이 기사는 Youerhut가 작성한 WeChat 공개 계정 "Youerhut"에서 복제되었습니다. 이 기사를 재인쇄하려면 Youerhut 공개 계정에 문의하세요.
안녕하세요 여러분 피터입니다~
최근 IC전자제품 전자상거래 데이터를 얻었고 추후 3가지 주제에 대한 데이터 분석 및 마이닝을 진행할 예정입니다.
이 글은 첫 번째입니다. 단계. 주요 내용에는 다음이 포함됩니다. data
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import time import os from datetime import datetime import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns %matplotlib inline #设置中文编码和负号的正常显示 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False import plotly_express as px import plotly.graph_objects as go import missingno as ms from sklearn.cluster import KMeans from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
읽은 후 데이터의 기본 정보를 확인하세요. 
df = pd.read_csv(
"ic_sale.csv",
encoding="utf-8",# 指定编码
cnotallow={"order_id":str,"product_id":str,"category_id":str,"user_id":str} # 指定字段类型
)
df.head()# 1、数据shape df.shape
In [4]:
(564169, 11)
# 2、数据字段类型 df.dtypes
기술 통계는 숫자 필드에 사용됩니다.
event_timeobject order_idobject product_idobject category_id object category_code object brand object pricefloat64 user_id object ageint64 sex object local object dtype: object
Out[5]:
나이ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ
208.269324
| std | 304.559875 | 10.122088 |
min | 0.000000 | 16.000000 |
25% | 23.130000 | 24.000000 |
50% | 87.940000 | 33.000000 |
75% | 277.750000 | 42.000000 |
max | 18328.680000 | 50.000000 |
In [6]:
# 4、总共多少个不同客户 df["user_id"].nunique()
Out[6]:
6908
In [7]:
# 5、总共多少个不同品牌 df["brand"].nunique()
Out[7]:
868
In [8]:
# 6、总共多少个订单 df["order_id"].nunique()
Out[8]:
234232
In [9]:
# 7、总共多少个产品 df["product_id"].nunique()
Out[9]:
3756
从描述统计信息中发现price字段的最小值是0,应该是没有成交的数据;我们选择price大于0的信息:
In [10]:
df = df[df["price"] > 0]
In [11]:
df.isnull().sum()
Out[11]:
event_time0 order_id0 product_id0 category_id 0 category_code129344 brand 27215 price 0 user_id 0 age 0 sex 0 local 0 dtype: int64
可以看到缺失值体现在字段:
In [12]:
ms.bar(df,color="blue")# 缺失值可视化 plt.show()
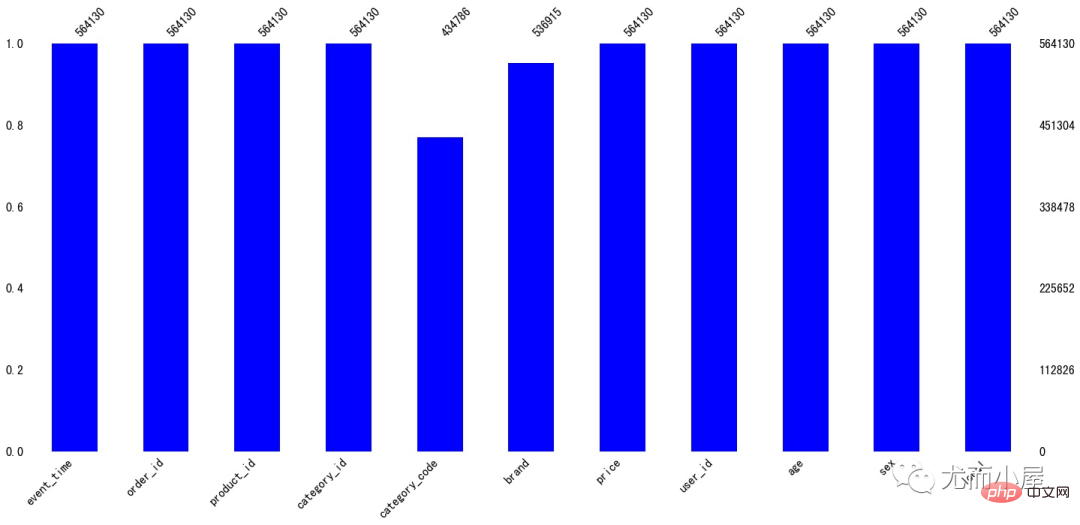
In [13]:
df.fillna("missing",inplace=True)In [14]:
df.isnull().sum()# 填充之后无缺失值
Out[14]:
event_time 0 order_id 0 product_id 0 category_id0 category_code0 brand0 price0 user_id0 age0 sex0 local0 dtype: int64
读进来的数据中时间字段是object类型,需要将其转成时间格式的类型
In [15]:
df["event_time"][:5] # 处理前
Out[15]:
02020-04-24 11:50:39 UTC 12020-04-24 11:50:39 UTC 22020-04-24 14:37:43 UTC 32020-04-24 14:37:43 UTC 42020-04-24 19:16:21 UTC Name: event_time, dtype: object
In [16]:
# 去掉最后的UTC df["event_time"] = df["event_time"].apply(lambda x: x[:19])
In [17]:
# 时间数据类型转化:字符类型---->指定时间格式 df['event_time'] = pd.to_datetime(df['event_time'], format="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
In [18]:
