How to install ssh service in linux

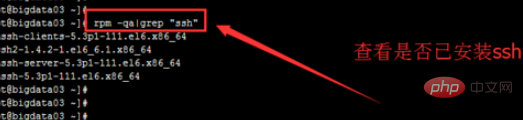
Check whether the ssh service has been installed
Execute on the terminal command line
rpm -qa | grep "ssh"
Please see the figure below for the execution results. Already installed; in fact, it will be installed by default when installing the Linux operating system.
How to install the ssh service:
1. Find the operating system image file, decompress it, find the ssh-related package, and upload it to the server
2. Execute the following installation command to install it
rpm -ivh rpm包名
3. If the server has a mirror mounted, you can directly use the following command to install it or
yum install ssh
Recommended tutorial:linuxtutorial
The above is the detailed content of How to install ssh service in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 Linux how to enable and disable services at boot
Aug 08, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Linux how to enable and disable services at boot
Aug 08, 2025 am 10:23 AM
To manage the startup of Linux services, use the systemctl command. 1. Check the service status: systemctlstatus can check whether the service is running, enabled or disabled. 2. Enable the service startup: sudosystemctlenable, such as sudosystemctlenablenginx. If it is started at the same time, use sudosystemctlenable--nownginx. 3. Disable the service startup: sudosystemctldisable, such as sudosystemctldisablecups. If it is stopped at the same time, use sudosystemctldisabl
 Linux how to list all running processes
Aug 08, 2025 am 06:42 AM
Linux how to list all running processes
Aug 08, 2025 am 06:42 AM
Usepsauxforacompletesnapshotofallrunningprocesses,showingdetailedinformationlikeUSER,PID,CPU,andmemoryusage.2.Usetoporhtopforreal-timemonitoringofprocesseswithdynamicupdates,wherehtopoffersamoreintuitiveinterface.3.UsepgreporpidoftoquicklyfindthePIDs
 How to clean up your Linux system
Aug 22, 2025 am 07:42 AM
How to clean up your Linux system
Aug 22, 2025 am 07:42 AM
Removeunusedpackagesanddependencieswithsudoaptautoremove,cleanpackagecacheusingsudoaptcleanorautoclean,andremoveoldkernelsviasudoaptautoremove--purge.2.Clearsystemlogswithsudojournalctl--vacuum-time=7d,deletearchivedlogsin/var/log,andempty/tmpand/var
 Linux how to view the contents of a file
Aug 19, 2025 pm 06:44 PM
Linux how to view the contents of a file
Aug 19, 2025 pm 06:44 PM
ToviewfilecontentsinLinux,usedifferentcommandsbasedonyourneeds:1.Forsmallfiles,usecattodisplaytheentirecontentatonce,withcat-ntoshowlinenumbers.2.Forlargefiles,uselesstoscrollpagebypageorlinebyline,searchwith/search_term,andquitwithq.3.Usemoreforbasi
 how to create an alias in linux
Aug 19, 2025 pm 08:13 PM
how to create an alias in linux
Aug 19, 2025 pm 08:13 PM
The steps to set up alias in Linux are as follows: 1. Temporarily set the use of the alias command such as aliasll='ls-la'; 2. Permanently set the shell configuration file, such as ~/.bashrc, and then execute the source to take effect; 3. Be careful to avoid overwriting the original command and the different shell configurations are independent. Alias can simplify complex commands and improve efficiency, but only after the current shell environment takes effect and closes the terminal, it needs to be reasonably defined and regularly checked for configuration.
![Windows could not complete the installation [FIXED]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/431/639/175606404166924.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Windows could not complete the installation [FIXED]
Aug 25, 2025 am 03:34 AM
Windows could not complete the installation [FIXED]
Aug 25, 2025 am 03:34 AM
IfWindowsinstallationfailsorgetsstuck,trythesesteps:1.Disconnectexternaldevices.2.BootintoSafeMode.3.RepairsystemfilesviaCommandPromptusingsfcandDISM.4.ClearTPMandresetBIOS.5.PerformacleaninstallusingabootableUSB.
 How to install Windows 11 on an unsupported PC?
Aug 07, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
How to install Windows 11 on an unsupported PC?
Aug 07, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
You can install Windows 11 on an unsupported computer. 1. Use the method of modifying the registry during installation: Press Shift F10 to open the command prompt when an error occurs, enter regedit to enter the registry editor, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup, create a new key named LabConfig, and create five DWORD values: BypassTPMCheck, BypassSecureBootCheck, BypassRAMCheck, BypassCPUCheck, BypassStorageCheck and BypassStorageCheck and set it to 1. After closing, return to the installer to continue installation; 2.
 192.168.10.1 login portal (Period routing/Asus management page)
Aug 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
192.168.10.1 login portal (Period routing/Asus management page)
Aug 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
First, confirm that the device is connected to the Wi-Fi of the target router or connected through a network cable; 2. Enter http://192.168.10.1 in the browser address bar and press Enter; 3. Enter the correct username and password (default is often admin/admin or view the back of the router); 4. If it cannot be opened, check whether it is connected to the wrong network, confirm the correct IP address (you can view the default gateway through ipconfig), restart the router, change the browser or turn off the firewall; 5. After logging in, you can modify the Wi-Fi name password, set security options, configure port forwarding, enable guest network, upgrade firmware, etc.; 6. If you forget your password, you can reset the factory settings by pressing and holding the router reset hole for 5-10 seconds, but all configurations will be cleared.







