Use Python to write the deletion operation code of B+ tree
B The tree deletion operation requires first finding the location of the deleted node, and then determining the number of keys of the node.
If the number of keys in the node exceeds the minimum number, just delete it directly.
As shown below, delete "40":
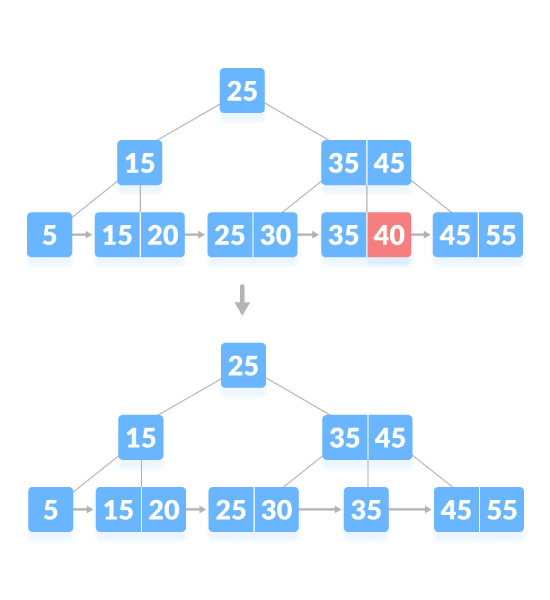
If there is an exact minimum number of keys in the node, deletion requires borrowing from the sibling node and adding the intermediate key of the sibling node to parent node. As shown below, delete "5":
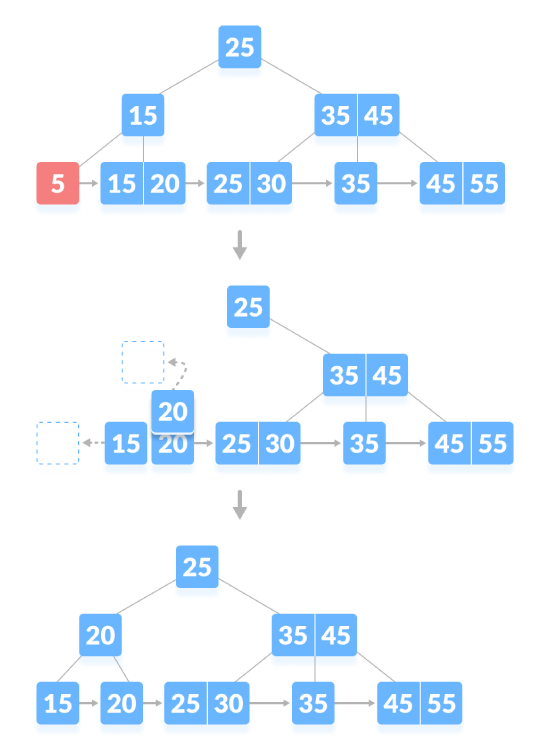
Delete the content node. If the number of keys in the node exceeds the minimum number, just delete it from the leaf node the key and delete the key from the internal node. Fill empty spaces in internal nodes with inorder successors. As shown below, delete "45":
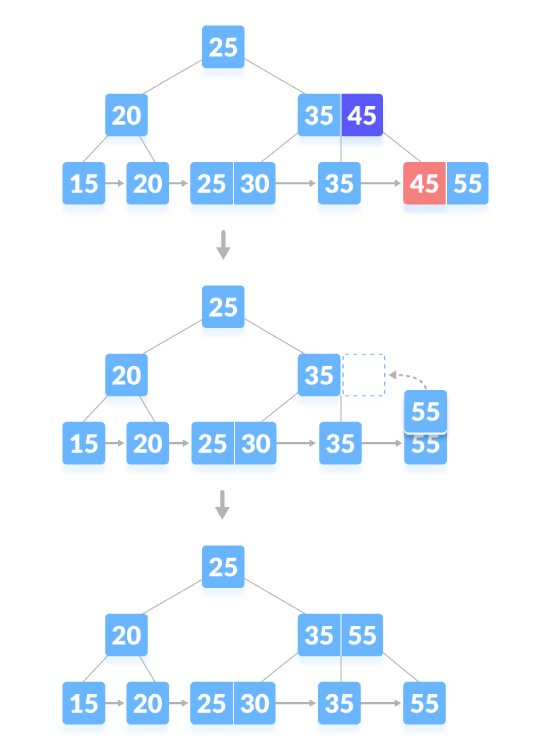
Delete the content node. If there is the exact minimum number of keys in the node, delete the key and directly The sibling borrows a key and fills the empty space in the index with the borrowed key. As shown below, delete "35":
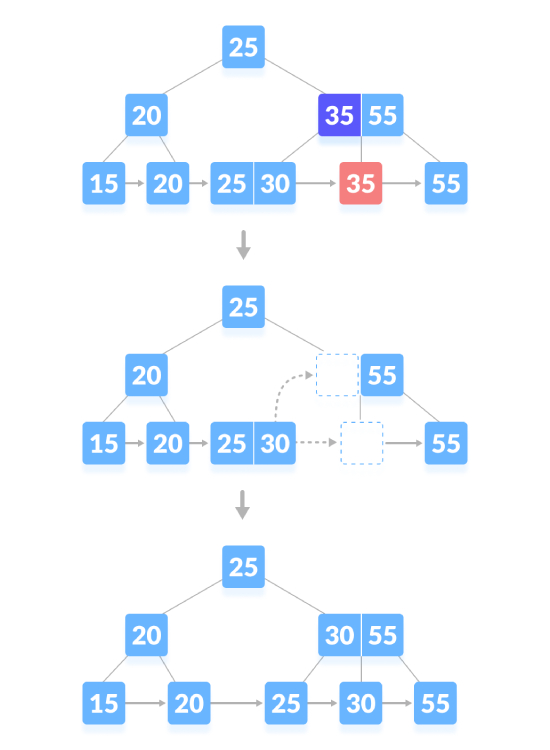
Delete the content node and generate a blank space above the parent node. After deleting a key, merge the empty space with its siblings, filling the empty space in the parent node with the inorder successor. As shown below, delete "25":
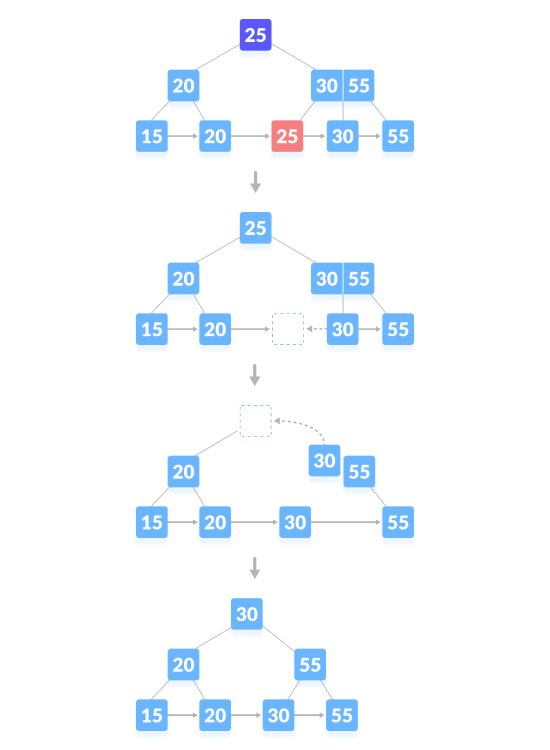
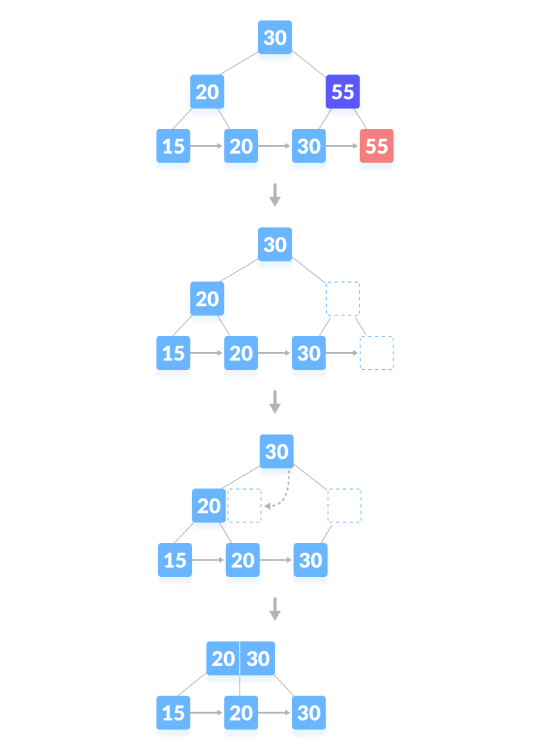
The deletion operation that causes the tree height to shrink, as shown below, delete "55":
Python implements B-tree deletion operation
import math
# 创建节点
class Node:
def __init__(self, order):
self.order = order
self.values = []
self.keys = []
self.nextKey = None
self.parent = None
self.check_leaf = False
# 插入叶子
def insert_at_leaf(self, leaf, value, key):
if (self.values):
temp1 = self.values
for i in range(len(temp1)):
if (value == temp1[i]):
self.keys[i].append(key)
break
elif (value < temp1[i]):
self.values = self.values[:i] + [value] + self.values[i:]
self.keys = self.keys[:i] + [[key]] + self.keys[i:]
break
elif (i + 1 == len(temp1)):
self.values.append(value)
self.keys.append([key])
break
else:
self.values = [value]
self.keys = [[key]]
# B+树
class BplusTree:
def __init__(self, order):
