
There are three major problems inRedis:Cache avalanche,Cache breakdown,Cache Penetration, today we will talk aboutCache Penetration.
I believe you have read a lot of theoretical articles related to cache breakdown, but you may be confused about how to implement it in the specific code and how to solve it.
Today, Lao Tian will take you to see the cache breakdown solution and code implementation.
Please look at the following code:
/** * @author 田维常 * @公众号 java后端技术全栈 * @date 2021/6/27 15:59 */ @Service public class UserInfoServiceImpl implements UserInfoService { @Resource private UserMapper userMapper; @Resource private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override public UserInfo findById(Long id) { //查询缓存 String userInfoStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(id); //如果缓存中不存在,查询数据库 //1 if (isEmpty(userInfoStr)) { UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.findById(id); //数据库中不存在 if(userInfo == null){ return null; } userInfoStr = JSON.toJSONString(userInfo); //2 //放入缓存 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(id, userInfoStr); } return JSON.parseObject(userInfoStr, UserInfo.class); } private boolean isEmpty(String string) { return !StringUtils.hasText(string); } }
The entire process:
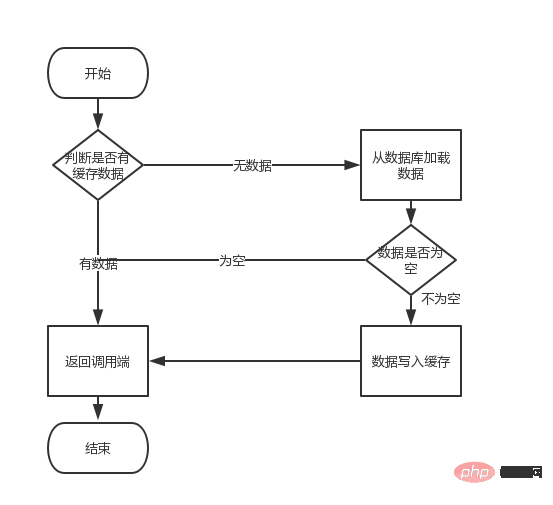
如果,在//1到//2之间耗时1.5秒,那就代表着在这1.5秒时间内所有的查询都会走查询数据库。这也就是我们所说的缓存中的“缓存击穿”。
其实,你们项目如果并发量不是很高,也不用怕,并且我见过很多项目也就差不多是这么写的,也没那么多事,毕竟只是第一次的时候可能会发生缓存击穿。
但,我们也不要抱着一个侥幸的心态去写代码,既然是多线程导致的,估计很多人会想到锁,下面我们使用锁来解决。
既然使用到锁,那么我们第一时间应该关心的是锁的粒度。
如果我们放在方法findById上,那就是所有查询都会有锁的竞争,这里我相信大家都知道我们为什么不放在方法上。
/** * @author 田维常 * @公众号 java后端技术全栈 * @date 2021/6/27 15:59 */ @Service public class UserInfoServiceImpl implements UserInfoService { @Resource private UserMapper userMapper; @Resource private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override public UserInfo findById(Long id) { //查询缓存 String userInfoStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(id); if (isEmpty(userInfoStr)) { //只有不存的情况存在锁 synchronized (UserInfoServiceImpl.class){ UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.findById(id); //数据库中不存在 if(userInfo == null){ return null; } userInfoStr = JSON.toJSONString(userInfo); //放入缓存 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(id, userInfoStr); } } return JSON.parseObject(userInfoStr, UserInfo.class); } private boolean isEmpty(String string) { return !StringUtils.hasText(string); } }
看似解决问题了,其实,问题还是没得到解决,还是会缓存击穿,因为排队获取到锁后,还是会执行同步块代码,也就是还会查询数据库,完全没有解决缓存击穿。
由此,我们引入双重检查锁,我们在上的版本中进行稍微改变,在同步模块中再次校验缓存中是否存在。
/** * @author 田维常 * @公众号 java后端技术全栈 * @date 2021/6/27 15:59 */ @Service public class UserInfoServiceImpl implements UserInfoService { @Resource private UserMapper userMapper; @Resource private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override public UserInfo findById(Long id) { //查缓存 String userInfoStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(id); //第一次校验缓存是否存在 if (isEmpty(userInfoStr)) { //上锁 synchronized (UserInfoServiceImpl.class){ //再次查询缓存,目的是判断是否前面的线程已经set过了 userInfoStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(id); //第二次校验缓存是否存在 if (isEmpty(userInfoStr)) { UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.findById(id); //数据库中不存在 if(userInfo == null){ return null; } userInfoStr = JSON.toJSONString(userInfo); //放入缓存 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(id, userInfoStr); } } } return JSON.parseObject(userInfoStr, UserInfo.class); } private boolean isEmpty(String string) { return !StringUtils.hasText(string); } }
这样,看起来我们就解决了缓存击穿问题,大家觉得解决了吗?
回顾上面的案例,在正常的情况下是没问题,但是一旦有人恶意攻击呢?
比如说:入参id=10000000,在数据库里并没有这个id,怎么办呢?
