linux查看进程的方法:1、使用“ps aux”命令来查看,能以简单列表的形式显示出进程信息;2、使用“ps -elf”命令来查看;3、使用“top”命令来查看;4、使用“pstree -aup”命令来查看。

本教程操作环境:linux5.9.8系统、thinkpad t480电脑。
linux查看进程的方法
进程是在 CPU 及内存中运行的程序代码,而每个进程可以创建一个或多个进程(父子进程)。
**查看进程方法:**
第一种:
ps aux
ps命令用于报告当前系统的进程状态。可以搭配kill指令随时中断、删除不必要的程序。ps命令是最基本同时也是非常强大的进程查看命令,使用该命令可以确定有哪些进程正在运行和运行的状态、进程是否结束、进程有没有僵死、哪些进程占用了过多的资源等等,总之大部分信息都是可以通过执行该命令得到的。
a:显示当前终端下的所有进程信息,包括其他用户的进程。
u:使用以用户为主的格式输出进程信息。
x:显示当前用户在所有终端下的进程。
示例:
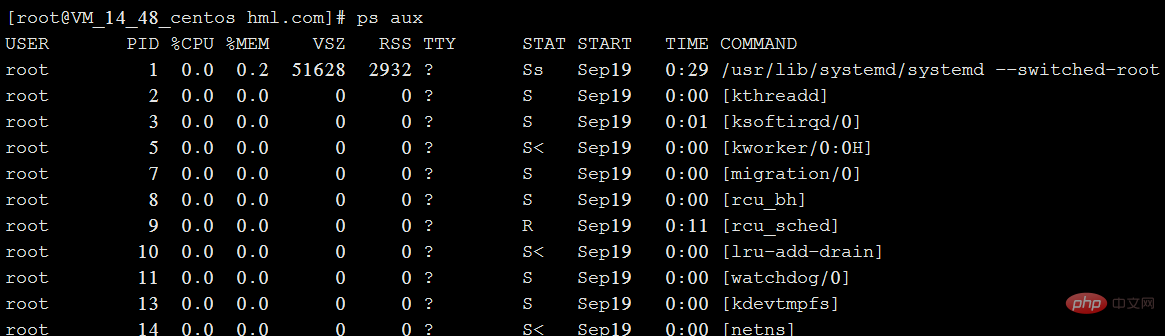
**上图中各字段解释:**
USER:启动该进程的用户账号名称
PID:该进程的ID号,在当前系统中是唯一的
%CPU:CPU占用的百分比
%MEM:内存占用的百分比
VSZ:占用虚拟内存(swap空间)的大小
RSS:占用常驻内存(物理内存)的大小
TTY:该进程在哪个终端上运行。“?”表未知或不需要终端
