
Author | William Chen, Automotive Field Application Engineering Manager, ON Semiconductor China
Intelligent driving has gradually become a common feature of cars, which enhances the comfort of cars and drivers. Perception ability reduces the driver's work intensity and can effectively improve driving safety. Among them, the camera based on CMOS image sensor is one of the main tools for the intelligent driving system to perceive the external environment.
CMOSThe image sensor is an imaging sensor, which is essentially a memory and analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) The combination. Based on the photoelectric effect of silicon, incident light will excite charges in the photosensitive diodes of the sensor pixels. The charges are collected and stored and converted into digital output through ADC.
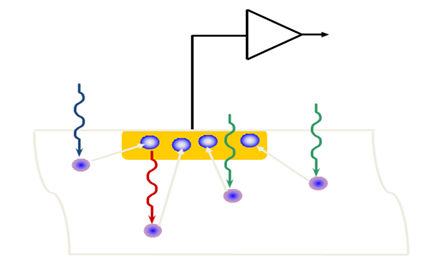
##Figure 1Photoelectric Effect
Architecturally, a CMOS image sensor is similar to a memory. It has a large number of storage cells and supports row and column addressing. Operation, the difference is that the memory is written by the circuit, while the content in the sensor is written by visible light or near-infrared light.
The charge collected by the sensor includes two parts: one part is the charge we expect, which comes from ambient light The effective signal excited; the other part is the charge generated by the interference that the user does not want. There are many sources of interference, which are generally referred to as noise.
We hope that the more effective information in the image, the better, and the less interference noise, the better. A common indicator to measure the effect of image noise is the signal-to-noise ratio SNR, which is the ratio of signal to noise. The greater the signal-to-noise ratio, the smaller the relative content of image noise and the better the image quality. The unit of SNR can be a ratio, or it can be converted into a logarithmic unit dB.
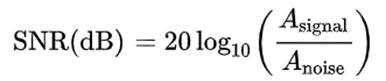

The sensor data sheet generally provides the signal-to-noise ratio parameter SNR, as shown below.

There is a common question: 46# Is the low-light effect of a sensor with ##dB signal-to-noise ratio better than that of a sensor with 43dB?
The answer is not necessarily, conclusions that are out of condition often fall into the pit.
SNR is not a point, it is a function of lighting conditions. As shown in Figure 2, SNR will become a line as the lighting intensity changes. curve. When it is used as a low-light effect indicator, it is required to select the SNR value under low-light conditions. The SNR parameter on the sensor data manual in the industry is usually the maximum SNR value, which corresponds to the SNR value when the lighting environment is very bright, that is, the SNR Max in the upper right corner of the blue SNR curve in the figure. point. The SNR value in the area where the blue line is located in the lower left corner is suitable as a parameter for evaluating low light. The illumination at this time is insufficient and corresponds to a low light environment. It's like selling apples. The top layer is the best. You need to open the basket to see the quality of the apples inside.
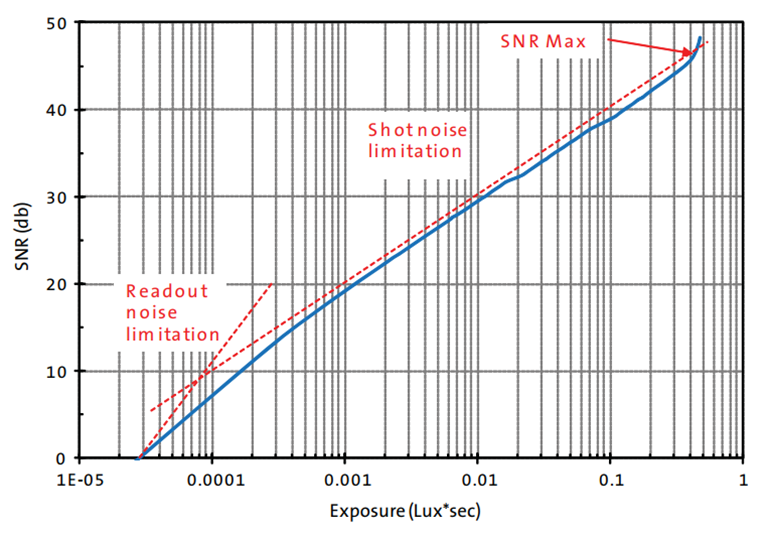 Figure
Figure
2Signal to noise ratio SNR curve
Judging the sensor based on the maximum SNR point has the problem of overgeneralization. According to needs, the user can select the SNR size corresponding to the specific exposure condition to evaluate the low-light noise. The larger the SNR, the better; the user can also limit the SNR to a fixed value, such as SNR=5, use the Exposure value of the exposure condition required at this time to judge the low-light noise. The smaller the Exposure value means that less lighting resources are needed to achieve the same SNR, and the better the low-light performance of the sensor.
