的网警后台查看到的。
1、开启软删除
Copy after login
2、 控制器里软删除,返回影响的行数
$res = Order::destroy(1);
执行删除后,就会更新delete_time字段,如果update_time字段也开启了自动完成,也会更新update_time字段。
3、如果开启了软删除,需要真正地删除数据,而不做软删除,用下面的方法
//destory()第二个参数传递true $res = Order::destroy(1,true); //delete()参数传递true $orderData = Order::get(1); $orderData ->delete(true);
4、查询已软删除的数据
$res = Order::withTrashed(true)->find(1);
5、查询仅包含已软删除的数据
$res = Order::onlyTrashed()->select();
推荐学习:《PHP视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of An article explaining in detail how to add, delete, modify and query the database in Thinkphp5. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!