STAT:显示了进程当前的状态,如S(休眠)、R(运行)、Z(僵死)、
START:启动该进程的时间
TIME:该进程占用CPU时间
COMMAND:启动该进程的命令的名称
**总结:ps aux 是以简单列表的形式显示出进程信息。**
第二种:
ps -elf
-e:显示系统内的所有进程信息。
-l:使用长(long)格式显示进程信息。
-f:使用完整的(full)格式显示进程信息。
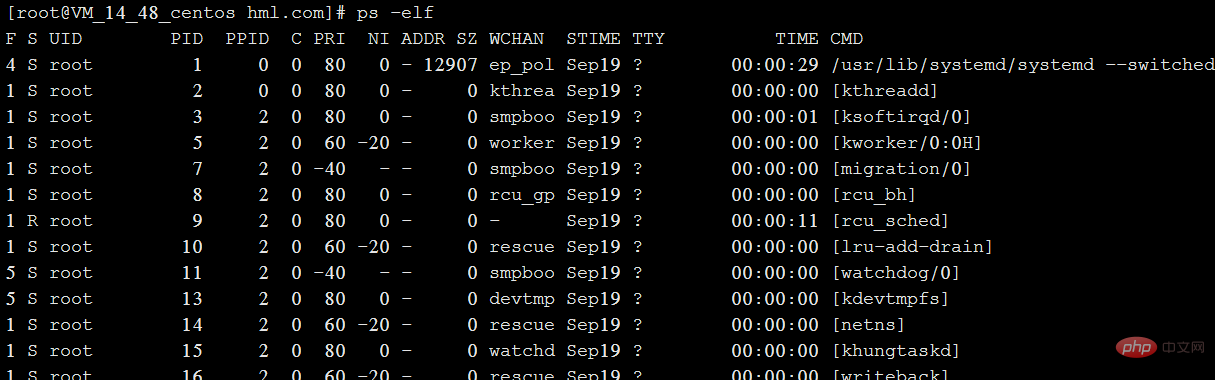
上图字段解释:
大部分跟第一种一样,PPID为父进程的PID。
第三种:
top
以全屏交互式的界面显示进程排名,及时跟踪包括CPU、内存等系统资源占用情况,默认情况下每三秒刷新一次,其作用基本类似于Windows系统中的任务管理器。
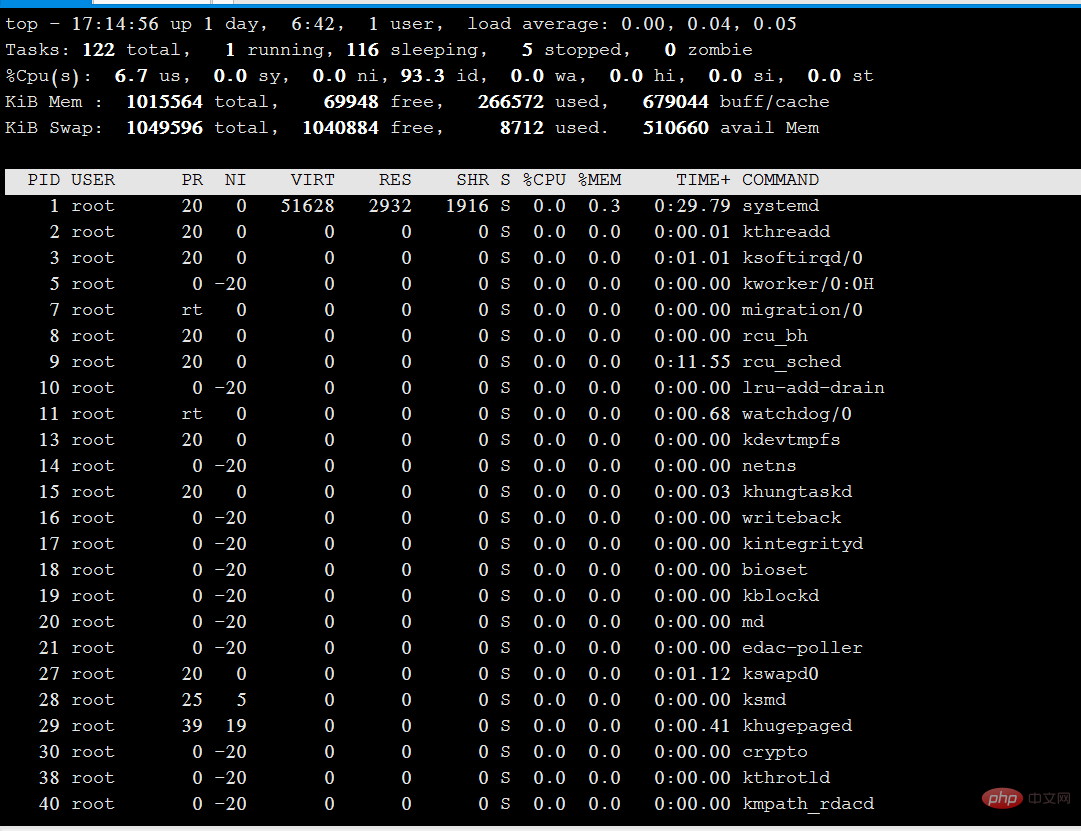
上图解释:
Tasks(系统任务)信息:total,总进程数;running,正在运行的进程数;sleeping,休眠的进程数;stopped,中止的进程数;zombie,僵死无响应的进程数。
CPU信息:us,用户占用;sy,内核占用;ni,优先级调度占用;id,空闲CPU;wa,I/O等待占用;hi,硬件中断占用;si,软件中断占用;st,虚拟化占用。了解空闲的CPU百分比,主要看%id部分。
Mem(内存)信息:total,总内存空间;used,已用内存;free,空闲内存;buffers,缓存区域。