Figure 2 shows the SNR of an ordinary sensor, which is a monotonically increasing curve. The CMOS sensor used in cars requires a high dynamic range HDR to match all-weather application scenarios. The common method for HDR is to change the sensitivity of the sensor and sample different brightnesses of the environment separately. Then map the multiple sampled image frames to a standardized linear data space, and finally select appropriate pixels from frames with different sensitivities to form a complete image frame. See "A Brief Discussion on Automotive Image Sensor Parameters - Dynamic Range".
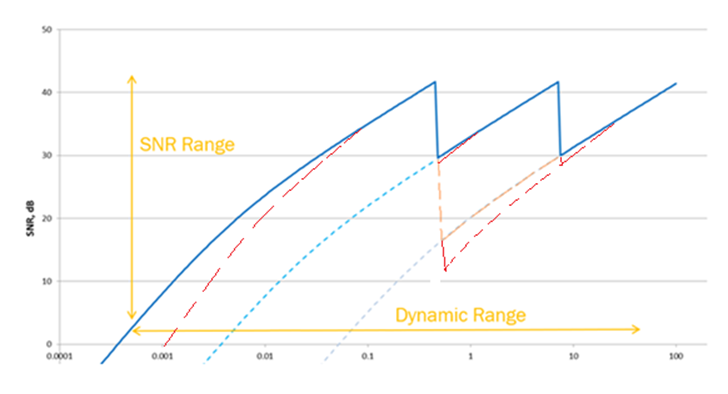
The sensitivity change of the sensor corresponds to the SNR line in the coordinate system moving to different positions, and the evolution of the SNR curve of the final HDR image The fitting results of multiple SNR curves, such as the blue line in Figure 3, are no longer a monotonic increasing curve. In addition to the low-light SNR being very small, there will also be multiple local minima in the highlight interval. When working When the point falls in the SNR drop range, the noise will worsen even if the environment is very bright at this time.
This will cause a phenomenon that goes against the perception of the human eye in the image, that is, as the brightness increases , the image quality will go from bad to good, and then suddenly deteriorate again. Therefore, unlike traditional linear sensors, the signal-to-noise ratio of automotive wide dynamic sensors also needs to evaluate the minimum value index under bright conditions.
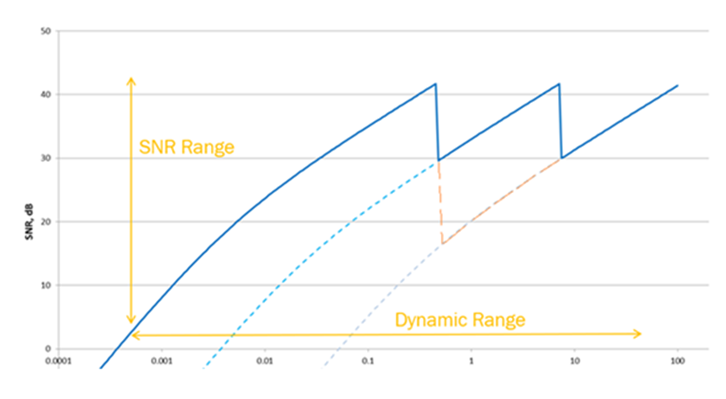
Figure 3 HDR image SNR

##Figure 4 SNR and Noise
The SNR of the automotive sensor is a non-monotone curve, and the automotive application environment will change the problem. More complex. The sensor is an analog device. Before the ADC, signal and noise data are stored in the form of charges. The dark current of the sensor will also accumulate charges. Its generation speed is roughly proportional to the exposure time and exponentially related to the temperature. So we must also consider the effects of temperature, exposure time, and analog gain on dark state noise. SNR is a function of temperature, exposure time and simulation gain at the same time, and its curve has become a multi-dimensional curve cluster.
