
The task is to print the left node of the given binary tree. First, the user will insert data, thus generating a binary tree, and then print the left view of the resulting tree.
Each node can have up to 2 child nodes, so this program must only iterate over the left pointer associated with the node
If the left pointer is not null, it means it will have some The associated data or pointer, otherwise it will be the left child to be printed and displayed as output.
Input : 1 0 3 2 4 Output : 1 0 2
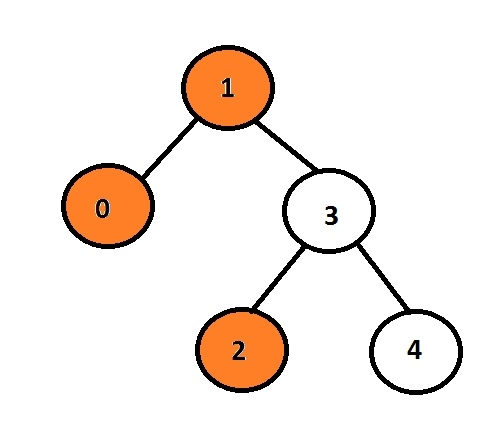
Here, the orange node represents the left view of the binary tree.
In the given graph, the node with data 1 is the root node, so it will be printed, instead of going to the left child node, it will print 0, then it will go to 3 and print its The left child node is 2.
We can use recursive method to store the levels of nodes and repeatedly transfer to
The code below shows the C implementation of the given algorithm
START
Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure
Declare int data
Declare pointer of type node using *left, *right
Step 2 -> create function for inserting node with parameter as new_data
Declare temp variable of node using malloc
Set temp->data = new_data
Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL
return temp
Step 3 -> declare function void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level)
IF root = NULL
Exit
End
IF *highest_level < level
Print root->data
Set *highest_level = level
End
Recursively call left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level)
Recursively call left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level)
Step 4 -> Declare Function void left(struct node* root)
Set int highest_level = 0
Call left_view(root, 1, &highest_level)
Step 5-> In main()
Call New passing value user want to insert as struct node* root = New(1)
Call left(root)
STOP#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//create a structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right; //this pointer will point to the nodes attached with a node
};
struct node* New(int new_data) {
struct node* temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
//allocating memory to a pointer dynamically
temp->data = new_data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) {
if (root == NULL) //if there is no node that means no data
return;
// this function will retrun the root node if there is only root node in a tree
if (*highest_level < level) {
printf("%d\t", root->data);
*highest_level = level;
}
// Recursive function
left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level);
left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level);
}
void left(struct node* root) {
int highest_level = 0;
left_view(root, 1, &highest_level);
}
int main() {
printf("left view of a binary tree is : ");
struct node* root = New(1);
root->left = New(0);
root->right = New(3);
root->right->left = New(2);
root->right->right = New(4);
left(root);
return 0;
}If we run the above program, it will generate the following output.
left view of a binary tree is : 1 0 2
The above is the detailed content of Print left view of binary tree in C language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




