
In the previous article "Let’s talk about the singleton mode in PHP" we introduced the singleton mode in PHP. The following article will take you to understand the state mode in PHP design pattern.

The state pattern is not very easy to understand literally. What does the status here mean? Save status? That's not the memo mode. In fact, the state here is the state of the class. By changing a certain state of the class, the class feels like a different class. It’s a bit hard to say, so let’s learn the concept first and then read it later.
GoF definition: Allows an object to change its behavior when its internal state changes. The object appears to have modified its class
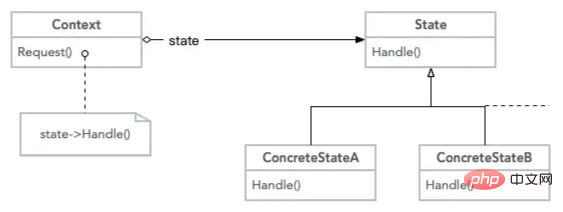
GoF Class Diagram
Code Implementation
class Context { private $state; public function SetState(State $state): void { $this->state = $state; } public function Request(): void { $this->state = $this->state->Handle(); } }
A context class can also be regarded as a target class, which has a state object inside it. When calling Request(), call the Handle() method of the status class. The purpose is that changes in the current context class state are controlled by the external state class.
interface State { public function Handle(): State; } class ConcreteStateA implements State { public function Handle(): State { echo '当前是A状态', PHP_EOL; return new ConcreteStateB(); } } class ConcreteStateB implements State { public function Handle(): State { echo '当前是B状态', PHP_EOL; return new ConcreteStateA(); } }
Abstract state interface and two concrete implementations. These two specific implementations are actually calling each other. The effect of the implementation is that every time the context class calls the Request() method, the internal state class changes to another state. It's like a switch that switches back and forth between on and off.
$c = new Context(); $stateA = new ConcreteStateA(); $c->SetState($stateA); $c->Request(); $c->Request(); $c->Request(); $c->Request();
The implementation of the client instantiates the context object and sets the initial state, and then continuously calls the Request() object to realize the switch state switching.
We have customized our own shopping mall system in the mobile phone system, so you can conveniently place orders and purchase our products on your mobile phone. An order (Context) will have multiple states (State), such as unpaid, paid, order completed, order refunded, and a lot of states. We put these states in the corresponding state classes to implement. Different state classes will call the next action of the state. For example, after payment, wait for the receipt of the goods, and after the refund, wait for the buyer to fill in the logistics form. Wait, in this way, the state mode can be flexibly used in our mall! !
Full code: https://github.com/zhangyue0503/designpatterns-php/blob/master/22.state/source/state.php
Usually there will be a membership system in shopping mall applications. Generally, the higher the level, the more discounts members can enjoy. At this time, the use of status mode can be very convenient. Easily get membership level discounts. Of course, the most important thing is that using the status mode, you can only add the corresponding member discount status subclass when you need to add or delete a membership level. No other business code needs to be changed, let’s take a look at the specific implementation!
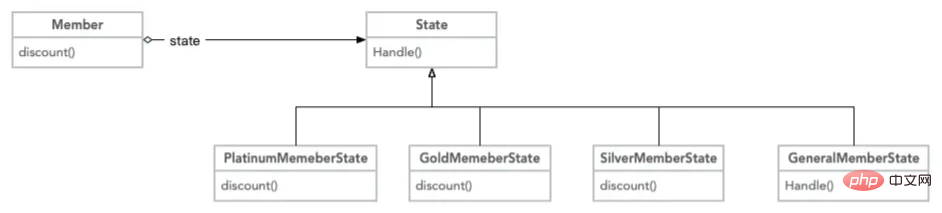
Member Discount Picture
Full source code: https://github.com/zhangyue0503/designpatterns-php/ blob/master/22.state/source/state-member.php
state = $state; } public function SetScore($score) { $this->score = $score; } public function GetScore() { return $this->score; } public function discount() { return $this->state->discount($this); } } interface State { public function discount($member); } class PlatinumMemeberState implements State { public function discount($member) { if ($member->GetScore() >= 1000) { return 0.80; } else { $member->SetState(new GoldMemberState()); return $member->discount(); } } } class GoldMemberState implements State { public function discount($member) { if ($member->GetScore() >= 800) { return 0.85; } else { $member->SetState(new SilverMemberState()); return $member->discount(); } } } class SilverMemberState implements State { public function discount($member) { if ($member->GetScore() >= 500) { return 0.90; } else { $member->SetState(new GeneralMemberState()); return $member->discount(); } } } class GeneralMemberState implements State { public function discount($member) { return 0.95; } } $m = new Member(); $m->SetState(new PlatinumMemeberState()); $m->SetScore(1200); echo '当前会员' . $m->GetScore() . '积分,折扣为:' . $m->discount(), PHP_EOL; $m->SetScore(990); echo '当前会员' . $m->GetScore() . '积分,折扣为:' . $m->discount(), PHP_EOL; $m->SetScore(660); echo '当前会员' . $m->GetScore() . '积分,折扣为:' . $m->discount(), PHP_EOL; $m->SetScore(10); echo '当前会员' . $m->GetScore() . '积分,折扣为:' . $m->discount(), PHP_EOL;
Description
Original address: https://juejin.cn/post/6844903991562731534
Author: Hardcore Project Manager
Recommended learning: "PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is the state pattern in PHP? Learn it through examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!