self.root = Node(order)
self.root.check_leaf = True
# 插入节点
def insert(self, value, key):
value = str(value)
old_node = self.search(value)
old_node.insert_at_leaf(old_node, value, key)
if (len(old_node.values) == old_node.order):
node1 = Node(old_node.order)
node1.check_leaf = True
node1.parent = old_node.parent
mid = int(math.ceil(old_node.order / 2)) - 1
node1.values = old_node.values[mid + 1:]
node1.keys = old_node.keys[mid + 1:]
node1.nextKey = old_node.nextKey
old_node.values = old_node.values[:mid + 1]
old_node.keys = old_node.keys[:mid + 1]
old_node.nextKey = node1
self.insert_in_parent(old_node, node1.values[0], node1)
def search(self, value):
current_node = self.root
while(current_node.check_leaf == False):
temp2 = current_node.values
for i in range(len(temp2)):
if (value == temp2[i]):
current_node = current_node.keys[i + 1]
break
elif (value < temp2[i]):
current_node = current_node.keys[i]
break
elif (i + 1 == len(current_node.values)):
current_node = current_node.keys[i + 1]
break
return current_node
# 查找节点
def find(self, value, key):
l = self.search(value)
for i, item in enumerate(l.values):
if item == value:
if key in l.keys[i]:
return True
else:
return False
return False
# 在父级插入
def insert_in_parent(self, n, value, ndash):
if (self.root == n):
rootNode = Node(n.order)
rootNode.values = [value]
rootNode.keys = [n, ndash]
self.root = rootNode
n.parent = rootNode
ndash.parent = rootNode
return
parentNode = n.parent
temp3 = parentNode.keys
for i in range(len(temp3)):
if (temp3[i] == n):
parentNode.values = parentNode.values[:i] + \
[value] + parentNode.values[i:]
parentNode.keys = parentNode.keys[:i +
1] + [ndash] + parentNode.keys[i + 1:]
if (len(parentNode.keys) > parentNode.order):
parentdash = Node(parentNode.order)
parentdash.parent = parentNode.parent
mid = int(math.ceil(parentNode.order / 2)) - 1
parentdash.values = parentNode.values[mid + 1:]
parentdash.keys = parentNode.keys[mid + 1:]
value_ = parentNode.values[mid]
if (mid == 0):
parentNode.values = parentNode.values[:mid + 1]
else:
parentNode.values = parentNode.values[:mid]
parentNode.keys = parentNode.keys[:mid + 1]
for j in parentNode.keys:
j.parent = parentNode
for j in parentdash.keys:
j.parent = parentdash
self.insert_in_parent(parentNode, value_, parentdash)
# 删除节点
def delete(self, value, key):
