
Introduction
People who have used JavaScript frameworks (such as AngularJS, Backbone or Ember) are familiar with the working mechanism of mvc in UI (user interface, front-end). These frameworks implement MVC, making it easier to change the view as needed in a single page. The core concepts of Model-View-Controller (mvc) are: a controller that handles incoming requests, a view that displays information, and a presentation Model for business rules and data access.
Therefore, when we need to create an application that needs to switch out different content in a single page, we usually choose to use one of the above frameworks. However, if we only need a framework that implements view switching in a URL without additional bundled functions, there is no need to use complex frameworks such as Angular and Ember. This article is an attempt to use simple and effective methods to solve the same problem.
Concept
The code in the application uses the "#" in urls to implement MVC mode navigation. The application starts with a default URL, hash-based code loads the application view and applies the object-model to the view template.
The URL format is as follows:
http://Domain Name/index.html#/Route Name
The view content must bind the values and properties of the object model in the form of {{Property-Name}}. The code looks for this specialized template format and replaces the property values in the object model.
The view loaded asynchronously via ajax will be placed in the placeholder of the page. The view placeholder can be any element (ideally a div), but it must have a special attribute, and the code positions it based on this special attribute, which also helps with the implementation of the code. When the url changes, the scenario is repeated and another view is loaded. Sounds simple? The flow diagram below explains the message jumps in this particular implementation.
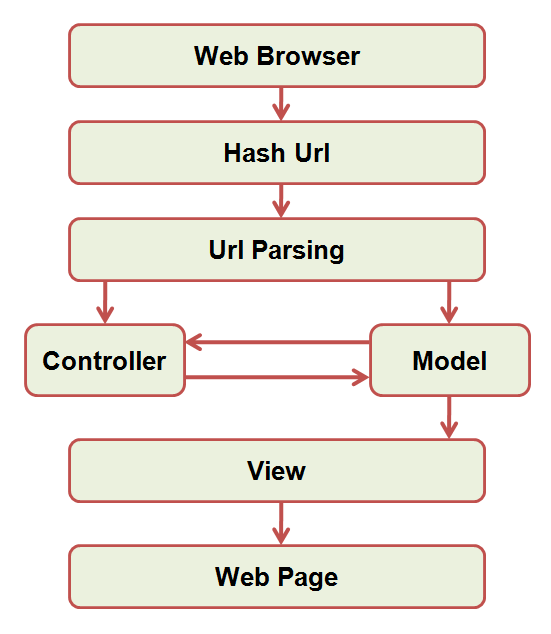
Write code
We started with the basic module design pattern, and finally used the facade design pattern to expose our libs to the global scope.
;(function(w,d,undefined){//restofthecode})(window,document);We need to store the view element into a variable so that it can be used multiple times.
var_viewElement=null;//elementthatwillbeusedtorendertheview
We need a default route to deal with the situation where there is no routing information in the url, so that the default view can be loaded instead of displaying a blank page.
var_defaultRoute=null;
Now let’s create the constructor of our main MVC object. We will store routing information in "_routeMap"
var jsMvc = function () {
//mapping object for the routes
this._routeMap = {};
}
It’s time to create a routing object. We will store routing, template, and controller information in this object.
var routeObj = function (c, r, t) {
this.controller = c;
this.route = r;
this.template = t;
}
Each URL will have a dedicated routing object routeObj. All these objects will be added to the _routeMap object, so that we can obtain them later through key-value.
In order to add routing information to MVC libs, we need to expose a method in the libs. So let's create a method that can be used by the respective controller to add new routes.
jsMvc.prototype.AddRoute = function (controller, route, template) {
this._routeMap[route] = new routeObj(controller, route, template);
}
Method AddRoute receives 3 parameters: controller, route and template. They are:
Controller: The function of the controller is to access specific routes.
route: route of routing. This is the part after # in the url.
Template: This is the external html file that is loaded as the view of this route. Now our libs need an entry point to parse the url and serve the associated html template page. To accomplish this, we need a method.