Swap(交换空间)信息:total,总交换空间;used,已用交换空间;free,空闲交换空间;cached,缓存空间。
第四种:
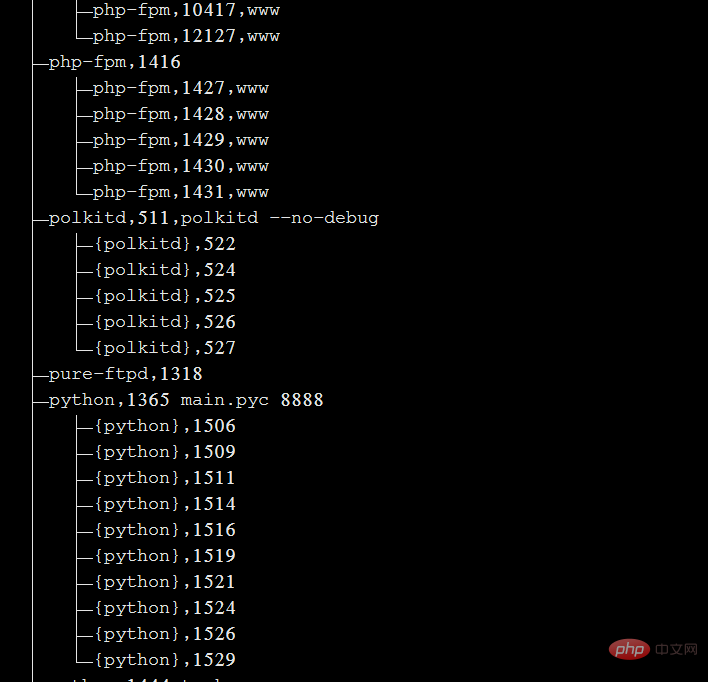
pstree -aup
可以带上|grep 查询特定进程。例如 pstree -aup | grep php
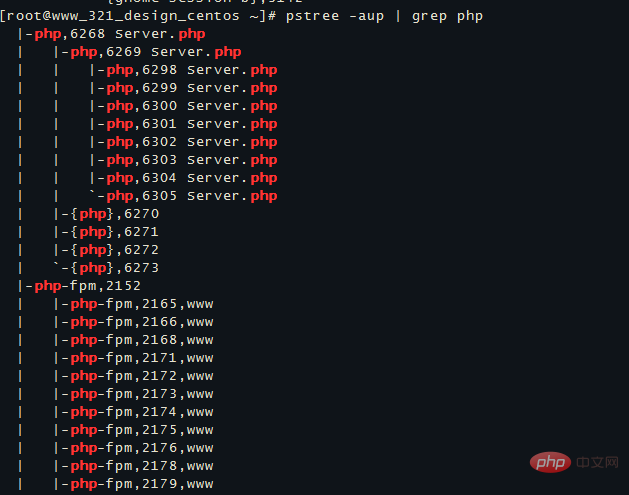
以树状图的方式展现进程之间的派生关系,显示效果比较直观。
-a:显示每个程序的完整指令,包含路径,参数或是常驻服务的标示;
-c:不使用精简标示法;
-G:使用VT100终端机的列绘图字符;
-h:列出树状图时,特别标明现在执行的程序;
-H:此参数的效果和指定"-h"参数类似,但特别标明指定的程序;
-l:采用长列格式显示树状图;
-n:用程序识别码排序。预设是以程序名称来排序;
-p:显示程序识别码;
-u:显示用户名称;
想要查阅更多相关文章,请访问PHP中文网!!
以上就是linux怎么查看进程?的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。




Copyright 2014-2025 //m.sbmmt.com/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号