#C provides programmers with a rich variety of built-in predefined data types and user-defined data types. Below we will introduce these two types of data to you in detail, which will serve as a reference and we hope it will be helpful to you.
c There are four integer types: short, int, long , long long, each has two categories: signed (signed, default) and unsigned (unsigned). Signed integers can represent both non-negative integers and negative integers; however, unsigned integers cannot represent negative numbers. Can only represent non-negative integers.
In the implementation of c, the number of storage bits (width) used by each type on different systems is different. The rules are:
##Type | Meaning | The minimum number of bits occupied by this type of data |
char | Character | 8 bits (can represent 28 characters) |
wchar_t | Wide characters | 16 bits |
char16_t | Unicode characters | 16 bits |
char32_t | Unicode character | 32 bits |
Boolean type
The Boolean type (bool) is a new basic data type in C. The bool type is not defined in the standard C language. If you need to use the bool type, the programmer can customize a bool type through macro definition. The definition statement is as follows:
#define bool int
#define false 0
#define true 1
Copy after login
That is, the int type is defined as the bool type. , define the two values of 0 and 1 of type int as the two values of type bool, true and false, respectively.

Floating point type
Floating point type is divided into the following types:
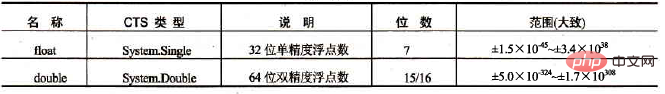
Empty type
The type defined by the keyword void cannot be used for declaration of ordinary variables and ordinary operations. It can only be used for pointer variables, function return values and functions. parameter.
Pointer type
Pointer is used to describe the memory address and implement memory-related program functions by providing pointer operations.
<类型>* <指针变量>;
Copy after login
Note:
The determines the size of the memory space pointed to.
A pointer variable is also a kind of variable, which has its own memory space, and the memory space of another variable is stored in this space.
2. Custom data type
Array type
The array type is A data type composed of a fixed number of elements of the same type in a certain order.
1. One-dimensional array type
1) Definition
数据类型 数组名[元素个数] ;
Copy after login
2) Operation
● Access elements through subscripts.
Pay attention to whether the subscript is out of bounds. (In order to ensure the execution efficiency of the program, C does not check subscript out-of-bounds. It can be run when out-of-bounds, but the results are unpredictable)
●Initialization
int a[10] = {1,2 ,3};//Other elements are initialized to 0
int a[] = {1,2,3};//The number of elements is 3
2, two-dimensional array type
1) Definition
数据类型 数组名[常量表达式1][常量表达式2]
Copy after login
2) Initialization
int a[2][3] = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
//等同于
int a[2][3] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};//二维数组可以转成一维数组进行处理,但是要注意下标Copy after login
int a[][3] = {{1,2},{3,4,5}};//第一个下标可以省略,其他的不能,更高维的数组也同此。Copy after login
Store by row!
Structure data type
1. Structure
A structure is a data collection composed of a series of data of the same type or different types. .
Definition:
struct 名称{
数据类型 变量名1;
数据类型 变量名2;
。。。。
数据类型 变量名n;
}结构体变量名;Copy after login
2. Structure array:
struct Info{
int age;
char name[32];
}info[SIZE];Copy after login
3. Structure nesting:
struct BookInfo{
char name[SIZE];
char author[SIZE];
int status;
};
struct ReadreInfo{
char Name[SIZE];
char Date[SIZE];
};
//结构体嵌套
struct LibraryInfo{
int ID;
struct BookInfo book;
struct ReadreInfo reader;
}LibraryInfo;Copy after login
Union type
The use of unions is similar to structures and ordinary variables.
union 名称{
类型变量符 变量名;
......
类型变量符 变量名;
};Copy after login
The main function of the union is to save memory, because the variables in the union are not like the member variables in the structure. The system will allocate corresponding memory to each variable. In a union, all member variables share a memory space. This memory space is the memory space occupied by the variable with the largest number of bytes among its member variables, and all member variables share this memory space, so the addresses of all member variables in the union are the same.
Enumeration type
The enumeration type (enumeration) is a derived data type in C. It is a number of enumeration constants defined by the user. collection.
If a variable has only a few possible values, it can be defined as an enumeration type. The so-called "enumeration" refers to listing the values of variables one by one. The value of a variable can only be within the range of the listed values.
To create an enumeration, you need to use the keyword enum. The general form of the enumeration type is:
enum 枚举名{
标识符[=整型常数],
标识符[=整型常数],
...
标识符[=整型常数]
} 枚举变量;Copy after login
If the enumeration is not initialized, that is, when "=integer constant" is omitted, it starts from the first identifier.
For example, the following code defines a color enumeration, and the type of variable c is color. Finally, c is assigned the value "blue".
enum color { red, green, blue } c;
c = blue;Copy after login
By default, the first name has a value of 0, the second name has a value of 1, the third name has a value of 2, and so on. However, you can also assign a special value to the name by adding an initial value. For example, in the enumeration below, green has a value of 5.
enum color { red, green=5, blue };Copy after login
Here, the value of blue is 6, because by default, each name will be 1 greater than the one before it, but the value of red is still 0.
The above is the detailed content of What are the data types in c++. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!


 What are the data types?
What are the data types?
 What are the differences between c++ and c language
What are the differences between c++ and c language
 Recommended learning order for c++ and python
Recommended learning order for c++ and python
 Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python and c++
Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python and c++
 Is c language the same as c++?
Is c language the same as c++?
 Which is better to learn first, c language or c++?
Which is better to learn first, c language or c++?
 The difference and connection between c language and c++
The difference and connection between c language and c++
 C++ software Chinese change tutorial
C++ software Chinese change tutorial