输入输出流可以分为以下几种类型(暂时不考虑File类)
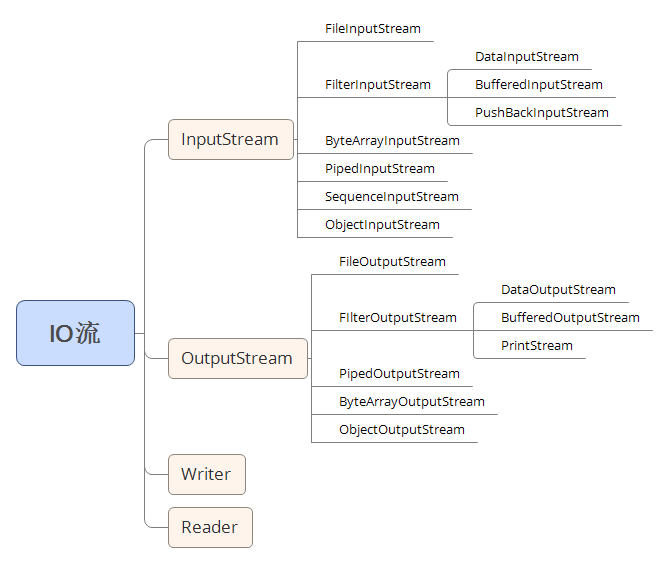
Java IO共涉及40多个类,下图是字节流各个类之间的关系
InputStream
InputStream的子类及其说明有如下所示

OutputStream
OutputStream的子类及其说明有如下所示

对于类中方法的熟悉不详述了,可以参照JDK文档,或者可以试着在IDE中,实例化上面的类,使用此类对象时,按下.之后,会出现提示框,再一个一个熟悉就好了。
简单示例
了解了常用的字节流类,下面以文件数据的输入输出说明以上类的使用。
1.在java程序中生成1~20的平方数,并输出到文件中。
package com.songpu;import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.PrintStream;public class MyFileOutputStream {
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException{ try{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("F:\\test1.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos,1024);
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(bos,false);
System.setOut(ps); for(int i= 0;i<20;i++){
System.out.println(i*i);
}
ps.close();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}2.将刚才生成的文件中的数据输入到程序,并将其打印到屏幕
package com.songpu;import java.io.*;public class MyFlieInputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("F:\\test1.txt");
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in); byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) file.length()];
do {
bis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}while (bis.read() != -1);
in.close();
}
}再以序列化与反序列化的例子说明ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream的使用
Java序列化是将对象变成二进制形式的一连串字符描述的过程,反序列化就是序列化的相反过程,把这些字符重建为对象。
序列化和反序列化的作用,是保存对象到文件或数据库中,使对象能够传输,序列化的要求是实现Serializable接口,代码如下所示
package com.songpu.serial;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.io.OutputStream;import java.io.Serializable;/*
* 待序列化的类,实现序列化接口
*/class Person implements Serializable{ public String name; public int age; public Person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age;
} public String getName() { return name;
} public void setName(String name) { this.name = name;
} public int getAge() { return age;
} public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age;
}
}/*
* 测试类
*/public class SerialTest{ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("F:\\test.txt"));
Person p0 = new Person("tangsong",21);
oos.writeObject(p0);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
deserial();
}
public static void deserial() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException{
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("F:\\test.txt"));
Person p1 = (Person)ois.readObject();
ois.close();
System.out.println("Name="+p1.getName()+";Age="+p1.getAge());
}
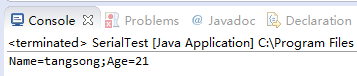
}运行上述代码的结果如下:

声明:本文原创发布php中文网,转载请注明出处,感谢您的尊重!如有疑问,请联系admin@php.cn处理













网友评论
文明上网理性发言,请遵守 新闻评论服务协议
我要评论