The Initialize method does the following:
1) Get the initialization of view-related elements. The code requires an element with a view attribute, which can be used to search in the HTML page:
2) Set the default route
3) Verify whether the view elements are reasonable
4) Bind the window hash change event. When the different hash values of the URL change, the view can be updated in time
5) Finally, start mvc
//Initialize the Mvc manager object to start functioning
jsMvc.prototype.Initialize = function () {
var startMvcDelegate = startMvc.bind(this);
//get the html element that will be used to render the view
_viewElement = d.querySelector('[view]');
if (!_viewElement) return; //do nothing if view element is not found
//Set the default route
_defaultRoute = this._routeMap[Object.getOwnPropertyNames(this._routeMap)[0]];
//start the Mvc manager
w.onhashchange = startMvcDelegate;
startMvcDelegate();
}In the above code, we created a proxy method startMvcDelegate from the startMvc method. This agent is called whenever the hash value changes. The following is the sequence of operations we do when the hash value changes:
1) Get the hash value
2) Get the routing value from the hash
3) Obtain the route object routeObj from the route map object _routeMap
4) If there is no routing information in the url, you need to obtain the default routing object
5) Finally, call the controller related to this route and provide services for the view of this view element
All the above steps are implemented by the startMvc method below
//function to start the mvc support
function startMvc() {
var pageHash = w.location.hash.replace('#', ''),
routeName = null,
routeObj = null;
routeName = pageHash.replace('/', ''); //get the name of the route from the hash
routeObj = this._routeMap[routeName]; //get the route object
//Set to default route object if no route found
if (!routeObj)
routeObj = _defaultRoute;
loadTemplate(routeObj, _viewElement, pageHash); //fetch and set the view of the route
}下一步,我们需要使用XML HTTP请求异步加载合适的视图。为此,我们会传递路由对象的值和视图元素给方法loadTemplate。
//Function to load external html data
function loadTemplate(routeObject, view) {
var xmlhttp;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
// code for IE7+, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, Safari
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else {
// code for IE6, IE5
xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP');
}
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {
loadView(routeObject, view, xmlhttp.responseText);
}
}
xmlhttp.open('GET', routeObject.template, true);
xmlhttp.send();
}当前只剩加载视图和将对象模型与视图模板绑定了。我们会创建一个空的模型对象,然后传递与方法相关的模型来唤醒路由控制器。更新后的模型对象会与先前已经加载的XHR调用中的HTML模板绑定。
loadView方法被用于调用控制器方法,以及准备模型对象。
replaceToken方法被用于与HTML模板一起绑定模型
//Function to load the view with the template
function loadView(routeObject, viewElement, viewHtml) {
var model = {};
//get the resultant model from the controller of the current route
routeObject.controller(model);
//bind the model with the view
viewHtml = replaceToken(viewHtml, model);
//load the view into the view element
viewElement.innerHTML = viewHtml;