# 提取多个时间相关字段 df['month']=df['event_time'].dt.month df['day'] = df['event_time'].dt.day df['dayofweek']=df['event_time'].dt.dayofweek df['hour']=df['event_time'].dt.hour
In [19]:
df["event_time"][:5] # 处理后
Out[19]:
0 2020-04-24 11:50:39 1 2020-04-24 11:50:39 2 2020-04-24 14:37:43 3 2020-04-24 14:37:43 4 2020-04-24 19:16:21 Name: event_time, dtype: datetime64[ns]
可以看到字段类型已经发生了变化
In [20]:
amount_by_month = df.groupby("month")["price"].sum().reset_index()
amount_by_monthOut[20]:
month | price | |
0 | 1 | 1953358.17 |
1 | 2 | 2267809.88 |
2 | 3 | 2897486.26 |
3 | 4 | 1704422.41 |
4 | 5 | 7768637.79 |
5 | 6 | 7691244.33 |
6 | 7 | 16354029.27 |
7 | 8 | 27982605.44 |
8 | 9 | 17152310.57 |
9 | 10 | 19765680.76 |
10 | 11 | 11961511.52 |
In [21]:
fig = px.scatter(amount_by_month,x="month",y="price",size="price",color="price") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交金额") fig.show()
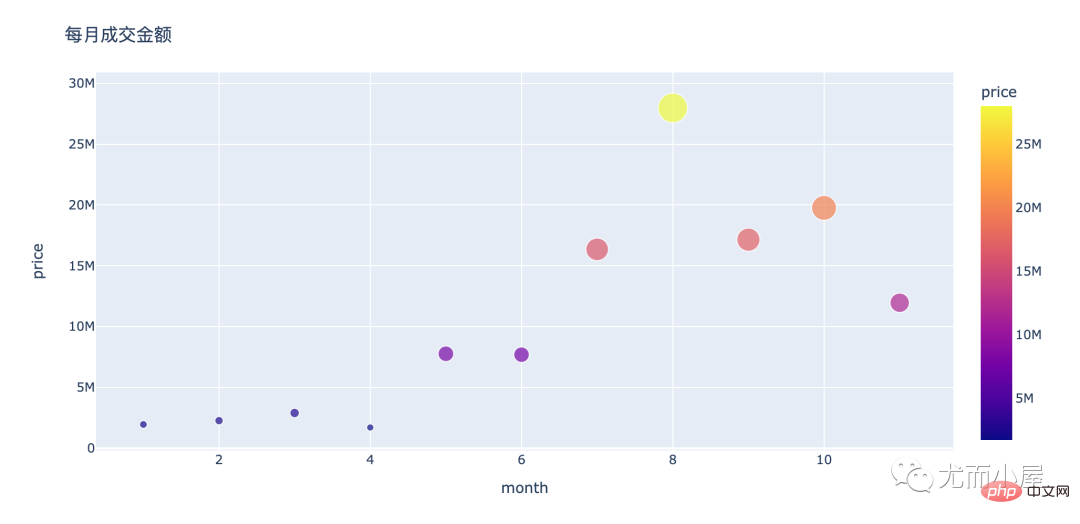
可以看到:
In [22]:
order_by_month = df.groupby("month")["order_id"].nunique().reset_index()
order_by_monthOut[22]:
month | order_id | |
0 | 1 | 10353 |
1 | 2 | 11461 |
2 | 3 | 12080 |
3 | 4 | 9001 |
4 | 5 | 30460 |
5 | 6 | 2897 8 |
6 | 7 | 57659 ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ 345 |
9 | 10 | 14 |
10 | 11 | 6 |
In [23]:
fig = px.line(order_by_month,x="month",y="order_id") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交订单量") fig.show()
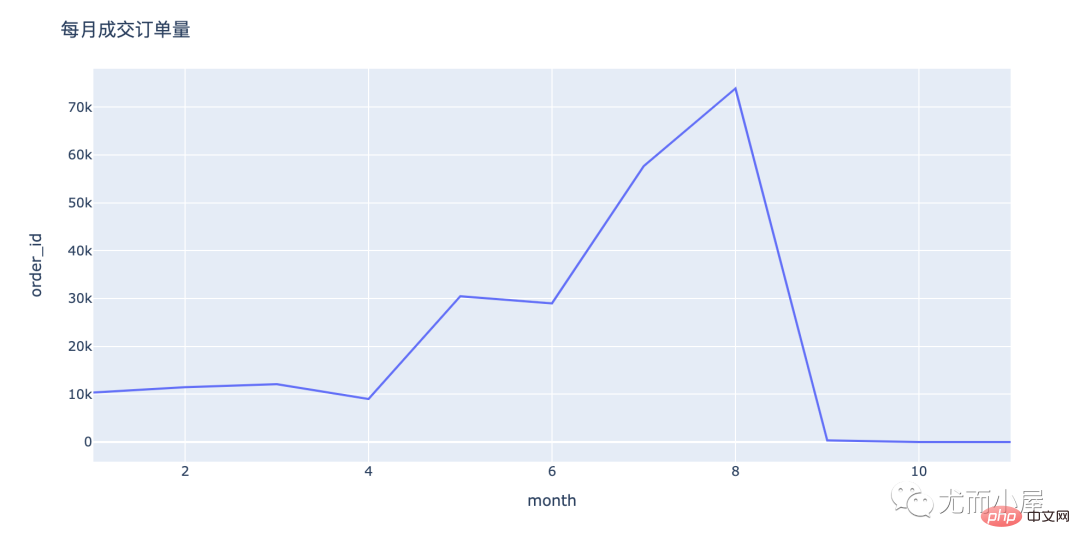
关于订单量:
In [24]:
# nunique:对每个user_id进行去重:消费人数
# count:统计user_id 的次数;消费人次(存在一人多次购买)
people_by_month = df.groupby("month")["user_id"].agg(["nunique","count"]).reset_index()
people_by_monthOut[24]:
month | nunique | count | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0 | 1 | 1388 | 15575 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 | 2 | 1508 | 17990 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2 | 3 | 1597 | 18687 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 | 4 | 1525 | 11867 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 5 | 3168 | 40332 | ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5159 | 76415 ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5497 | 70496 | 9 | 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4597 | 104075 | 10 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 134 | 67332 | In [25]: fig = px.line(people_by_month,x="month",y="nunique") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交人数") fig.show() 로그인 후 복사