node_ = self.search(value)
temp = 0
for i, item in enumerate(node_.values):
if item == value:
temp = 1
if key in node_.keys[i]:
if len(node_.keys[i]) > 1:
node_.keys[i].pop(node_.keys[i].index(key))
elif node_ == self.root:
node_.values.pop(i)
node_.keys.pop(i)
else:
node_.keys[i].pop(node_.keys[i].index(key))
del node_.keys[i]
node_.values.pop(node_.values.index(value))
self.deleteEntry(node_, value, key)
else:
print("Value not in Key")
return
if temp == 0:
print("Value not in Tree")
return
# 删除条目
def deleteEntry(self, node_, value, key):
if not node_.check_leaf:
for i, item in enumerate(node_.keys):
if item == key:
node_.keys.pop(i)
break
for i, item in enumerate(node_.values):
if item == value:
node_.values.pop(i)
break
if self.root == node_ and len(node_.keys) == 1:
self.root = node_.keys[0]
node_.keys[0].parent = None
del node_
return
elif (len(node_.keys) < int(math.ceil(node_.order / 2)) and node_.check_leaf == False) or (len(node_.values) < int(math.ceil((node_.order - 1) / 2)) and node_.check_leaf == True):
is_predecessor = 0
parentNode = node_.parent
PrevNode = -1
NextNode = -1
PrevK = -1
PostK = -1
for i, item in enumerate(parentNode.keys):
if item == node_:
if i > 0:
PrevNode = parentNode.keys[i - 1]
PrevK = parentNode.values[i - 1]
if i < len(parentNode.keys) - 1:
NextNode = parentNode.keys[i + 1]
PostK = parentNode.values[i]
if PrevNode == -1:
ndash = NextNode
value_ = PostK
elif NextNode == -1:
is_predecessor = 1
ndash = PrevNode
value_ = PrevK
else:
if len(node_.values) + len(NextNode.values) < node_.order:
ndash = NextNode
value_ = PostK
else:
is_predecessor = 1
ndash = PrevNode
value_ = PrevK
if len(node_.values) + len(ndash.values) < node_.order:
if is_predecessor == 0:
node_, ndash = ndash, node_
ndash.keys += node_.keys
if not node_.check_leaf:
ndash.values.append(value_)
else:
ndash.nextKey = node_.nextKey
ndash.values += node_.values
if not ndash.check_leaf:
for j in ndash.keys:
j.parent = ndash
self.deleteEntry(node_.parent, value_, node_)
del node_
else:
if is_predecessor == 1:
if not node_.check_leaf:
ndashpm = ndash.keys.pop(-1)
ndashkm_1 = ndash.values.pop(-1)
node_.keys = [ndashpm] + node_.keys
node_.values = [value_] + node_.values
parentNode = node_.parent
for i, item in enumerate(parentNode.values):
if item == value_:
