
In JavaScript, the Object.is() method can be used to determine whether two values are the same. The following article will introduce to you how to use the JavaScript Object.is() method and understand the difference between the Object.is() method and the == operator. I hope it will be helpful to you. [Video tutorial recommendation: JavaScript tutorial]
JavaScript Object.is() method
The Object.is() method is used to determine whether two values are the same; it accepts two parameters, which are the values to be compared, and returns a Boolean value indicating whether the two parameters are the same. Syntax:
Object.is(value1, value2)
Two values can be the same if they have one of the following properties:
●If both values are undefined .
● If both values are null.
● If both values are true or false.
● If two strings have the same length, the same characters and the same order.
● If both values are numbers and both are "0".
● If both values are numbers and both are "-0".
● If both values are numbers and both are "NaN"; or neither is NaN, both are non-zero, and both have the same value.
Object.is() method can be applied to:
●Object.is() is used to compare two strings.
●Object.is() is used to compare two numbers.
●Object.is() is used to compare two objects.
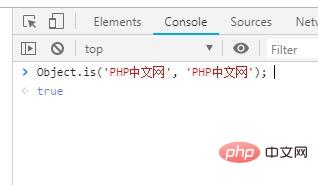
Example 1:
Object.is('PHP中文网', 'PHP中文网');
Output:
Example 2:
Object.is(0,-0);
Output:
Difference between Object.is() method and "==" operator
1. The "==" and "===" operators treat the numeric values "0" and "-0" as equal, while the Object.is() method treats them as equal. is not equal to.
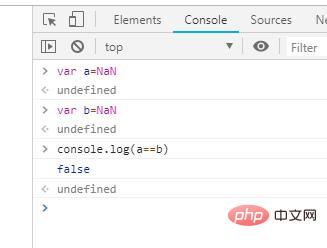
2. If both values are numbers and both are "NaN", the "==" and "===" operators will not treat them as equal; and the Object.is() method are considered equal.
var a=NaN; var b=NaN; console.log(a==b);
Output:
The above is the detailed content of How to use the Object.is() method in JavaScript? (code example). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!