fig = px.line(people_by_month,x="month",y="count") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月成交人次") fig.show() 로그인 후 복사
分析4:每月订单价多少?In [27]: amount_by_month# 每月成交金额 로그인 후 복사 Out[27]:
In [28]: order_by_month# 每月订单数 로그인 후 복사 Out[28]:
In [29]: amount_by_userid = pd.merge(amount_by_month,order_by_month) amount_by_userid 로그인 후 복사 Out[29]:
In [30]: amount_by_userid["average"] = amount_by_userid["price"] / amount_by_userid["order_id"] amount_by_userid 로그인 후 복사
fig = px.line(amount_by_userid,x="month",y="average") fig.update_layout(height=500, width=1000, title_text="每月客单价") fig.show() 로그인 후 복사
从上面的折线图可以看出来:
分析5:每个订单包含多少产品In [32]: product_by_order = df.groupby("order_id")["product_id"].count().reset_index().sort_values("product_id",ascending=False)
product_by_order.head(10)로그인 후 복사 Out[32]:
In [33]: fig = px.bar(product_by_order[:20], x="order_id", y="product_id", text="product_id" ) fig.show() 로그인 후 복사
一个订单下包含的产品数量是不同;上万的订单可能是小型的ic元器件产品。 不同省份对比分析6:订单量、用户量和成交金额对比不同省份下的订单量、用户量和成交金额对比 In [34]: local = df.groupby("local").agg({"order_id":"nunique","user_id":"nunique","price":sum}).reset_index()
local.head()로그인 후 복사 Out[34]:
In [35]: df1 = local.sort_values("order_id",ascending=True)# 订单量升序
df1로그인 후 복사 Out[35]:
In [36]: fig = px.pie(df1, names="local",labels="local",values="price") fig.update_traces( textpositinotallow="inside", textinfo="percent+label" ) fig.show() 로그인 후 복사
无疑:广东省No.1 每个省份的订单量对比: fig = px.bar(df1,x="order_id",y="local",orientatinotallow="h") fig.show() 로그인 후 복사
# 整体的可视化效果 fig = px.scatter_3d(local, x="order_id", y="user_id", z="price", color="order_id", hover_name="local" ) fig.show() 로그인 후 복사
通过3D散点图我们发现:广东省真的是一骑绝尘!
分析7:不同省份的客户钟爱哪些品牌?In [39]: local_brand = df.groupby(["local","brand"]).size().to_frame().reset_index() local_brand.columns = ["local","brand","number"]# 修改字段名 local_brand 로그인 후 복사
# 根据local和number进行排序
local_brand.sort_values(["local","number"],ascending=[True,False],inplace=True,ignore_index=True)
local_brand = local_brand[local_brand["brand"] != "missing"]
# 每个local下面最受欢迎的前3个品牌
local_brand = local_brand.groupby("local").head(3)
local_brand로그인 후 복사
fig = px.bar(local_brand, x="brand", y="number", color="number", facet_col="local") fig.update_layout(height=500,width=1000) fig.show() 로그인 후 복사
看来大家都很喜欢: samsung 、apple、ava 不同时间对比分析8:下单时间对比In [43]: df.columns 로그인 후 복사 Out[43]: Index(['event_time', 'order_id', 'product_id', 'category_id', 'category_code', 'brand', 'price', 'user_id', 'age', 'sex', 'local', 'month', 'day', 'dayofweek', 'hour'], dtype='object') 로그인 후 복사 In [44]: df2 = df.groupby("dayofweek")["order_id"].nunique().reset_index()
df2로그인 후 복사 Out[44]:
|