p.values[i] = ndashkm_1
break
else:
ndashpm = ndash.keys.pop(-1)
ndashkm = ndash.values.pop(-1)
node_.keys = [ndashpm] + node_.keys
node_.values = [ndashkm] + node_.values
parentNode = node_.parent
for i, item in enumerate(p.values):
if item == value_:
parentNode.values[i] = ndashkm
break
else:
if not node_.check_leaf:
ndashp0 = ndash.keys.pop(0)
ndashk0 = ndash.values.pop(0)
node_.keys = node_.keys + [ndashp0]
node_.values = node_.values + [value_]
parentNode = node_.parent
for i, item in enumerate(parentNode.values):
if item == value_:
parentNode.values[i] = ndashk0
break
else:
ndashp0 = ndash.keys.pop(0)
ndashk0 = ndash.values.pop(0)
node_.keys = node_.keys + [ndashp0]
node_.values = node_.values + [ndashk0]
parentNode = node_.parent
for i, item in enumerate(parentNode.values):
if item == value_:
parentNode.values[i] = ndash.values[0]
break
if not ndash.check_leaf:
for j in ndash.keys:
j.parent = ndash
if not node_.check_leaf:
for j in node_.keys:
j.parent = node_
if not parentNode.check_leaf:
for j in parentNode.keys:
j.parent = parentNode
# 输出B+树
def printTree(tree):
lst = [tree.root]
level = [0]
leaf = None
flag = 0
lev_leaf = 0
node1 = Node(str(level[0]) + str(tree.root.values))
while (len(lst) != 0):
x = lst.pop(0)
lev = level.pop(0)
if (x.check_leaf == False):
for i, item in enumerate(x.keys):
print(item.values)
else:
for i, item in enumerate(x.keys):
print(item.values)
if (flag == 0):
lev_leaf = lev
leaf = x
flag = 1
record_len = 3
bplustree = BplusTree(record_len)
bplustree.insert('5', '33')
bplustree.insert('15', '21')
bplustree.insert('25', '31')
bplustree.insert('35', '41')
bplustree.insert('45', '10')
printTree(bplustree)
if(bplustree.find('5', '34')):
print("Found")
else:
print("Not found")The above is the detailed content of Use Python to write the deletion operation code of B+ tree. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)
 How to audit database activity in MySQL?
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:34 PM
How to audit database activity in MySQL?
Aug 05, 2025 pm 01:34 PM
UseMySQLEnterpriseAuditPluginifonEnterpriseEditionbyenablingitinconfigurationwithserver-audit=FORCE_PLUS_PERMANENTandcustomizeeventsviaserver_audit_events;2.Forfreealternatives,usePerconaServerorMariaDBwiththeiropen-sourceauditpluginslikeaudit_log;3.