Taking the influence of temperature as an example, Figure 5 is SNR=10The required Exposure value changes as the internal temperature of the sensor increases. We can see that different sensorThe sensitivity to temperature drift is different. The SNR exposure values of these two sensors cross at 60°C, which means that at room temperature 2# When ##5℃ and high temperature 80℃ were evaluated separately, the SNR conclusions reached were completely opposite.
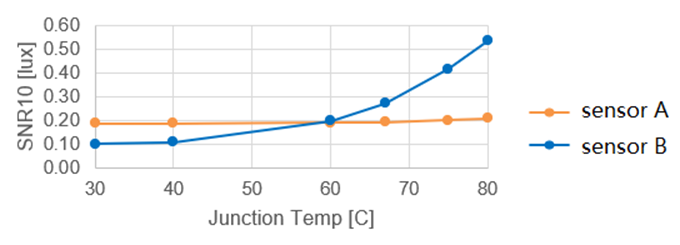 ##Figure
##Figure
5 Inside the wafer Temperature impact
According to the temperature distribution of the effective life cycle of the automotive camera, it exceeds 8# During the life cycle of ##8%, the temperature inside the sensor exceeds 40℃ and exceeds 80% The section temperature exceeds 60℃ within the time, and exceeds 65% The section temperature exceeds 8## within the time #0℃. The influence of temperature drift will cause further changes in the SNR curve. As shown by the red dotted line in Figure 6, when the temperature increases, the SNR curve will continue to decrease in low-illumination areas and highlighted local areas.
Figure
 6
6
Temperature versus HDR SNR impact
Currently in the industry, the impact on automotive images The evaluation of sensor SNR is often tested using the European Machine Vision Association's EMVA1288 standard. The signal-to-noise ratio SNR in the EMVA1288 standard is defined based on the traditional monotonic linear sensor model, and the description of the SNR characteristics of the automotive wide dynamic image sensor is not complete. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers IEEE is defining a new quality test standard for automotive images P2020. As a member of the working group, ON Semiconductor has undertaken the IEEE The drafting of the image noise standard in the P2020 standard includes the SNR parameter.
Finally, to summarize, the signal-to-noise ratio SNR of the automotive CMOS image sensor is a key image quality indicator. It has non-monotonic characteristics and is affected by many factors in the automotive application environment. SNR evaluation is a multi-dimensional comprehensive evaluation task. Only objective and comprehensive SNR evaluation can truly describe the performance of the sensor and correctly guide the development of automotive imaging products.
The above is the detailed content of A brief discussion on automotive image sensor parameters - signal-to-noise ratio. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 mysql paging
mysql paging
 What is the shortcut key for switching users?
What is the shortcut key for switching users?
 How to solve the problem that Win10 folder cannot be deleted
How to solve the problem that Win10 folder cannot be deleted
 How to open ramdisk
How to open ramdisk
 What to do if your IP address is attacked
What to do if your IP address is attacked
 How to cut long pictures on Huawei mobile phones
How to cut long pictures on Huawei mobile phones
 mybatis first level cache and second level cache
mybatis first level cache and second level cache
 Usage of get function in c language
Usage of get function in c language