第一步、缓存中不存在
第二步、查询数据库
第三步、由于数据库中不存在,直接返回了,并没有操作缓存
第四步、再次执行第一步.....死循环了吧
就是当缓存中和数据库中都不存在的情况下,以id为key,空对象为value。
set(id,空对象);
回到上面的四步,就变成了。
比如说:入参
id=10000000,在数据库里并没有这个id,怎么办呢?第一步、缓存中不存在
第二步、查询数据库
第三步、由于数据库中不存在,以id为
key,空对象为value放入缓存中第四步、执行第一步,此时,缓存就存在了,只是这时候只是一个空对象。
代码实现部分:
/** * @author 田维常 * @公众号 java后端技术全栈 * @date 2021/6/27 15:59 */ @Service public class UserInfoServiceImpl implements UserInfoService { @Resource private UserMapper userMapper; @Resource private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override public UserInfo findById(Long id) { String userInfoStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(id); //判断缓存是否存在,是否为空对象 if (isEmpty(userInfoStr)) { synchronized (UserInfoServiceImpl.class){ userInfoStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(id); if (isEmpty(userInfoStr)) { UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.findById(id); if(userInfo == null){ //构建一个空对象 userInfo= new UserInfo(); } userInfoStr = JSON.toJSONString(userInfo); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(id, userInfoStr); } } } UserInfo userInfo = JSON.parseObject(userInfoStr, UserInfo.class); //空对象处理 if(userInfo.getId() == null){ return null; } return JSON.parseObject(userInfoStr, UserInfo.class); } private boolean isEmpty(String string) { return !StringUtils.hasText(string); } }
布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter):是一种空间效率极高的概率型算法和数据结构,用于判断一个元素是否在集合中(类似Hashset)。它的核心一个很长的二进制向量和一系列hash函数,数组长度以及hash函数的个数都是动态确定的。
Hash函数:
SHA1,SHA256,MD5..
布隆过滤器的用处就是,能够迅速判断一个元素是否在一个集合中。因此他有如下三个使用场景:
URLto avoid crawling the same
URLaddress
It internally maintains abit arraythat is all 0. It should be noted that the Bloom filter has a concept of false positive rate. The higher the false positive rate, the higher the false positive rate. If it is low, the longer the array is, the more space it takes up. The higher the false positive rate, the smaller the array and the smaller space it occupies. The relevant theories and algorithms of Bloom filters will not be discussed here. Those who are interested can study it by themselves.
Advantages
O(k), far more than the general algorithm
Disadvantages
False Positive),默认
0.03,随着存入的元素数量增加,误算率随之增加;
代码实现:
/** * @author 田维常 * @公众号 java后端技术全栈 * @date 2021/6/27 15:59 */ @Service public class UserInfoServiceImpl implements UserInfoService { @Resource private UserMapper userMapper; @Resource private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; private static Long size = 1000000000L; private static BloomFilter bloomFilter = BloomFilter.create(Funnels.longFunnel(), size); @Override public UserInfo findById(Long id) { String userInfoStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(id); if (isEmpty(userInfoStr)) { //校验是否在布隆过滤器中 if(bloomFilter.mightContain(id)){ return null; } synchronized (UserInfoServiceImpl.class){ userInfoStr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(id); if (isEmpty(userInfoStr) ) { if(bloomFilter.mightContain(id)){ return null; } UserInfo userInfo = userMapper.findById(id); if(userInfo == null){ //放入布隆过滤器中 bloomFilter.put(id); return null; } userInfoStr = JSON.toJSONString(userInfo); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(id, userInfoStr); } } } return JSON.parseObject(userInfoStr, UserInfo.class); } private boolean isEmpty(String string) { return !StringUtils.hasText(string); } }
使用Redis实现分布式的时候,有用到setnx,这里大家可以想象,我们是否可以使用这个分布式锁来解决缓存击穿的问题?
这个方案留给大家去实现,只要掌握了Redis的分布式锁,那这个实现起来就非常简单了。
搞定缓存击穿、使用双重检查锁的方式来解决,看到双重检查锁,大家肯定第一印象就会想到单例模式,这里也算是给大家复习一把双重检查锁的使用。
Due to cache breakdown caused by malicious attacks, we have also implemented two solutions. At least at work and interviews, we can definitely deal with it.
In addition, when using locks, pay attention to thelock strength. It is recommended to replace it withdistributed lock(RedisorZookeeperImplementation), because since we have introduced cache, in most cases we will deploy multiple nodes, and at the same time, introduced distributed locks, we can use the methodInput parameter idto use, this is Isn’t it more exciting!
I hope everyone can understand some of the ideas in the article and not memorize the technology by rote.
The above is the detailed content of Cache breakdown! Don't even know how to write code? ? ?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Commonly used database software
Commonly used database software What are the in-memory databases?
What are the in-memory databases? Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis?
Which one has faster reading speed, mongodb or redis? How to use redis as a cache server
How to use redis as a cache server How redis solves data consistency
How redis solves data consistency How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency?
How do mysql and redis ensure double-write consistency? What data does redis cache generally store?
What data does redis cache generally store? What are the 8 data types of redis
What are the 8 data types of redis