 Securing MySQL with Object-Level Privileges
Jul 29, 2025 am 01:34 AM
Securing MySQL with Object-Level Privileges
Jul 29, 2025 am 01:34 AM
TosecureMySQLeffectively,useobject-levelprivilegestolimituseraccessbasedontheirspecificneeds.Beginbyunderstandingthatobject-levelprivilegesapplytodatabases,tables,orcolumns,offeringfinercontrolthanglobalprivileges.Next,applytheprincipleofleastprivile
 Optimizing MySQL for Financial Data Storage
Jul 27, 2025 am 02:06 AM
Optimizing MySQL for Financial Data Storage
Jul 27, 2025 am 02:06 AM
MySQL needs to be optimized for financial systems: 1. Financial data must be used to ensure accuracy using DECIMAL type, and DATETIME is used in time fields to avoid time zone problems; 2. Index design should be reasonable, avoid frequent updates of fields to build indexes, combine indexes in query order and clean useless indexes regularly; 3. Use transactions to ensure consistency, control transaction granularity, avoid long transactions and non-core operations embedded in it, and select appropriate isolation levels based on business; 4. Partition historical data by time, archive cold data and use compressed tables to improve query efficiency and optimize storage.
 How to use check constraints to enforce data rules in MySQL?
Aug 06, 2025 pm 04:49 PM
How to use check constraints to enforce data rules in MySQL?
Aug 06, 2025 pm 04:49 PM
MySQL supports CHECK constraints to force domain integrity, effective from version 8.0.16; 1. Add constraints when creating a table: Use CREATETABLE to define CHECK conditions, such as age ≥18, salary > 0, department limit values; 2. Modify the table to add constraints: Use ALTERTABLEADDCONSTRAINT to limit field values, such as name non-empty; 3. Use complex conditions: support multi-column logic and expressions, such as end date ≥start date and completion status must have an end date; 4. Delete constraints: use ALTERTABLEDROPCONSTRAINT to specify the name to delete; 5. Notes: MySQL8.0.16, InnoDB or MyISAM needs to be quoted
 How to implement a tagging system in a MySQL database?
Aug 05, 2025 am 05:41 AM
How to implement a tagging system in a MySQL database?
Aug 05, 2025 am 05:41 AM
Useamany-to-manyrelationshipwithajunctiontabletolinkitemsandtagsviathreetables:items,tags,anditem_tags.2.Whenaddingtags,checkforexistingtagsinthetagstable,insertifnecessary,thencreatemappingsinitem_tagsusingtransactionsforconsistency.3.Queryitemsbyta
 Optimizing MySQL for Real-time Data Feeds
Jul 26, 2025 am 05:41 AM
Optimizing MySQL for Real-time Data Feeds
Jul 26, 2025 am 05:41 AM
TooptimizeMySQLforreal-timedatafeeds,firstchoosetheInnoDBstorageenginefortransactionsandrow-levellocking,useMEMORYorROCKSDBfortemporarydata,andpartitiontime-seriesdatabytime.Second,indexstrategicallybyonlyapplyingindexestoWHERE,JOIN,orORDERBYcolumns,
 MySQL Database Cost-Benefit Analysis for Cloud Migration
Jul 26, 2025 am 03:32 AM
MySQL Database Cost-Benefit Analysis for Cloud Migration
Jul 26, 2025 am 03:32 AM
Whether MySQL is worth moving to the cloud depends on the specific usage scenario. If your business needs to be launched quickly, expand elastically and simplify operations and maintenance, and can accept a pay-as-you-go model, then moving to the cloud is worth it; but if your database is stable for a long time, latency sensitive or compliance restrictions, it may not be cost-effective. The keys to controlling costs include selecting the right vendor and package, configuring resources reasonably, utilizing reserved instances, managing backup logs and optimizing query performance.
 Best Practices for Managing Large MySQL Tables
Aug 05, 2025 am 03:55 AM
Best Practices for Managing Large MySQL Tables
Aug 05, 2025 am 03:55 AM
When dealing with large tables, MySQL performance and maintainability face challenges, and it is necessary to start from structural design, index optimization, table sub-table strategy, etc. 1. Reasonably design primary keys and indexes: It is recommended to use self-increment integers as primary keys to reduce page splits; use overlay indexes to improve query efficiency; regularly analyze slow query logs and delete invalid indexes. 2. Rational use of partition tables: partition according to time range and other strategies to improve query and maintenance efficiency, but attention should be paid to partitioning and cutting issues. 3. Consider reading and writing separation and library separation: Read and writing separation alleviates the pressure on the main library. The library separation and table separation are suitable for scenarios with a large amount of data. It is recommended to use middleware and evaluate transaction and cross-store query problems. Early planning and continuous optimization are the key.