}
function replaceToken(viewHtml, model) {
var modelProps = Object.getOwnPropertyNames(model),
modelProps.forEach(function (element, index, array) {
viewHtml = viewHtml.replace('{{' + element + '}}', model[element]);
});
return viewHtml;
}最后,我们将插件曝光于js全局范围外
//attach the mvc object to the window w['jsMvc'] = new jsMvc();
现在,是时候在我们单页应用中使用这个MVC插件。在下一个代码段中,下面这些会实现:
1)在web页面中引入这个代码
2)用控制器添加路由信息和视图模板信息
3)创建控制器功能
4)最后,初始化lib。
除了上面我们需要的链接让我们导航到不同的路径外,一个容器元素的视图属性包含着视图模板html。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Mvc</title>
<script src="jsMvc.js"></script>
<!--[if lt IE 9]> <script src="jsMvc-ie8.js"></script> <![endif]-->
<style type="text/css">
.NavLinkContainer {
padding: 5px;
background-color: lightyellow;
}
.NavLink {
background-color:black;
color: white;
font-weight:800;
text-decoration:none;
padding:5px;
border-radius:4px;
}
.NavLink:hover {
background-color:gray;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Navigation Links</h3>
<div class="NavLinkContainer">
<a class="NavLink" href="index.html#/home">Home</a>
<a class="NavLink" href="index.html#/contact">Contact</a>
<a class="NavLink" href="index.html#/admin">Admin</a>
</div>
<br />
<br />
<h3>View</h3>
<div view></div>
<script>
jsMvc.AddRoute(HomeController, 'home', 'Views/home.html');
jsMvc.AddRoute(ContactController, 'contact', 'Views/contact.html');
jsMvc.AddRoute(AdminController, 'admin', 'Views/admin.html');
jsMvc.Initialize();
function HomeController(model) {
model.Message = 'Hello World';
}
function ContactController(model) {
model.FirstName = "John";
model.LastName = "Doe";
model.Phone = '555-123456';
}
function AdminController(model) {
model.UserName = "John";
model.Password = "MyPassword";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>上面的代码有一段包含一个为IE的条件注释。
<!--[if lt IE 9]> <script src="jsMvc-ie8.js"></script> <![endif]-->
如果IE的版本低于9,那么function.bind,Object.getOwnPropertyNames和Array.forEach属性将不会被支持。因此我们要通过判断浏览器是否低于IE9来反馈代码是否支持。
其中的内容有home.html, contact.html 和 admin.html 请看下面:
home.html:
{{Message}}
contact.html:
{{FirstName}} {{LastName}}
<br />
{{Phone}}
admin.html:
<div style="padding:2px;margin:2px;text-align:left;">
<label for="txtUserName">User Name</label>
<input type="text" id="txtUserName" value="{{UserName}}" />
</div>
<div style="padding:2px;margin:2px;text-align:left;">
<label for="txtPassword">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="txtPassword" value="{{Password}}" />
</div>
完整的代码可以从给定的下载链接中得到。
如何运行代码
运行该代码比较简单,需要在你喜欢的Web服务器上创建一个Web应用,下面以IIS为例来说明。
首先在默认站点中新增一个Web应用.
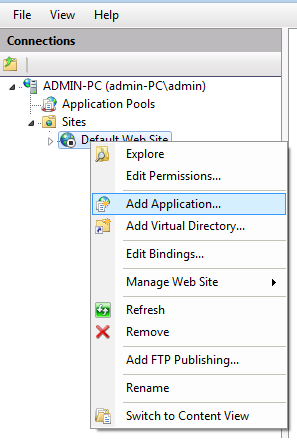
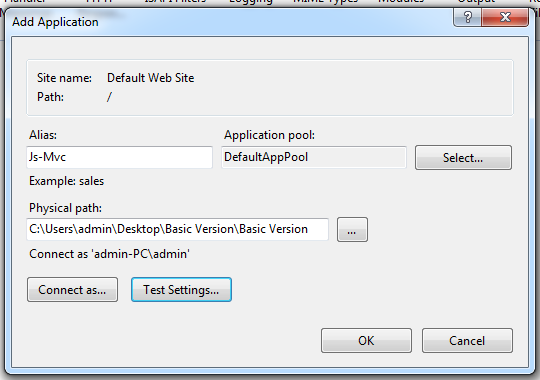
然后设置必填信息:别名,物理路径,应用池,用户认证信息,点击OK。
最后定位到Web应用的内容目录,浏览你想打开的HTML页面即可。

跑在服务器里是必要的,因为代码加载从存储于外部文件中的视图,浏览器不会允许我们的代码在非宿主服务器环境下执行。当然如果你使用Visual Studio那么直接在目标html文件上右键,选择‘View In Browser'即可。
浏览器支持
大部分的现代浏览器都支持本代码。针对IE8及以下的浏览器,有一份单独的代码来支持,但很不幸,这份代码远多于100行。因此这代码不是百分百跨浏览器兼容的,所以当你决定在项目中使用时需要对代码进行微调。
兴趣点
This example demonstrates这个示例向我们展示了对于非常明确地需求来说,真没必要全部使用js库和框架来实现。Web应用是资源密集型的,最好只使用必要的代码而丢掉其他多余部分。
目前的代码能做的就这些了。没有诸如Web服务调用,动态事件绑定功能的。很快我会提供支持更多特性的升级版本。
以上所述就是本文的全部内容了,希望能对大家熟练掌握javascript有所帮助。




