
As the frequency of computer use increases, slow computer speed has become a problem that plagues many users. In response to this problem, PHP editor Xinyi has specially collected a series of speed-up techniques suitable for Windows 10 systems, aiming to help everyone solve the problem of slow computers. The following will introduce these tips in detail to help you quickly increase the speed of your computer, improve work efficiency and entertainment experience.
1. Click on the search bar, enter [powershell], and run Windows Powershell as an administrator.
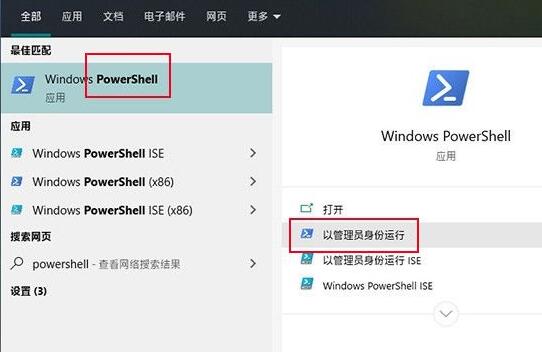
Run Powershell as administrator
2. According to your hard disk type, copy the following code to Powershell and execute it.
1) SATA hard disk
powercfg -attributes 0012ee47-9041-4b5d-9b77-535fba8b1442 0b2d69d7-a2a1-449c-9680-f91c70521c60 -ATTRIB_HIDE
powercfg -attributes 0012ee4 7- 9041-4b5d-9b77-535fba8b1442 dab60367-53fe-4fbc-825e-521d069d2456 -ATTRIB_HIDE
2) M.2 hard drive
powercfg -attributes 0012ee47-9041-4b5d-9b77-535fba8 b1442 d639518a- e56d-4345-8af2-b9f32fb26109 -ATTRIB_HIDE
powercfg -attributes 0012ee47-9041-4b5d-9b77-535fba8b1442 fc95af4d-40e7-4b6d-835a-56d131dbc80e -ATTRIB_HIDE
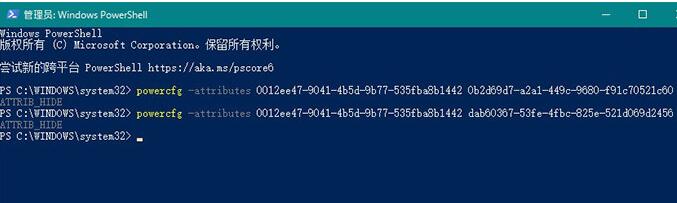
Paste the code directly into Powershell and execute it (pay attention to distinguish your own hard disk type)
3. After execution, directly open [Settings] → [System] → [Power and Sleep] → [Other Power Settings], select [Change Plan Settings] → [Change Advanced Power Settings], then you will see that several new contents have been added to the original hard disk settings, which are also divided into SATA hard disks and M.2 hard disks.
1) SATA hard disk
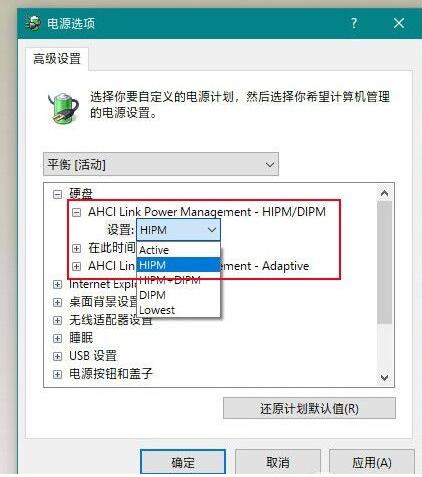
The picture shows the settings of the SATA hard disk
SATA hard disk mainly adds two settings, namely AHCI Link Power Management- HIPM/DIPM and AHCI Link Power Management-Adaptive. Among them, [AHCI Link Power Management-HIPM/DIPM] is the mode option of LPM (Link Power Management, a power-saving mode of SATA). Simply put, it is which energy-saving mode the SSD will execute.
WIN10 provides a total of five sets of options, namely: Active (always active), HIPM (LPM initiated by the host), DIPM (LPM initiated by the hard disk), and Lowest (low energy consumption mode). Usually the cause of hard disk freeze is due to the LPM mode incompatibility between the hard disk and the operating system (for example, SSD only supports DIPM, but it is set to HIPM in WIN10). The solution is to change it to [Active] to turn off the energy-saving mode.
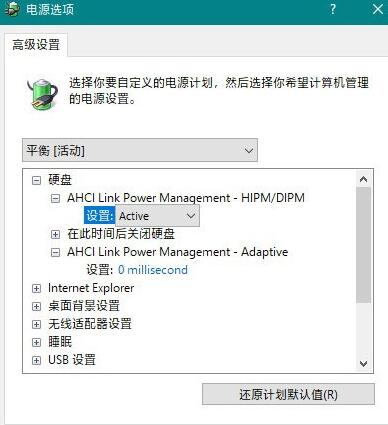
SATA users are recommended to use the above settings
[AHCI Link Power Management-Adaptive] is the waiting time for LPM to transition from light sleep (Partial) to deep sleep (Slumber) , the smaller the value, the higher the frequency of entering deep sleep (that is, the more obvious the freeze). It is recommended to set it to [0 millisecond] to cancel deep energy saving.
2) M.2 hard drive
The settings of M.2 hard drive are slightly different, they are [Primary NVMe Idle Timeout] and [Primary NVMe Power State Transition Latency Tolerance], among which [Primary NVMe Idle Timeout] is similar to [AHCI Link Power Management-Adaptive] in SATA. It is also the waiting time before automatically entering energy-saving mode. If you are pursuing performance, you can set this value to a larger value, such as 600. If you need to cool down, you can set this value to a smaller value, such as 100.
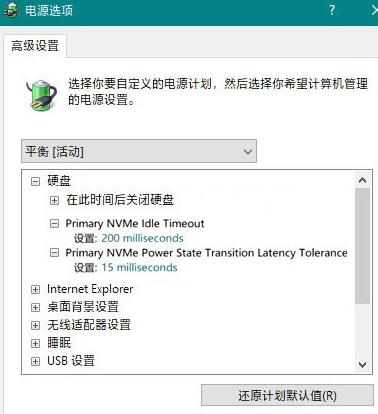
The picture shows the settings of the M.2 hard disk
[Primary NVMe Power State Transition Latency Tolerance] is the switching delay time of the power mode. The smaller the value, the worse the lag. The less (such as 10). However, it should be noted that M.2 hard drives are different from SATA, and the overall heat generation is relatively abnormal, so you should be more cautious when adjusting these two values.
If the computer system is obviously lagging, you can try the above method. At the same time, pay special attention to the heat of the M.2 hard drive.
The above is the detailed content of WIN10 computer speed-up tips and content. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 win10 bluetooth switch is missing
win10 bluetooth switch is missing Why do all the icons in the lower right corner of win10 show up?
Why do all the icons in the lower right corner of win10 show up? The difference between win10 sleep and hibernation
The difference between win10 sleep and hibernation Win10 pauses updates
Win10 pauses updates What to do if the Bluetooth switch is missing in Windows 10
What to do if the Bluetooth switch is missing in Windows 10 win10 connect to shared printer
win10 connect to shared printer Clean up junk in win10
Clean up junk in win10 How to share printer in win10
How to share printer in win10



