

The remote connection tool is: Xmanager Enterprise 5-->Xshell
The Linux distribution version is: CentOS-6.3-x86_64
The solution is as follows :
(Online learning video tutorial sharing:linux video tutorial)
1. Check whether the IP in the network configuration file has changed
First check whether the IPADDR has changed. If it has not been changed, then proceed to step 2; if it has changed, change the IPADDR to the previous one, and then proceed to step 2.
[root@fanycb ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 DEVICE="eth0" BOOTPROTO=none NM_CONTROLLED="yes" ONBOOT="yes" TYPE="Ethernet" UUID="e57636db-84f8-4c15-af74-97d44a107fa2" HWADDR=00:0C:29:14:5A:57 IPADDR=192.168.1.100 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=yes IPV6INIT=no NAME="System eth0" [root@fanycb ~]#
2. Check the status of the sshd service and whether the port is normal
1. Check whether the 22 port of sshd is in the normal LISTEN state. If it is normal, proceed to the steps 3; If it is abnormal, restart the sshd service, and then proceed to step 3;
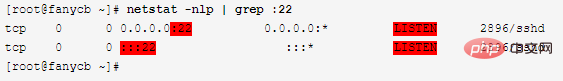
2. Restart the sshd service
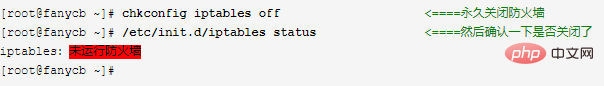
3. Check whether the firewall is turned on
If the firewall is turned off, go to step 4; if the firewall is not turned off, turn it off permanently, and then go to step 4.
4. Check whether SELinux is turned on
Check the current status of system SELinux

If the result is also "disabled", then all the checks are ok and you can connect.
But if the result is "Enforcing" or "permissive", it means that SELinux on the system is turned on and needs to be turned off.
Because the opening and closing of SELinux is related to two important configuration files, namely /etc/selinux/config and /boot/grub/menu.lst, so to close SELinux, you need to modify these two files. , the method is as follows:
[root@fanycb ~]# cat /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. #SELINUX=enforcing SELINUX=disabled <====将=号后改为disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted [root@fanycb ~]# cat /boot/grub/menu.lst # grub.conf generated by anaconda # # Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file # NOTICE: You have a /boot partition. This means that # all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /boot/, eg. # root (hd0,0) # kernel /vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/sda5 # initrd /initrd-[generic-]version.img #boot=/dev/sda default=0 timeout=5 splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gz hiddenmenu title CentOS (2.6.32-279.el6.x86_64) root (hd0,0) kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.32-279.el6.x86_64 ro root=UUID=edc1b124-6bc5-4dbe-b2d4-88805da96d4d rd_NO_LUKS KEYBOARDTYPE=pc KEYTABLE=us rd_NO_MD crashkernel=128M.UTF-8 rd_NO_LVM rd_NO_DM rhg b quiet selinux=0 <====seliux=0 是添加上去的 initrd /initramfs-2.6.32-279.el6.x86_64.img [root@fanycb ~]#
Done!
Recommended related articles and tutorials:linux tutorial
The above is the detailed content of ssh cannot connect to linux remotely. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!